Beam Dynamics in High Energy Colliders
... twist and turn so as to give an intended interpretation, "The President's spokesmen had to spin the story to make it less embarrassing" a distinctive interpretation (especially as used by politicians to sway public opinion), "the campaign put a favorable spin on the story" ...
... twist and turn so as to give an intended interpretation, "The President's spokesmen had to spin the story to make it less embarrassing" a distinctive interpretation (especially as used by politicians to sway public opinion), "the campaign put a favorable spin on the story" ...
Nonlocal Effects in the Plasmons of Strongly Interacting
... by a common multiplicative factor to fit the calculated cross section. The relative shift and broadening of the observed extinction spectra are well reproduced by the calculated cross section, as it should in the small-concentration limit. The experimental curves have wider long-wavelength tails, ge ...
... by a common multiplicative factor to fit the calculated cross section. The relative shift and broadening of the observed extinction spectra are well reproduced by the calculated cross section, as it should in the small-concentration limit. The experimental curves have wider long-wavelength tails, ge ...
The Polycluster Theory for the Structure of Glasses: Evidence from
... research effort. These substances of extraordinary practical and technological importance still present considerable scientific challenges in the description of the glass-formation mechanism (nature of the glass transformation) and of the nature of the atomic structure at intermediate- and long-rang ...
... research effort. These substances of extraordinary practical and technological importance still present considerable scientific challenges in the description of the glass-formation mechanism (nature of the glass transformation) and of the nature of the atomic structure at intermediate- and long-rang ...
Astroparticle physics at LHC - Institute of Physics (IoP)
... physical matter density in the Universe. The leading candidate for dark matter is an undetected heavy elementary relic particle which interact only trough gravitation and the weak force. Such a Weakly Interacting Massive Particle (WIMP) is often predicted in theories beyond the standard model and is ...
... physical matter density in the Universe. The leading candidate for dark matter is an undetected heavy elementary relic particle which interact only trough gravitation and the weak force. Such a Weakly Interacting Massive Particle (WIMP) is often predicted in theories beyond the standard model and is ...
Electrically driven flow near a colloidal particle close to an electrode
... measured the approach velocity of particle pairs in steady fields and found a linear dependence on the field strength.13,14 Reversal of the field polarity causes aggregates to disperse, indicative of a flow directed away from individual particles.6,12-14 Both the linear field strength dependence and ...
... measured the approach velocity of particle pairs in steady fields and found a linear dependence on the field strength.13,14 Reversal of the field polarity causes aggregates to disperse, indicative of a flow directed away from individual particles.6,12-14 Both the linear field strength dependence and ...
Thomson first investigated the magnetic deflection
... Thomson, in 1897, was the first to suggest that the fundamental unit was over 1000 times smaller than an atom, suggesting the sub-atomic particles now known as electrons. Thomson discovered this through his explorations on the properties of cathode rays. Thomson made his suggestion on 30 April 1897 ...
... Thomson, in 1897, was the first to suggest that the fundamental unit was over 1000 times smaller than an atom, suggesting the sub-atomic particles now known as electrons. Thomson discovered this through his explorations on the properties of cathode rays. Thomson made his suggestion on 30 April 1897 ...
Kinetic temperature of dust particle motion in gas
... gas discharge plasma to an abnormally large kinetic energy is of great interest [1–3]. Dust particles under certain conditions can acquire kinetic energy of the order of 10 eV and higher, far above the temperature of gas and temperatures of ions and electrons in the discharge. The evidence of this p ...
... gas discharge plasma to an abnormally large kinetic energy is of great interest [1–3]. Dust particles under certain conditions can acquire kinetic energy of the order of 10 eV and higher, far above the temperature of gas and temperatures of ions and electrons in the discharge. The evidence of this p ...
"Tailored Particle Beams from Single-Component Plasmas" Non-Neutral Plasma Physics VII , J.R. Danielson and T.S. Pedersen Eds., AIP Conf. Proc. No. 1114 (New York, 2009), pp. 171-178. T. R. Weber, J. R. Danielson, and C. M. Surko (PDF)
... potential. Much of this paper is an overview of recent work that is described in more detail elsewhere [5, 6]. Many applications require positron or antiproton beams with small transverse spatial extent and small energy spreads [4, 7-9]. We describe here techniques to create such beams with radii, p ...
... potential. Much of this paper is an overview of recent work that is described in more detail elsewhere [5, 6]. Many applications require positron or antiproton beams with small transverse spatial extent and small energy spreads [4, 7-9]. We describe here techniques to create such beams with radii, p ...
a timeline of particle accelerators
... spark formation between the spheres. Van de Graaff discovered he could reach and maintain higher voltages without sparking by increasing the size of the spheres—since if the potential is constant, an increase in sphere size will decrease the strength of the electric field. Other laboratories, such a ...
... spark formation between the spheres. Van de Graaff discovered he could reach and maintain higher voltages without sparking by increasing the size of the spheres—since if the potential is constant, an increase in sphere size will decrease the strength of the electric field. Other laboratories, such a ...
Physics 30 - Alberta Education
... light. Magnetic fields are used to produce the circular path that these protons follow in the accelerator. The Large Hadron Collider is designed to accelerate protons to an energy of 7.00 TeV. 23. Which of the following diagrams shows the orientation that the magnetic field must have in order to ...
... light. Magnetic fields are used to produce the circular path that these protons follow in the accelerator. The Large Hadron Collider is designed to accelerate protons to an energy of 7.00 TeV. 23. Which of the following diagrams shows the orientation that the magnetic field must have in order to ...
History of Instrumentation
... large distance to find distance / time. Rejecting particles that passed These at the speed of a pion left (hopefully) only antiprotons that registered with this method. ...
... large distance to find distance / time. Rejecting particles that passed These at the speed of a pion left (hopefully) only antiprotons that registered with this method. ...
Electrostatics practice test
... 2. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk and becomes positively charged, a. electrons are removed from the rod. c. protons are added to the silk. b. protons are removed from the silk. d. the silk remains neutral. 3. Charge is most easily transferred in a. nonconductors. c. semiconductors. b. conducto ...
... 2. When a glass rod is rubbed with silk and becomes positively charged, a. electrons are removed from the rod. c. protons are added to the silk. b. protons are removed from the silk. d. the silk remains neutral. 3. Charge is most easily transferred in a. nonconductors. c. semiconductors. b. conducto ...
Liquid Crystal Order in Colloidal Suspensions of Spheroidal
... sufficient for the system to reach a steady-state structure, as per the kinetics reported previously in Figure 3. Figure 4a and b show that this structure is orientationally and positionally disordered at applied voltages of 1.0 and 1.25 V. (Regions of the images with radially symmetric intensity re ...
... sufficient for the system to reach a steady-state structure, as per the kinetics reported previously in Figure 3. Figure 4a and b show that this structure is orientationally and positionally disordered at applied voltages of 1.0 and 1.25 V. (Regions of the images with radially symmetric intensity re ...
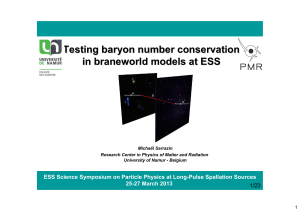
Testing baryon number conservation in braneworld models
... Rabi oscillations between branes: Matter swapping effect - A neutron undergoes gravitational potentials V≤ in each brane + and - Under the influence of a magnetic vector potential, the neutron presents Rabi oscillations between both branes ...
... Rabi oscillations between branes: Matter swapping effect - A neutron undergoes gravitational potentials V≤ in each brane + and - Under the influence of a magnetic vector potential, the neutron presents Rabi oscillations between both branes ...
Subatomic Physics Notes
... What do you think? • When the idea of the atom was first conceived, it was thought to be a fundamental particle, indivisible and indestructible. We now know differently. • List every particle you can think of that is smaller than an atom. • If you know the properties of these particles, list them as ...
... What do you think? • When the idea of the atom was first conceived, it was thought to be a fundamental particle, indivisible and indestructible. We now know differently. • List every particle you can think of that is smaller than an atom. • If you know the properties of these particles, list them as ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.