MFF 1a: Electric Charge and A Bar Magnet
... How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure ...
... How sure were you of your ranking? (circle one) Basically Guessed Sure ...
x - The General Science Journal, Science Journals
... equations suffice to allow magnetic charges in electrodynamics. However, no magnetic monopole has been found to this date. To resolve these and other difficulties, we develop a fundamental geometrical theory of motion and interaction, which shows that the Lorentz force and Maxwell’s equations are si ...
... equations suffice to allow magnetic charges in electrodynamics. However, no magnetic monopole has been found to this date. To resolve these and other difficulties, we develop a fundamental geometrical theory of motion and interaction, which shows that the Lorentz force and Maxwell’s equations are si ...
Deflection by the Image Current and Charges of a Beam
... flection of a particle in the bunch, due to the bunch passage offcenter by the entrance or exit of a small radius pipe, is shown in Fig. 3 as a function of the position of the particle in the bunch for several different bunch lengths. The bunch enters (or exits) off-center by 0.25 mm from a large pi ...
... flection of a particle in the bunch, due to the bunch passage offcenter by the entrance or exit of a small radius pipe, is shown in Fig. 3 as a function of the position of the particle in the bunch for several different bunch lengths. The bunch enters (or exits) off-center by 0.25 mm from a large pi ...
Accelerator and detector prospects of elementary particle physics
... of proton-antiproton colliding beams. The use of ionization cooling*'5 can open up very interesting possibilities in getting intense muon beams of high energy including implementation of muon colliding beams of sufficiently high luminosity. Continuous cooling of the particle beam in a storage ring o ...
... of proton-antiproton colliding beams. The use of ionization cooling*'5 can open up very interesting possibilities in getting intense muon beams of high energy including implementation of muon colliding beams of sufficiently high luminosity. Continuous cooling of the particle beam in a storage ring o ...
Wave Optics Module Model Library
... 1 On the Model toolbar, click Add Plot Group and choose 1D Plot Group. 2 In the Settings window for 1D Plot Group, locate the Plot Settings section. 3 Select the x-axis label check box. 4 In the associated text field, type Angle of Incidence. 5 Select the y-axis label check box. 6 In the associated ...
... 1 On the Model toolbar, click Add Plot Group and choose 1D Plot Group. 2 In the Settings window for 1D Plot Group, locate the Plot Settings section. 3 Select the x-axis label check box. 4 In the associated text field, type Angle of Incidence. 5 Select the y-axis label check box. 6 In the associated ...
Chapter 7 -- Removal of Particles from Gas Streams
... 3. Inertial deposition. When a gas stream changes direction as it flows around an object in its path, suspended particles tend to keep moving in their original direction due to their inertia. Particulate collection devices based on this principle include cyclones, scrubbers, and filters. 4. Brownian ...
... 3. Inertial deposition. When a gas stream changes direction as it flows around an object in its path, suspended particles tend to keep moving in their original direction due to their inertia. Particulate collection devices based on this principle include cyclones, scrubbers, and filters. 4. Brownian ...
Relationships between the Electric and Magnetic Fields
... can be induced when the negatively charged particles such as electrons move. The relationships between the magnetic forces, gravity, electric forces, and electromagnetic forces are also discussed. We show that the element of the gravity (i.e., mass) and electric forces (i.e., electric charge) can be ...
... can be induced when the negatively charged particles such as electrons move. The relationships between the magnetic forces, gravity, electric forces, and electromagnetic forces are also discussed. We show that the element of the gravity (i.e., mass) and electric forces (i.e., electric charge) can be ...
faraday`s field
... polarized by influence, and therefore, without adopting any particular mechanical hypothesis, we may make use of them to form a mathematical theory of electrical influence in dielectrics, the truth of which can only be established by a rigorous comparison of its results with experiment.” 8 Denìs Poi ...
... polarized by influence, and therefore, without adopting any particular mechanical hypothesis, we may make use of them to form a mathematical theory of electrical influence in dielectrics, the truth of which can only be established by a rigorous comparison of its results with experiment.” 8 Denìs Poi ...
Lecture Notes in Statistical Mechanics and Mesoscopics Thermal
... Let us outline some major observations with regard to the dynamics of classical Hamiltonian systems. Simple 1D system:– The student is expected to be familiar with the dynamics of harmonic oscillator; potential well; pendulum. In the case of non-linear oscillations we have the spreading effect. In t ...
... Let us outline some major observations with regard to the dynamics of classical Hamiltonian systems. Simple 1D system:– The student is expected to be familiar with the dynamics of harmonic oscillator; potential well; pendulum. In the case of non-linear oscillations we have the spreading effect. In t ...
Shining Light on Modifications of Gravity
... The second term in equation (1.1) is the disformal term. On its own, when A ≡ const, this term is not problematic for fifth force experiments because as we will see a scalar field that couples to matter in this way is not sourced by a static non-relativistic mass distribution. All of the objects use ...
... The second term in equation (1.1) is the disformal term. On its own, when A ≡ const, this term is not problematic for fifth force experiments because as we will see a scalar field that couples to matter in this way is not sourced by a static non-relativistic mass distribution. All of the objects use ...
Recent advances in drug delivery and medical imaging using
... composed of a wide range of lipids which self-assemble into a bilayer arrangement, the bilayer structure being represented in Figure 3 by the lamellar phase. Variations in the headgroup and/or the tail section of the amphiphile can encourage the formation of thermodynamically stable phases with inte ...
... composed of a wide range of lipids which self-assemble into a bilayer arrangement, the bilayer structure being represented in Figure 3 by the lamellar phase. Variations in the headgroup and/or the tail section of the amphiphile can encourage the formation of thermodynamically stable phases with inte ...
Origin of Cosmic Rays
... database for titles including these words returned 1009 hits! However despite its deceptive simplicity we still do not have a definitive and universally accepted answer to the implicit question it poses. In part this is because there is a level of ambiguity in the word "origin" and there are at leas ...
... database for titles including these words returned 1009 hits! However despite its deceptive simplicity we still do not have a definitive and universally accepted answer to the implicit question it poses. In part this is because there is a level of ambiguity in the word "origin" and there are at leas ...
367_1.PDF
... instability and good agreement with theoretical models, but instability of the bunched beam have not an acceptable understanding. Typical development of an e-p instability of coasting beam in the LANSCE PSR shown in Fig.l. It is absolutely identical to the corresponding picture from the INP PSR in F ...
... instability and good agreement with theoretical models, but instability of the bunched beam have not an acceptable understanding. Typical development of an e-p instability of coasting beam in the LANSCE PSR shown in Fig.l. It is absolutely identical to the corresponding picture from the INP PSR in F ...
Introduction to solid state theory
... of charge −e, so that charge neutrality is preserved. As solids are stable up to temperatures T ≈ 103 K only, we need not bother with the question of the internal structure of the nuclei or things like the weak or strong interaction. Consequently, both nuclei and electrons can be treated as point ch ...
... of charge −e, so that charge neutrality is preserved. As solids are stable up to temperatures T ≈ 103 K only, we need not bother with the question of the internal structure of the nuclei or things like the weak or strong interaction. Consequently, both nuclei and electrons can be treated as point ch ...
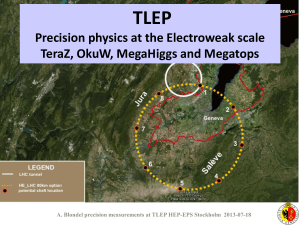
Blondel-precision-measts-18-07-2013
... The two most promising lines of development towards the new high energy frontier after the LHC are proton-proton and electron-positron colliders. Focused design studies are required in both fields, together with vigorous accelerator • adequate Excerpt from the CERN Council deliberationinvolving docu ...
... The two most promising lines of development towards the new high energy frontier after the LHC are proton-proton and electron-positron colliders. Focused design studies are required in both fields, together with vigorous accelerator • adequate Excerpt from the CERN Council deliberationinvolving docu ...
The Internal and External Problems of String Theory
... well as interactions mediated by spin-1 gauge fields. And finally, in the ten-dimensional supersymmetric formulation of string theory it also included fermionic matter fields. Exclusively the fact that the quantized string has spin-2 states which can be interpreted as gravitons and which are complet ...
... well as interactions mediated by spin-1 gauge fields. And finally, in the ten-dimensional supersymmetric formulation of string theory it also included fermionic matter fields. Exclusively the fact that the quantized string has spin-2 states which can be interpreted as gravitons and which are complet ...
enlargement
... Membership brings about substantial, additional benefits in a win-win-scenario for all partners: – Staff employment and participation in the Fellows, Associates and Student programmes; – The possibility to submit own research proposals – Participation in all training and education programmes – Indus ...
... Membership brings about substantial, additional benefits in a win-win-scenario for all partners: – Staff employment and participation in the Fellows, Associates and Student programmes; – The possibility to submit own research proposals – Participation in all training and education programmes – Indus ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.