Atomic Theory The Atom
... Atomic Mass Scale On the atomic mass scale for subatomic particles • 1 atomic mass unit (amu) is equal to 1/12 of the mass of the carbon-12 atom. ...
... Atomic Mass Scale On the atomic mass scale for subatomic particles • 1 atomic mass unit (amu) is equal to 1/12 of the mass of the carbon-12 atom. ...
Document
... The diagram contains two vertices where the coupling constants appear. The diagram REPRESENTS the exchange of a virtual particle (the photon) between the charged particles that are the sources of the electromagnetic field. ...
... The diagram contains two vertices where the coupling constants appear. The diagram REPRESENTS the exchange of a virtual particle (the photon) between the charged particles that are the sources of the electromagnetic field. ...
Spring 2006 Seminar Series
... The second part of the seminar will be presented by Professor Gonzales to highlight the basic research on light scattering by ensembles of particles (in free space or located on surfaces). This work is shown to be of interest in many fields like cell inspection in biology, detection and monitoring o ...
... The second part of the seminar will be presented by Professor Gonzales to highlight the basic research on light scattering by ensembles of particles (in free space or located on surfaces). This work is shown to be of interest in many fields like cell inspection in biology, detection and monitoring o ...
here - islam-science.net
... tracker and before the HCAL. This is where the CMS stops electrons, photons, and jets. It can then measure the energies of these electrons and photons, because they interact electromagnetically (hence the name). ...
... tracker and before the HCAL. This is where the CMS stops electrons, photons, and jets. It can then measure the energies of these electrons and photons, because they interact electromagnetically (hence the name). ...
Ideas about Atoms
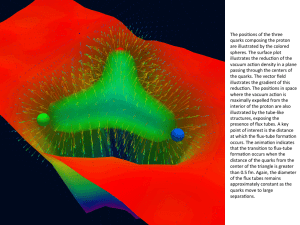
... to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never found in isolation; they can only be found within hadrons. ...
... to a phenomenon known as color confinement, quarks are never found in isolation; they can only be found within hadrons. ...
The Semiotic Flora of Elementary Particles
... The physical concept of a particle — a point with mass — is, semiotically speaking, an icon — a sign whose object is potential or virtual. The particle as the physical object the icon refers to has definite properties, but not necessarily existence. A virtual particle is just a possibility for excit ...
... The physical concept of a particle — a point with mass — is, semiotically speaking, an icon — a sign whose object is potential or virtual. The particle as the physical object the icon refers to has definite properties, but not necessarily existence. A virtual particle is just a possibility for excit ...
IMFUFA- Roskilde Universitetscenter- postbox 260
... The physical concept of a particle — a point with mass — is, semiotically speaking, an icon — a sign whose object is potential or virtual. The particle as the physical object the icon refers to has definite properties, but not necessarily existence. A virtual particle is just a possibility for excit ...
... The physical concept of a particle — a point with mass — is, semiotically speaking, an icon — a sign whose object is potential or virtual. The particle as the physical object the icon refers to has definite properties, but not necessarily existence. A virtual particle is just a possibility for excit ...
MALE AFRICAN ELEPHANT (about 6,000 kilograms) and the
... theory. Leading contenders are extensions of the Standard Model known as Supersymmetric Standard Models (SSMs). In these models, each Standard Model particle has a so-called superpartner (as yet undetected) with closely related properties [see “The Dawn of Physics beyond the Standard Model,” by Gord ...
... theory. Leading contenders are extensions of the Standard Model known as Supersymmetric Standard Models (SSMs). In these models, each Standard Model particle has a so-called superpartner (as yet undetected) with closely related properties [see “The Dawn of Physics beyond the Standard Model,” by Gord ...
3. (a) The force on the electron is Thus, the magnitude of FB is 6.2
... to repeating the above computation with a change in the sign in the charge. Thus, FB has the same magnitude but points in the negative z direction, namely, ...
... to repeating the above computation with a change in the sign in the charge. Thus, FB has the same magnitude but points in the negative z direction, namely, ...
Ex4
... two capacitor plates of area A, separated by distance L. The capacitors produce a force f perpendicular to the plates which pushes the particles to the lower plate. The particles can be absorbed on either plate, with an absorption potential ...
... two capacitor plates of area A, separated by distance L. The capacitors produce a force f perpendicular to the plates which pushes the particles to the lower plate. The particles can be absorbed on either plate, with an absorption potential ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.