Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter J3
... there is a strange quark on the left hand side of the decay but none on the right hand side. If this were a strong interaction process (or electromagnetic) the lifetime would be very short (less than about 10 20 s ). However, the decay of the lambda has a much larger lifetime (of order 10 10 s ). ...
... there is a strange quark on the left hand side of the decay but none on the right hand side. If this were a strong interaction process (or electromagnetic) the lifetime would be very short (less than about 10 20 s ). However, the decay of the lambda has a much larger lifetime (of order 10 10 s ). ...
The New Minimal Standard Model
... with t = log µ. We require that none of the couplings be driven negative below the Planck scale (stability bound) and stay below 10 (triviality bound). The region of (mh , k(mZ )) is shown in Fig. 1 for three values of h(mZ ) = 0, 1.0, 1.2. The region disappears when h(mZ ) > ∼ 1.3. The Higgs boson ...
... with t = log µ. We require that none of the couplings be driven negative below the Planck scale (stability bound) and stay below 10 (triviality bound). The region of (mh , k(mZ )) is shown in Fig. 1 for three values of h(mZ ) = 0, 1.0, 1.2. The region disappears when h(mZ ) > ∼ 1.3. The Higgs boson ...
GonzalesMestres
... [arXiv:1009.1855 ] Measurements by the Pierre Auger Observatory of the depth shower maximum and its fluctuations indicate a trend toward heavy nuclei with increasing energy. Although the measurements available now are only up to about 55 EeV, the trend suggests that primary CRs are likely to be domi ...
... [arXiv:1009.1855 ] Measurements by the Pierre Auger Observatory of the depth shower maximum and its fluctuations indicate a trend toward heavy nuclei with increasing energy. Although the measurements available now are only up to about 55 EeV, the trend suggests that primary CRs are likely to be domi ...
Unit 3 Study Guide
... subatomic particles, know where subatomic particles are located, their charges, relative masses, and symbols Bohr model Basically the nuclear model + electrons organized into quantized circular orbits Quantum mechanics Currently accepted atomic theory; Basically the nuclear model + electrons organiz ...
... subatomic particles, know where subatomic particles are located, their charges, relative masses, and symbols Bohr model Basically the nuclear model + electrons organized into quantized circular orbits Quantum mechanics Currently accepted atomic theory; Basically the nuclear model + electrons organiz ...
Higgs colloquium - High Energy Physics
... Coupling probabilities at low energy: EM: ~2, Weak: ~2/(MW,Z)4 Fundamental difference in the coupling strengths at low energy, but apparently governed by the same constant Difference due to the massive nature and short lifetime of the W and Z bosons. At high energy the strengths become the same. W ...
... Coupling probabilities at low energy: EM: ~2, Weak: ~2/(MW,Z)4 Fundamental difference in the coupling strengths at low energy, but apparently governed by the same constant Difference due to the massive nature and short lifetime of the W and Z bosons. At high energy the strengths become the same. W ...
The Atom
... Electrons are negatively charged and matter is neutral. If the electrons are so small, what accounts for the rest of the mass in a typical atom? JJ Thomson proposed a model of atom to answer these questions. The model consisted of a spherically shaped atom composed of a uniformly distributed pos ...
... Electrons are negatively charged and matter is neutral. If the electrons are so small, what accounts for the rest of the mass in a typical atom? JJ Thomson proposed a model of atom to answer these questions. The model consisted of a spherically shaped atom composed of a uniformly distributed pos ...
Blue Border - Michigan State University
... equally. Another way of saying it is: a balanced perspective. This is extremely difficult in science, in practice, because we're human beings and, somewhat automatically, have a preference for: ideas/concepts which fit our rational framework, ideas/concepts which fit our belief/religious system, and ...
... equally. Another way of saying it is: a balanced perspective. This is extremely difficult in science, in practice, because we're human beings and, somewhat automatically, have a preference for: ideas/concepts which fit our rational framework, ideas/concepts which fit our belief/religious system, and ...
ASEPS_Poster_Ishihara1_A0
... Abstract: Neutrinoless double beta decay (0) takes place only when neutrinos are Majorana neutrinos that have the nature of no distinction between particles and their own anti-particles. Majorana neutrino plays important role in the theory called Seesaw Mechanism, in which a left-handed Majorana ...
... Abstract: Neutrinoless double beta decay (0) takes place only when neutrinos are Majorana neutrinos that have the nature of no distinction between particles and their own anti-particles. Majorana neutrino plays important role in the theory called Seesaw Mechanism, in which a left-handed Majorana ...
Screen-Based Graphic Design: Tips for non
... particles: W+, W-, W0, and B0 • The W0 and B0 cannot be observed directly • But at ordinary energies they combine to form either the Z0 or the massless photon • In order to work, electroweak theory requires the existence of a particle called the Higgs Boson – The Higgs Boson is expected have a rest ...
... particles: W+, W-, W0, and B0 • The W0 and B0 cannot be observed directly • But at ordinary energies they combine to form either the Z0 or the massless photon • In order to work, electroweak theory requires the existence of a particle called the Higgs Boson – The Higgs Boson is expected have a rest ...
Recitation Week 7
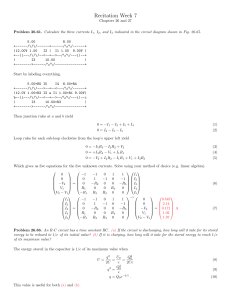
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
... Problem 26.86. An R-C circuit has a time constant RC. (a) If the circuit is discharging, how long will it take for its stored energy to be reduced to 1/e of its initial value? (b) If it is charging, how long will it take for the stored energy to reach 1/e of its maximum value? The energy stored in t ...
Standard Model
The Standard Model of particle physics is a theory concerning the electromagnetic, weak, and strong nuclear interactions, as well as classifying all the subatomic particles known. It was developed throughout the latter half of the 20th century, as a collaborative effort of scientists around the world. The current formulation was finalized in the mid-1970s upon experimental confirmation of the existence of quarks. Since then, discoveries of the top quark (1995), the tau neutrino (2000), and more recently the Higgs boson (2013), have given further credence to the Standard Model. Because of its success in explaining a wide variety of experimental results, the Standard Model is sometimes regarded as a ""theory of almost everything"".Although the Standard Model is believed to be theoretically self-consistent and has demonstrated huge and continued successes in providing experimental predictions, it does leave some phenomena unexplained and it falls short of being a complete theory of fundamental interactions. It does not incorporate the full theory of gravitation as described by general relativity, or account for the accelerating expansion of the universe (as possibly described by dark energy). The model does not contain any viable dark matter particle that possesses all of the required properties deduced from observational cosmology. It also does not incorporate neutrino oscillations (and their non-zero masses).The development of the Standard Model was driven by theoretical and experimental particle physicists alike. For theorists, the Standard Model is a paradigm of a quantum field theory, which exhibits a wide range of physics including spontaneous symmetry breaking, anomalies, non-perturbative behavior, etc. It is used as a basis for building more exotic models that incorporate hypothetical particles, extra dimensions, and elaborate symmetries (such as supersymmetry) in an attempt to explain experimental results at variance with the Standard Model, such as the existence of dark matter and neutrino oscillations.