Solubility of Copper Oxides in Water and Steam
... provided data on CuO solubility in “pure” water from ambient to the critical temperature of water. Hearn et al. [12] claimed that the small amount of solid oxide exposed to a relatively fast flow of steam in the former experiments [11] may have led to non-equilibrium results. They also sited the pre ...
... provided data on CuO solubility in “pure” water from ambient to the critical temperature of water. Hearn et al. [12] claimed that the small amount of solid oxide exposed to a relatively fast flow of steam in the former experiments [11] may have led to non-equilibrium results. They also sited the pre ...
Chapter 3. Analysis of Environmental System 3.1 Analysis of a
... When chemical reaction for (3.2.11) is expressed like Eq. (3.2.12), and Eq. (3.2.13), the reactions are 2nd order reaction. As shown so far, order of chemical reaction may be determined by type of chemical reaction. In water chemistry, chemical reaction rates generally follows to Eq.(3.2.2)~Eq.(3.2. ...
... When chemical reaction for (3.2.11) is expressed like Eq. (3.2.12), and Eq. (3.2.13), the reactions are 2nd order reaction. As shown so far, order of chemical reaction may be determined by type of chemical reaction. In water chemistry, chemical reaction rates generally follows to Eq.(3.2.2)~Eq.(3.2. ...
([Cu(NH3)4](MnO4)2)
... temperatures. One of the possible precursors, tetraamminecopper(2 ) bis(permanganate) ([Cu(NH3 )4 ](MnO4 )2 ; 1), was discovered by Klobb [2]. M¸ller et al. [3] studied its IR spectrum and determined its powder diffractogram, but this diffractogram could not be indexed due to the presence of an uni ...
... temperatures. One of the possible precursors, tetraamminecopper(2 ) bis(permanganate) ([Cu(NH3 )4 ](MnO4 )2 ; 1), was discovered by Klobb [2]. M¸ller et al. [3] studied its IR spectrum and determined its powder diffractogram, but this diffractogram could not be indexed due to the presence of an uni ...
hong kong diploma of secondary education examination
... The plunger is quickly pushed from position A to position B at time t while the temperature of the mixture is kept constant. Which of the following graphs represents how the concentration of NO2(g) in the mixture varies until a new state of equilibrium is established? ...
... The plunger is quickly pushed from position A to position B at time t while the temperature of the mixture is kept constant. Which of the following graphs represents how the concentration of NO2(g) in the mixture varies until a new state of equilibrium is established? ...
1. General introduction 1.1 Organometallic chemistry and homogeneous catalysis
... The success of organometallic catalysts lies in the easy modification of their environment by ligand exchange. A very large number of different types of ligands can coordinate to transition metal ions. Once the ligands are coordinated, the reactivity of the metals may change dramatically. In fact th ...
... The success of organometallic catalysts lies in the easy modification of their environment by ligand exchange. A very large number of different types of ligands can coordinate to transition metal ions. Once the ligands are coordinated, the reactivity of the metals may change dramatically. In fact th ...
New directions in synthetic solid state chemistry: chalcophosphate
... around in AzQx fluxes provides an important foundation for exploratory synthesis by promoting species, other than polychalcogenides, which could be formed in situ and then used for coordination chemistry. In this context the molten polychalcogenide approach becomes less like a low temperature ‘heat ...
... around in AzQx fluxes provides an important foundation for exploratory synthesis by promoting species, other than polychalcogenides, which could be formed in situ and then used for coordination chemistry. In this context the molten polychalcogenide approach becomes less like a low temperature ‘heat ...
L-11 Chemical thermodynamics
... determine these energy changes? You know that we cannot create or destroy energy. Energy only changes from one form to another. This is the observation made by many scientists over the years. This observation has taken the form of first law of thermodynamics. It has been found valid for various situ ...
... determine these energy changes? You know that we cannot create or destroy energy. Energy only changes from one form to another. This is the observation made by many scientists over the years. This observation has taken the form of first law of thermodynamics. It has been found valid for various situ ...
here - University of Alberta
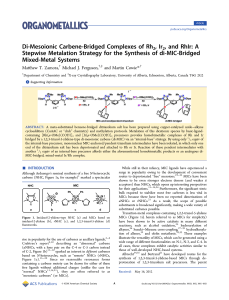
... unidentified product in each case, which slowly appears subsequent to formation of 9 and 10. This decomposition can be halted by the removal of solvent once carbonylation is complete, followed by recrystallization by quick injection of diethyl ether into a dichloromethane solution of 9 or 10 (see the ...
... unidentified product in each case, which slowly appears subsequent to formation of 9 and 10. This decomposition can be halted by the removal of solvent once carbonylation is complete, followed by recrystallization by quick injection of diethyl ether into a dichloromethane solution of 9 or 10 (see the ...
Web Supplement 7.2
... If the redox reaction is too complicated to be balanced by the inspection method just outlined, the following stepwise approach can be used. To illustrate, we return to the chromate example in which you are given the identities of the reactants and products and are told that the reaction proceeds un ...
... If the redox reaction is too complicated to be balanced by the inspection method just outlined, the following stepwise approach can be used. To illustrate, we return to the chromate example in which you are given the identities of the reactants and products and are told that the reaction proceeds un ...
Slide 1
... • At any given temperature, density does not change. • No matter how much or how little C2H5OH is present, its concentration remains constant. • Therefore, the term in the denominator is a constant and can be combined with K. ...
... • At any given temperature, density does not change. • No matter how much or how little C2H5OH is present, its concentration remains constant. • Therefore, the term in the denominator is a constant and can be combined with K. ...
Chelates for Micronutrient Nutrition among Crops
... Chelates and Chelating Agents A chelate describes a kind of organic chemical complex in which the metal part of the molecule is held so tightly that it cannot be 'stolen' by contact with other substances, which could convert it to an insoluble form. This is especially true for many soil types in Ind ...
... Chelates and Chelating Agents A chelate describes a kind of organic chemical complex in which the metal part of the molecule is held so tightly that it cannot be 'stolen' by contact with other substances, which could convert it to an insoluble form. This is especially true for many soil types in Ind ...
52 - University of Strathclyde
... hydrogen is replaced by zinc but require the presence of the alkali-metal to succeed are best described as alkali-metalmediated zincations (AMMZn).5–9 Exporting this bimetallic approach into new territory, herein we report the rst study in which AMMZn through 1 has been applied to a free N-heterocy ...
... hydrogen is replaced by zinc but require the presence of the alkali-metal to succeed are best described as alkali-metalmediated zincations (AMMZn).5–9 Exporting this bimetallic approach into new territory, herein we report the rst study in which AMMZn through 1 has been applied to a free N-heterocy ...
Kinetics
... Rate = - [A]/at = - [B]/ b t= [C]/ct = [D]/dt Dependence of rate on concentration In general, rate increases with increased concentration of Reactants and decreases with decreasing concentration We often examine the effect of concentration by measuring the reaction rate at the beginning ...
... Rate = - [A]/at = - [B]/ b t= [C]/ct = [D]/dt Dependence of rate on concentration In general, rate increases with increased concentration of Reactants and decreases with decreasing concentration We often examine the effect of concentration by measuring the reaction rate at the beginning ...
Reaction Energy
... Heat and Temperature • The energy absorbed or released as heat in a chemical or physical change is measured in a calorimeter. • In one kind of calorimeter, known quantities of reactants are sealed in a reaction chamber that is immersed in a known quantity of water. • Energy given off by the reaction ...
... Heat and Temperature • The energy absorbed or released as heat in a chemical or physical change is measured in a calorimeter. • In one kind of calorimeter, known quantities of reactants are sealed in a reaction chamber that is immersed in a known quantity of water. • Energy given off by the reaction ...
Magnetic Exchange Coupling in Actinide
... the decrease in the angular momentum manifests itself as a decrease in the magnetic susceptibility, which can obscure other simultaneous effects, such as magnetic exchange coupling between bridged metal centers. Additionally, if such an exchange coupling between the actinide ion and other metals in ...
... the decrease in the angular momentum manifests itself as a decrease in the magnetic susceptibility, which can obscure other simultaneous effects, such as magnetic exchange coupling between bridged metal centers. Additionally, if such an exchange coupling between the actinide ion and other metals in ...
Synthesis and structure characterization of zinc
... theoretical value is 20.3 wt% of Cd, while the measured value is 20.4 wt% of Cd. The thermal stability of similar MOFs, consisting only of dipeptides as linkers, are mainly up to 250 1C,10–13 but recently, Co(Gly-L-Glu)2 was synthesized having thermal stability up to 400 1C.14 Structure determinatio ...
... theoretical value is 20.3 wt% of Cd, while the measured value is 20.4 wt% of Cd. The thermal stability of similar MOFs, consisting only of dipeptides as linkers, are mainly up to 250 1C,10–13 but recently, Co(Gly-L-Glu)2 was synthesized having thermal stability up to 400 1C.14 Structure determinatio ...
Beyond Conventional N-Heterocyclic Carbenes
... stabilized by two adjacent heteroatoms, as in Arduengo-type carbenes, and also not necessarily with heteroatoms placed in a position R to the carbene carbon was revived by a serendipitous discovery of C4 bonding in imidazolylidenes.6 The large class of heterocyclic carbenes that can be grouped toget ...
... stabilized by two adjacent heteroatoms, as in Arduengo-type carbenes, and also not necessarily with heteroatoms placed in a position R to the carbene carbon was revived by a serendipitous discovery of C4 bonding in imidazolylidenes.6 The large class of heterocyclic carbenes that can be grouped toget ...

2)](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015968611_1-56df287e8435abc2be6b0a2948d2417f-300x300.png)