3.98 MB - KFUPM Resources v3
... When aqueous solutions of Na2SO4 and Pb(NO3)2 are mixed, PbSO4 precipitates. Calculate the mass of PbSO4 formed when 1.25L of 0.0500M Pb(NO3)2 and 2.00L of 0.0250M Na2SO4 are mixed. How many ions of Pb2+ will remain unreacted in the solution? 1. Identify the ions and possible solid product. ...
... When aqueous solutions of Na2SO4 and Pb(NO3)2 are mixed, PbSO4 precipitates. Calculate the mass of PbSO4 formed when 1.25L of 0.0500M Pb(NO3)2 and 2.00L of 0.0250M Na2SO4 are mixed. How many ions of Pb2+ will remain unreacted in the solution? 1. Identify the ions and possible solid product. ...
Using a Spectrophotometer
... bonds and thus is structurally similar to simple peptides. This molecule when treated with copper sulfate in alkaline solution (the biuret reaction) gives an intense purple color. The reaction is based on the formation of a purple-colored complex between copper ions and two or more peptide bonds. Pr ...
... bonds and thus is structurally similar to simple peptides. This molecule when treated with copper sulfate in alkaline solution (the biuret reaction) gives an intense purple color. The reaction is based on the formation of a purple-colored complex between copper ions and two or more peptide bonds. Pr ...
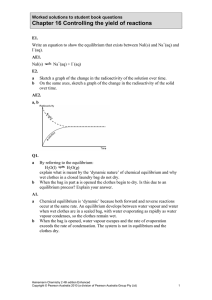
Chapter 16 Controlling the yield of reactions
... 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g) is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium 0. ...
... 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g) is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium 0. ...
AP® Chemistry
... 121 g mol−1) contains 11.0 percent RbCl by mass. From the following information, what is needed to determine the molarity of RbCl in the solution? ...
... 121 g mol−1) contains 11.0 percent RbCl by mass. From the following information, what is needed to determine the molarity of RbCl in the solution? ...
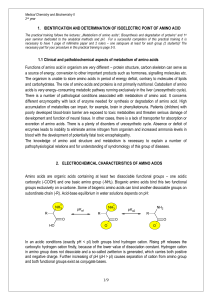
Identification and determination of pI of amino acids
... Functions of amino acid in organism are very different – protein structure, carbon skeleton can serve as a source of energy, conversion to other important products such as hormones, signalling molecules etc. The organism is unable to store amino acids in period of energy deficit, contrary to molecul ...
... Functions of amino acid in organism are very different – protein structure, carbon skeleton can serve as a source of energy, conversion to other important products such as hormones, signalling molecules etc. The organism is unable to store amino acids in period of energy deficit, contrary to molecul ...
Equilibrium
... Chemical equilibrium can be attained whether the reaction begins with all reactants and no products, all products and no reactants, or some of both. Illustrated in the Figure 1.2 are the changes in the concentrations of H2 , I2 , and HI for two different initial reaction mixtures. In the situation d ...
... Chemical equilibrium can be attained whether the reaction begins with all reactants and no products, all products and no reactants, or some of both. Illustrated in the Figure 1.2 are the changes in the concentrations of H2 , I2 , and HI for two different initial reaction mixtures. In the situation d ...
Solids Chemistry XII - The Gurukul Institute
... a) What is meant by the term ‘Crystalline of a solid’? b) Why is quartz regarded as a crystalline solid while glass an amorphous solid? ‘Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting point’ justify the statement. Explain with the help of diagrams the structural differences bet ...
... a) What is meant by the term ‘Crystalline of a solid’? b) Why is quartz regarded as a crystalline solid while glass an amorphous solid? ‘Stability of a crystal is reflected in the magnitude of its melting point’ justify the statement. Explain with the help of diagrams the structural differences bet ...
Syntheses and characterization of [4
... mononuclear ferrocenophane in which one or more bridging units are introduced. Based on the number of the bridges, mononuclear ferrocenophanes can be divided into two subgroups: single bridge ferrocenophanes ([m]) and multiply-bridged ferrocenophanes ([m]n). The second class is defined as multinucle ...
... mononuclear ferrocenophane in which one or more bridging units are introduced. Based on the number of the bridges, mononuclear ferrocenophanes can be divided into two subgroups: single bridge ferrocenophanes ([m]) and multiply-bridged ferrocenophanes ([m]n). The second class is defined as multinucle ...
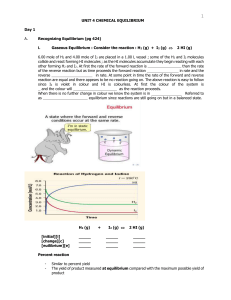
Unit 4 - Chemical Equilibrium
... concentration of products rises. The forward reaction gets gradually slower and the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reaction gets gradually faster. It follows that there must come a time when the reactions are happening in both _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ at the same _ _ _ _ and the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ of reactants and produ ...
... concentration of products rises. The forward reaction gets gradually slower and the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ reaction gets gradually faster. It follows that there must come a time when the reactions are happening in both _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ at the same _ _ _ _ and the _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ of reactants and produ ...
REVIEWS - cchem.berkeley.edu - University of California, Berkeley
... Box 1 j Relativistic effects The theoretical underpinning for relativistic effects arises from the confluence of quantum mechanics and special relativity3,96. Schrödinger’s equation, unveiled in 1926, correctly predicts the atomic orbital energy levels for hydrogen but is unable to account for the ...
... Box 1 j Relativistic effects The theoretical underpinning for relativistic effects arises from the confluence of quantum mechanics and special relativity3,96. Schrödinger’s equation, unveiled in 1926, correctly predicts the atomic orbital energy levels for hydrogen but is unable to account for the ...
Phage display - Miltenyi Biotec
... filamentous bacteriophages, "phage display", has become a cornerstone of techniques to investigate molecular interactions. Phage display is used: - to identify and analyze features of surface proteins that interact with other proteins. - to isolate new ligand that bind to particular amino acid sequen ...
... filamentous bacteriophages, "phage display", has become a cornerstone of techniques to investigate molecular interactions. Phage display is used: - to identify and analyze features of surface proteins that interact with other proteins. - to isolate new ligand that bind to particular amino acid sequen ...
Chapter 4
... The outward appearance of an aqueous solution does not tell us what is present at the microscopic level, that is, whether the solute particles are ions, molecules, or a mixture of the two. Nevertheless, some of the earliest insights into the microscopic nature of aqueous solutions came through macro ...
... The outward appearance of an aqueous solution does not tell us what is present at the microscopic level, that is, whether the solute particles are ions, molecules, or a mixture of the two. Nevertheless, some of the earliest insights into the microscopic nature of aqueous solutions came through macro ...
Ch16
... 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g) is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium ...
... 2HI(g) H2(g) + I2(g) is 48.8 at 455°C. An equilibrium mixture in a 2.0 L vessel at this temperature contains 0.220 mol of H2 and 0.110 mol of I2. a Calculate the concentration of HI in this mixture. b Another mixture was prepared by placing 4.0 mol of HI in a 2.0 L vessel at 330°C. At equilibrium ...