Chapter 25 - Houston ISD
... PH OF A SOLUTION • The pH of a solution is a measure of the concentration of H+ ions in it. • The greater the H+ concentration is, the lower the pH is and the more acidic the solution is. • The pH measures how acidic or basic a solution is. ...
... PH OF A SOLUTION • The pH of a solution is a measure of the concentration of H+ ions in it. • The greater the H+ concentration is, the lower the pH is and the more acidic the solution is. • The pH measures how acidic or basic a solution is. ...
T 1g A 2g
... for d2 using the methods applied earlier to p2, etc. They are 3F, 1D, 3P, 1G, 1S. We identify the GS as 3F. How? We saw earlier that F in octahedral environment splits to A2g + T1g + T2g; in tetrahedral we would get A2 + T1 + T2. Our problem is the energy ordering. Which is GS? Thus the 3F GS for d2 ...
... for d2 using the methods applied earlier to p2, etc. They are 3F, 1D, 3P, 1G, 1S. We identify the GS as 3F. How? We saw earlier that F in octahedral environment splits to A2g + T1g + T2g; in tetrahedral we would get A2 + T1 + T2. Our problem is the energy ordering. Which is GS? Thus the 3F GS for d2 ...
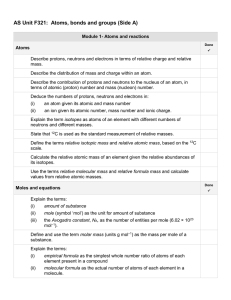
AS Unit F321 Unit 1 Side A check list
... Construct balanced chemical equations for reactions studied and for unfamiliar reactions given reactants and products. Carry out calculations, using amount of substance in mol, involving: (i) ...
... Construct balanced chemical equations for reactions studied and for unfamiliar reactions given reactants and products. Carry out calculations, using amount of substance in mol, involving: (i) ...
complex ion
... • The species formed by linking of а number of ions or molecules by co-ordinate bonds to the central metal atom (or ion) carries positive or negative charge, it is called a complex ion (coordination sphera). [Fe(СN)6]4-, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, [Ag(CN)2]- ...
... • The species formed by linking of а number of ions or molecules by co-ordinate bonds to the central metal atom (or ion) carries positive or negative charge, it is called a complex ion (coordination sphera). [Fe(СN)6]4-, [Cu(NH3)4]2+, [Ag(CN)2]- ...
RESEARCH ARTICLE Coordination Chemistry of Cadmium
... them to settle. Molten autoclaved agar media that had been kept at 48 ◦C was incubated with a broth culture of the microbial species and then poured over the base plate. The discs were air dried and placed on the top of agar layer. The plates were incubated for 24– 30 h and the inhibition zones (mm) ...
... them to settle. Molten autoclaved agar media that had been kept at 48 ◦C was incubated with a broth culture of the microbial species and then poured over the base plate. The discs were air dried and placed on the top of agar layer. The plates were incubated for 24– 30 h and the inhibition zones (mm) ...
topic 1 sol review homework
... a) left, increase b) right, increase c) left, decrease d) right, decrease 6. What color is phenolphthalein in a basic solution? a) blue b) pink c) yellow d) colorless 7.Given the reaction at equilibrium: 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) + heat, which change will shift the equilibrium to the right? a) addi ...
... a) left, increase b) right, increase c) left, decrease d) right, decrease 6. What color is phenolphthalein in a basic solution? a) blue b) pink c) yellow d) colorless 7.Given the reaction at equilibrium: 2SO2(g) + O2(g) 2SO3(g) + heat, which change will shift the equilibrium to the right? a) addi ...
Chapter 19 Worksheet
... 3. The prefixes di, tri etc. are used to denote the number of simple ligands. The prefixes bis, tris and tetrakis etc. are used for more complicated ligands (polydentates), or ones with names that contain di, tri and so on. 4. The oxidation state of the central metal ion is designated with a Roman n ...
... 3. The prefixes di, tri etc. are used to denote the number of simple ligands. The prefixes bis, tris and tetrakis etc. are used for more complicated ligands (polydentates), or ones with names that contain di, tri and so on. 4. The oxidation state of the central metal ion is designated with a Roman n ...
Lecture 02
... Transport Number of an ionic species in the solution Transport number (tB) of an ionic species B, in a solution is defined as the fraction of current carried by that particular ion. ...
... Transport Number of an ionic species in the solution Transport number (tB) of an ionic species B, in a solution is defined as the fraction of current carried by that particular ion. ...
EFFECT OF AMINO ACID (GLYCINE)
... decreases more or less considerably (Dooba~~ Drefo..... ). Thus, in the series of the four elements (Co, Ni, Cu and Zn), Cu, the element having the greatest affinity for complexing agents (Irving & Williams, 1953), is the most strongly affected by the introduction of glycine in the experimental syst ...
... decreases more or less considerably (Dooba~~ Drefo..... ). Thus, in the series of the four elements (Co, Ni, Cu and Zn), Cu, the element having the greatest affinity for complexing agents (Irving & Williams, 1953), is the most strongly affected by the introduction of glycine in the experimental syst ...
Click Here To File
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
... -There are 4 unpaired electrons. -Water is a weak ligand. Thus the hybridisation involved is sp3d2 (marks to be granted if hybridisation is depicted diagrammatically) (ii) The ionisation isomer is [Co(NH3)5SO4]Br. The IUPAC name is pentaamminesulphatocobalt(III)bromide. Chemical test to distinguish ...
Learning objectives: Recall the reactivity of magnesium, zinc, iron
... Predict and explain displacement reactions between metals and metal salt solutions. Explain oxidation and reduction in terms of loss or gain of electrons (H). Explain displacement reactions as examples of redox reactions (H). Suggested time: 30–45 minutes Name: ________________________________ ...
... Predict and explain displacement reactions between metals and metal salt solutions. Explain oxidation and reduction in terms of loss or gain of electrons (H). Explain displacement reactions as examples of redox reactions (H). Suggested time: 30–45 minutes Name: ________________________________ ...
Electrophoretic Studies of Biologically Important Mixed Metal
... strength and temperature) obviously vitiate the ionophoretic mobility of a particular ion. The technique described here is almost free of these vitiating factors and the reliability may vary to ± 2 %. As for the possibility of hydroxy compound formation, we had considered this aspect in our earlier ...
... strength and temperature) obviously vitiate the ionophoretic mobility of a particular ion. The technique described here is almost free of these vitiating factors and the reliability may vary to ± 2 %. As for the possibility of hydroxy compound formation, we had considered this aspect in our earlier ...
CHM 312
... the central metal. The unshared electron pairs are donated into vacant orbitals of the transition metal ion. The number of coordinate bonds from the ligands to the central ion is known as the coordination number of the central ion. Coordination compounds, such as the [FeCl4]- ion and CrCl3 6 NH3, ar ...
... the central metal. The unshared electron pairs are donated into vacant orbitals of the transition metal ion. The number of coordinate bonds from the ligands to the central ion is known as the coordination number of the central ion. Coordination compounds, such as the [FeCl4]- ion and CrCl3 6 NH3, ar ...
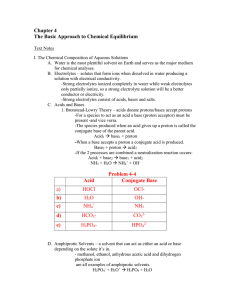
Chapter 4
... - the concentration of water in dilute solutions is very large compared with the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions, so the concentration of water can be re-written as the ion product constant for water: K[H2O]2 = Kw = [H3O+] [OH-] Because OH- and H3O+ are formed only from the dissociation ...
... - the concentration of water in dilute solutions is very large compared with the concentration of hydrogen and hydroxide ions, so the concentration of water can be re-written as the ion product constant for water: K[H2O]2 = Kw = [H3O+] [OH-] Because OH- and H3O+ are formed only from the dissociation ...
ORDANOCHROMIUM CHEMISTRY SUPPORTED BY -DIIMINE LIGANDS
... α-Diimine ligands can accept up to two electrons; thus they can be used to stabilize organometallic compounds in unusually low formal oxidation states of the central metal. This redox ambiguity may be useful for facilitating catalytic reactions involving different oxidation states. We are exploring ...
... α-Diimine ligands can accept up to two electrons; thus they can be used to stabilize organometallic compounds in unusually low formal oxidation states of the central metal. This redox ambiguity may be useful for facilitating catalytic reactions involving different oxidation states. We are exploring ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... PXRD patterns were obtained using Bruker AXSd8 advance X-ray diffractometer with Mo-Kα (λ = 0.7107 Å) and Cu-Kα (λ = 1.54184 Å) radiation sources. The measurements were made at a temperature of 25 °C (RT) and a 2θ angle range of 10°-80°.A step resolution of 0.019° was used with a step time of 19.2 s ...
... PXRD patterns were obtained using Bruker AXSd8 advance X-ray diffractometer with Mo-Kα (λ = 0.7107 Å) and Cu-Kα (λ = 1.54184 Å) radiation sources. The measurements were made at a temperature of 25 °C (RT) and a 2θ angle range of 10°-80°.A step resolution of 0.019° was used with a step time of 19.2 s ...
24 COORDINATION COMPOUNDS Y MODULE - 6
... What is shape associated with a six-coordinated complex? ...
... What is shape associated with a six-coordinated complex? ...
Shapes of d
... Rule: The electrons in the s-orbital are the first to be lost Hence the only valance electrons available in a transition metal ion are d-electrons ...
... Rule: The electrons in the s-orbital are the first to be lost Hence the only valance electrons available in a transition metal ion are d-electrons ...