AP Chemistry - Partners4results
... 2. A Brønsted-Lowry base is defined as a substance that a. increases [H+] when placed in H2O. b. decreases [H+] when placed in H2O. c. increases [OH-] when placed in H2O. d. acts as a proton acceptor. e. acts as a proton donor. 3. A substance that is capable of acting as both an acid and as a base i ...
... 2. A Brønsted-Lowry base is defined as a substance that a. increases [H+] when placed in H2O. b. decreases [H+] when placed in H2O. c. increases [OH-] when placed in H2O. d. acts as a proton acceptor. e. acts as a proton donor. 3. A substance that is capable of acting as both an acid and as a base i ...
Forming Ligand in Homo-and Heterometallic Complexes - Hal-CEA
... there is some uncertainty as to the subsequent deprotonation order, with either the protons at positions 2 and 5 being the more acidic,1 or a 2, 4, 5, 3 deprotonation sequence.14 However, esterification of H4thftc in methanol gave the 2,5-diester, thus showing that the carboxylic groups at those pos ...
... there is some uncertainty as to the subsequent deprotonation order, with either the protons at positions 2 and 5 being the more acidic,1 or a 2, 4, 5, 3 deprotonation sequence.14 However, esterification of H4thftc in methanol gave the 2,5-diester, thus showing that the carboxylic groups at those pos ...
complexometric titration -
... between the analyte and titrant. • Complexometric titrations are particularly useful f l ffor determination d t i ti off a mixture i t off different metal ions in solution. An indicator with a marked color change is usually used to detect the end-point end point of the titration. ...
... between the analyte and titrant. • Complexometric titrations are particularly useful f l ffor determination d t i ti off a mixture i t off different metal ions in solution. An indicator with a marked color change is usually used to detect the end-point end point of the titration. ...
Arrhenius Theory The Arrhenius theory, named after Swedish
... The Arrhenius theory, named after Swedish physicist Svante August Arrhenius, views an acid as a substance that increases the concentration of the hydronium ion (H3O+) in an aqueous solution and a base as a substance that increases the hydroxide ion (OH−) concentration. Well-known acids include hydro ...
... The Arrhenius theory, named after Swedish physicist Svante August Arrhenius, views an acid as a substance that increases the concentration of the hydronium ion (H3O+) in an aqueous solution and a base as a substance that increases the hydroxide ion (OH−) concentration. Well-known acids include hydro ...
Chapter 4: Solution Chemistry and the Hydrosphere
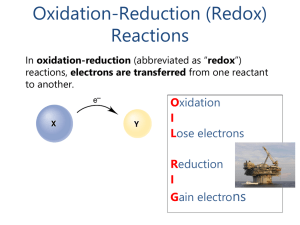
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In Al2O3, the ions are Al+3 and O2–, so oxidation #’s: Al = +3 and O = -2 3. In a compound or polyatomic ion, – Group I elements are always +1. – Group ...
... 2. The oxidation number of a monatomic ion is the charge on the ion. Examples: Na3N, the ions are Na+ and N3–, so oxidation #’s: Na = +1 and N = -3. In Al2O3, the ions are Al+3 and O2–, so oxidation #’s: Al = +3 and O = -2 3. In a compound or polyatomic ion, – Group I elements are always +1. – Group ...
Crystal Field Theory and the Spectrochemical Series for Cobalt (III
... understand the interaction of a transition metal ion with light, we must first explore how d-orbitals and their electrons are affected by bound ligands. In a free transition metal ion with no bound ligands, the 5 d-orbitals all have the same energy and are said to be degenerate. Ligand binding leads ...
... understand the interaction of a transition metal ion with light, we must first explore how d-orbitals and their electrons are affected by bound ligands. In a free transition metal ion with no bound ligands, the 5 d-orbitals all have the same energy and are said to be degenerate. Ligand binding leads ...
BCC-44-4-289-298 - Bulgarian Chemical Communications
... X-ray powder analyses and SEM measurements were used and the corresponding data are given in Tables 1-3. The metal-to-ligand ratio in the mononuclear Cu(II) and Co(II) complexes was found to be 1:1. The interaction of the ligands (L1H2, L2H2, L3H2 and L4H2) with Cu(II) and Co(II) salt yielded comple ...
... X-ray powder analyses and SEM measurements were used and the corresponding data are given in Tables 1-3. The metal-to-ligand ratio in the mononuclear Cu(II) and Co(II) complexes was found to be 1:1. The interaction of the ligands (L1H2, L2H2, L3H2 and L4H2) with Cu(II) and Co(II) salt yielded comple ...
Ligand Conformation Enforces Trigonal
... crystallography and was found to consist of two nearly identical discrete dinuclear molecules with bis(pyrazolato) bridges. The copper(II) ion has a trigonal bipyramid geometry achieved by the coordination of an aliphatic nitrogen, two pyridine moieties, and two pyrazolato nitrogens. Variable temper ...
... crystallography and was found to consist of two nearly identical discrete dinuclear molecules with bis(pyrazolato) bridges. The copper(II) ion has a trigonal bipyramid geometry achieved by the coordination of an aliphatic nitrogen, two pyridine moieties, and two pyrazolato nitrogens. Variable temper ...
Color and Bonding in Transition Metal Complexes
... Diamagnetism – All electrons are paired up, which leads to equal numbers of spin up and spin down electrons (i.e. [Co(CN)6]3-) Paramagnetism – Unpaired electrons, which leads to unequal numbers of spin up and spin down electrons ((i.e. [CoF6]3-) ...
... Diamagnetism – All electrons are paired up, which leads to equal numbers of spin up and spin down electrons (i.e. [Co(CN)6]3-) Paramagnetism – Unpaired electrons, which leads to unequal numbers of spin up and spin down electrons ((i.e. [CoF6]3-) ...
Lecture 10 -Further Consequences of d-Orbital
... Nickel(II) vs. platinum(II): why is Pt2+ found only in square planar coordination but Ni2+ is found in several geometries? Let's consider a single example. Nickel forms the octahedral hexaammine complex, [Ni(NH3)6]2+ , but platinum forms the square planar tetraammine complex [Pt(NH3)4]2+ . Both meta ...
... Nickel(II) vs. platinum(II): why is Pt2+ found only in square planar coordination but Ni2+ is found in several geometries? Let's consider a single example. Nickel forms the octahedral hexaammine complex, [Ni(NH3)6]2+ , but platinum forms the square planar tetraammine complex [Pt(NH3)4]2+ . Both meta ...
193 - Wayne State Chemistry
... It has been proposed that the lack of d-block metal complexes bearing η2-pz ligands can be attributed to the directional nature of the nitrogen lone pairs,3 which does not allow simultaneous coordination of both nitrogens by a single metal. In lanthanides and actinides, the metals are larger and the ...
... It has been proposed that the lack of d-block metal complexes bearing η2-pz ligands can be attributed to the directional nature of the nitrogen lone pairs,3 which does not allow simultaneous coordination of both nitrogens by a single metal. In lanthanides and actinides, the metals are larger and the ...
Spin states (d electrons)
... configurations. These configurations can be understood through the two major models used to describe coordination complexes; ligand field theory, which is an application of molecular orbital theory to transition metals, and crystal field theory, which has roots in VSEPR theory.[1] ...
... configurations. These configurations can be understood through the two major models used to describe coordination complexes; ligand field theory, which is an application of molecular orbital theory to transition metals, and crystal field theory, which has roots in VSEPR theory.[1] ...
Lecture 10 -Further Consequences of d
... complexes have shorter bonds than six-coordinate complexes, and shorter bonds are stronger bonds bonds. For a divalent ion such as Ni(II), Ni(II) the estimated bond energy for each Ni-OH2 bond in [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is about 300 kJ/mol; for the tetraaquo complex. In either tetrahedral or square geometry it ...
... complexes have shorter bonds than six-coordinate complexes, and shorter bonds are stronger bonds bonds. For a divalent ion such as Ni(II), Ni(II) the estimated bond energy for each Ni-OH2 bond in [Ni(H2O)6]2+ is about 300 kJ/mol; for the tetraaquo complex. In either tetrahedral or square geometry it ...
Student Projects for B.Sc. Chemistry
... • In acid medium Titanium ions give an yellow orange complex with H2O2 which forms the basis of spectrometric method for determination of Titanium. • The interference from other elements can be eliminated by the addition of citric acid / tartaric acid ...
... • In acid medium Titanium ions give an yellow orange complex with H2O2 which forms the basis of spectrometric method for determination of Titanium. • The interference from other elements can be eliminated by the addition of citric acid / tartaric acid ...
18 - Wiley
... for charges on all species other than the transition metal. Here, en is neutral. Each Cl– anion contributes –1 charge, so the oxidation number of Fe is +3. Fe is in Column 8 of the periodic table, so its valence configuration is 3d5. (c) Coordination number 6 means octahedral geometry. (d) With an o ...
... for charges on all species other than the transition metal. Here, en is neutral. Each Cl– anion contributes –1 charge, so the oxidation number of Fe is +3. Fe is in Column 8 of the periodic table, so its valence configuration is 3d5. (c) Coordination number 6 means octahedral geometry. (d) With an o ...
Rare Oxidation-State Combinations and Unusual Structural Motifs in
... μ4-O2- group. Peripheral ligation is provided by six PhCO2and four phpao- ligands. Each Mn center is six-coordinate and possesses distorted octahedral geometry. The PhCO2groups separate into two classes. Four are η1:η1:μ and the other two are η1:η2:μ3. Two phpao- groups are η1:η1:η1:μ, with the N at ...
... μ4-O2- group. Peripheral ligation is provided by six PhCO2and four phpao- ligands. Each Mn center is six-coordinate and possesses distorted octahedral geometry. The PhCO2groups separate into two classes. Four are η1:η1:μ and the other two are η1:η2:μ3. Two phpao- groups are η1:η1:η1:μ, with the N at ...