High Mass Resolution Plasma Desorption and
... The negative SIMS and PDM S spectra of all com pounds are dom inated by nickel sulfur cluster ions o f the com position (Ni^S^)- . F or most of these ions an excess of metal atom s is observed: i.e. x > y. The distribution o f these cluster ions ranges from x, y = 4 up to x, y « 30. The highest inte ...
... The negative SIMS and PDM S spectra of all com pounds are dom inated by nickel sulfur cluster ions o f the com position (Ni^S^)- . F or most of these ions an excess of metal atom s is observed: i.e. x > y. The distribution o f these cluster ions ranges from x, y = 4 up to x, y « 30. The highest inte ...
Activation Energy
... Dissociative (D or Id) from experiment 1. Rate of reaction changes only slightly or not at all with changes in the incoming ligand – Aquation (incoming ligand is water) and anation (incoming ligand is an anion) are similar 2. Increasing positive charge on complex decreases the rate of substitution ...
... Dissociative (D or Id) from experiment 1. Rate of reaction changes only slightly or not at all with changes in the incoming ligand – Aquation (incoming ligand is water) and anation (incoming ligand is an anion) are similar 2. Increasing positive charge on complex decreases the rate of substitution ...
Chapter 1
... B) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between atoms. C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between atoms. D) Covalent bonds involve the s ...
... B) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between atoms. C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between atoms. D) Covalent bonds involve the s ...
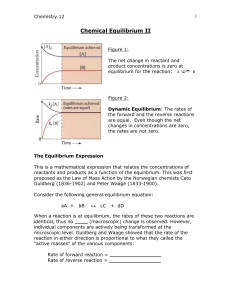
Chemical Equilibrium II
... concentrations in terms of _________ for aqueous solutions or _________________ for gases (although for the purposes of Chemistry 12, we will not be using partial pressures) Some rules to follow when writing equilibrium expressions: “____________” concentrations in equilibrium expressions: Substance ...
... concentrations in terms of _________ for aqueous solutions or _________________ for gases (although for the purposes of Chemistry 12, we will not be using partial pressures) Some rules to follow when writing equilibrium expressions: “____________” concentrations in equilibrium expressions: Substance ...
`Relaxing` The Orbital Selection Rule
... The width of a band relates to the vibrational excitation that accompanies the electronic transition: narrow bands: excited state has similar geometry to the ground state broad bands: excited state has different geometry to the ground state The height or area of a band relates to the number of p ...
... The width of a band relates to the vibrational excitation that accompanies the electronic transition: narrow bands: excited state has similar geometry to the ground state broad bands: excited state has different geometry to the ground state The height or area of a band relates to the number of p ...
Transition metal complexes of NO
... NO, NO,, and NO, complexes of transition metals comprise a class of materials with many potential uses as catalysts, as oxidants and as precursors to new and otherwise inaccessible compounds. As yet, much of this potential is unrealized because NO, and NO, compounds which are soluble in organic medi ...
... NO, NO,, and NO, complexes of transition metals comprise a class of materials with many potential uses as catalysts, as oxidants and as precursors to new and otherwise inaccessible compounds. As yet, much of this potential is unrealized because NO, and NO, compounds which are soluble in organic medi ...
Chapter 2
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory Examine Dalton's Atomic Theory. ❶All matter is composed of atoms, indivisible particles that are exceedingly small. ❷All atoms of a given element are identical, both in mass and in chemical properties. However, they are different from atoms of other elements. ❸Atoms are not cr ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory Examine Dalton's Atomic Theory. ❶All matter is composed of atoms, indivisible particles that are exceedingly small. ❷All atoms of a given element are identical, both in mass and in chemical properties. However, they are different from atoms of other elements. ❸Atoms are not cr ...
The concept of pH and pKa
... equilibrium moves to the left (as there are hydrogen ions on the right-hand side of the equilibrium expression) hydroxide ions are added the equilibrium moves to the right (as hydrogen ions are removed in the reaction H+ + OH- → H2O) some of the added reagent is consumed in shifting the equilibriu ...
... equilibrium moves to the left (as there are hydrogen ions on the right-hand side of the equilibrium expression) hydroxide ions are added the equilibrium moves to the right (as hydrogen ions are removed in the reaction H+ + OH- → H2O) some of the added reagent is consumed in shifting the equilibriu ...
Complexes of The Group 6 Elements
... of the similar 31 P- 13 C coupling of the carbonyl carbon to two phosphorus atoms. In line with the metal dependence of the 31 P-NMR chemical shift, one observes the largest downfield shift in the 13 C-NMR signals of the carbonyl groups for the chromium upon phosphine substitution. This reflects the ...
... of the similar 31 P- 13 C coupling of the carbonyl carbon to two phosphorus atoms. In line with the metal dependence of the 31 P-NMR chemical shift, one observes the largest downfield shift in the 13 C-NMR signals of the carbonyl groups for the chromium upon phosphine substitution. This reflects the ...
1999 Advanced Placement Chemistry Exam Section I: Multiple
... (C) all points on the curve between Q and S (A) The pressure on the walls of the balloon in(D) all points on the curve between R and T creases with increasing temperature. (E) no point on the curve (B) The difference in temperature between the air inside and outside the balloon produces ... C10H12O4 ...
... (C) all points on the curve between Q and S (A) The pressure on the walls of the balloon in(D) all points on the curve between R and T creases with increasing temperature. (E) no point on the curve (B) The difference in temperature between the air inside and outside the balloon produces ... C10H12O4 ...
Topics 7 and 17 Outlines
... • The characteristics of chemical and physical systems in a state of equilibrium. • Deduction of the equilibrium constant expression (Kc) from an equation for a homogeneous reaction. • Determination of the relationship between different equilibrium constants (Kc) for the same reaction at the same te ...
... • The characteristics of chemical and physical systems in a state of equilibrium. • Deduction of the equilibrium constant expression (Kc) from an equation for a homogeneous reaction. • Determination of the relationship between different equilibrium constants (Kc) for the same reaction at the same te ...
Activities 2
... B) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between atoms. C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between atoms. D) Covalent bonds involve the s ...
... B) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of pairs of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of single electrons between atoms. C) Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between atoms. D) Covalent bonds involve the s ...
The Copper Cycle
... 1st Beaker: At the end of Part I, hydrated copper complex, Cu2+ are present, making the solution blue, and excess hydronium ions (H3O+) remain from the nitric acid used. 2nd Beaker: Adding NaOH(aq) to the blue solution results in the OH– ions neutralizing the H3O+ ions to form water: H3O+(aq) + OH–( ...
... 1st Beaker: At the end of Part I, hydrated copper complex, Cu2+ are present, making the solution blue, and excess hydronium ions (H3O+) remain from the nitric acid used. 2nd Beaker: Adding NaOH(aq) to the blue solution results in the OH– ions neutralizing the H3O+ ions to form water: H3O+(aq) + OH–( ...
Strong Antiferromagnetic Coupling at Long Distance through a
... understood by analyzing the possible charge transfer (CT) states for a model for two orbitals a and b interacting trough a diamagnetic π system, schematically depicted in 4. CT states corresponding to a one-electron transfer, responsible for the decreased spin population at Cr atoms with increasing ...
... understood by analyzing the possible charge transfer (CT) states for a model for two orbitals a and b interacting trough a diamagnetic π system, schematically depicted in 4. CT states corresponding to a one-electron transfer, responsible for the decreased spin population at Cr atoms with increasing ...
Bonding Notes
... Ionic bonds can happen when metals and non-metals (especially halogens, Oxygen, or Sulfur) react: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) —> 2NaCl(s) [the subscripts (s) and (g) indicate solid and gas states respectively] They also can form when the ions already exist, such as when a solution evaporates: [the subscript (aq ...
... Ionic bonds can happen when metals and non-metals (especially halogens, Oxygen, or Sulfur) react: 2Na(s) + Cl2(g) —> 2NaCl(s) [the subscripts (s) and (g) indicate solid and gas states respectively] They also can form when the ions already exist, such as when a solution evaporates: [the subscript (aq ...
makeup2
... 61. 2.80 grams of a monoprotic weak acid, HX, was dissolved in water. Titration of the acid to its equivalence point required 29.2 mL of 0.500 M NaOH solution. What is the molecular weight of the acid, HX? (A) 192 g/mol (B) 164 g/mol (C) 96.0 g/mol (D) 5.21 g/mol 62. The ionic reaction 3 I¯ + S2O82¯ ...
... 61. 2.80 grams of a monoprotic weak acid, HX, was dissolved in water. Titration of the acid to its equivalence point required 29.2 mL of 0.500 M NaOH solution. What is the molecular weight of the acid, HX? (A) 192 g/mol (B) 164 g/mol (C) 96.0 g/mol (D) 5.21 g/mol 62. The ionic reaction 3 I¯ + S2O82¯ ...
Chapter 3 Ligand Effects
... Research on ligand effects in aqueous solution has mainly focused on two types of organic reactions: decarboxylation and hydrolysis reactions. In section 2.1.1 the Lewis-acid catalysis of the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate was discussed. The mechanism of this reaction is outlined in entry 4 in Sche ...
... Research on ligand effects in aqueous solution has mainly focused on two types of organic reactions: decarboxylation and hydrolysis reactions. In section 2.1.1 the Lewis-acid catalysis of the decarboxylation of oxaloacetate was discussed. The mechanism of this reaction is outlined in entry 4 in Sche ...