Chemical Equilibrium Stress? What stress? 1
... liquid cannot change, it is fixed and equal to the liquid’s K = [H2]2 [O2] density. [H2O]2 We know that K remains constant for all combinations of reactant and product K[H2O]2 = [H2]2 [O2] = K concentrations at equilibrium. Therefore, since K is constant and the concentration of water is constan ...
... liquid cannot change, it is fixed and equal to the liquid’s K = [H2]2 [O2] density. [H2O]2 We know that K remains constant for all combinations of reactant and product K[H2O]2 = [H2]2 [O2] = K concentrations at equilibrium. Therefore, since K is constant and the concentration of water is constan ...
test question - Oregon State chemistry
... Discuss the true nature of the acidic species (proton, hydronium, more complex) in aqueous solutions. Define, determine, and use Ka, Kb, Kw and pK values. List common strong and weak acids and bases. Explain solvent leveling and provide significant examples. Write equations and that generate polyoxo ...
... Discuss the true nature of the acidic species (proton, hydronium, more complex) in aqueous solutions. Define, determine, and use Ka, Kb, Kw and pK values. List common strong and weak acids and bases. Explain solvent leveling and provide significant examples. Write equations and that generate polyoxo ...
File - cpprashanths Chemistry
... CO as a ligand binds itself to metal through C atom to central atom. CO is also an acceptor ligand as there are vacant pie molecular orbitals in CO. This is called back bonding. This stabilizes metal ligand interactions. ...
... CO as a ligand binds itself to metal through C atom to central atom. CO is also an acceptor ligand as there are vacant pie molecular orbitals in CO. This is called back bonding. This stabilizes metal ligand interactions. ...
Divalent Metal-Ion Complexes with Dipeptide
... here. The overall theme is elucidating the factors that determine the preferred binding mode for a given complex. Within this framework we will address four specific questions: (1) Considering the choice between ZW and CS, these modes are competitive for the weak-binding metals, and we will be lookin ...
... here. The overall theme is elucidating the factors that determine the preferred binding mode for a given complex. Within this framework we will address four specific questions: (1) Considering the choice between ZW and CS, these modes are competitive for the weak-binding metals, and we will be lookin ...
Unit 5 - Ionic Compounds
... An Ionic Bond is a chemical bond caused by electrostatic attraction between cations and anions that is formed by transferring electrons between atoms. Electrostatic attraction simply means the attraction of opposite charges. ...
... An Ionic Bond is a chemical bond caused by electrostatic attraction between cations and anions that is formed by transferring electrons between atoms. Electrostatic attraction simply means the attraction of opposite charges. ...
Course Notes
... acceptor is a base. In the first reaction water accepted a proton from the bicarbonate ion. In this reaction water donates a proton. ...
... acceptor is a base. In the first reaction water accepted a proton from the bicarbonate ion. In this reaction water donates a proton. ...
Sample Paper Chemistry - Educomp Solutions Ltd.
... (ii) What can be inferred from the magnetic moment of the complex K4[Mn(CN)6] Magnetic moment: 2.2 BM? ...
... (ii) What can be inferred from the magnetic moment of the complex K4[Mn(CN)6] Magnetic moment: 2.2 BM? ...
Chemistry 30 Review of Basic Chemistry 20
... elements with more than one charge: • use Roman numerals to indicate the charge of the ion used. Example: CuCl is copper (I) chloride Example: CuCl2 is copper (II) chloride ...
... elements with more than one charge: • use Roman numerals to indicate the charge of the ion used. Example: CuCl is copper (I) chloride Example: CuCl2 is copper (II) chloride ...
The strict determination of the term volatility is based on the
... phase exchange KNdCl4(g) + KCl(g) = NdCl3(g) + K2Cl2(g) allows to suggest that the structural change during the reaction is not drastic and that the KNdCl4(g) complex has two bridging and two terminal chlorine atoms [4]. It is well known that aluminum trichloride (as well as FeCl3, GaCl3) due to th ...
... phase exchange KNdCl4(g) + KCl(g) = NdCl3(g) + K2Cl2(g) allows to suggest that the structural change during the reaction is not drastic and that the KNdCl4(g) complex has two bridging and two terminal chlorine atoms [4]. It is well known that aluminum trichloride (as well as FeCl3, GaCl3) due to th ...
Net ionic equation
... Soluble only means greater than 0.01 moles dissolve in 1 L of solution 1. All nitrates, acetates, ammonium and Group 1 salts are soluble 2. Solubility of chlorides, bromides and iodides (all soluble except Ag+ Pb2+ and Hg22+) 3. Hydroxides (all insoluble except rule 1, Ca, Sr, Ba) ...
... Soluble only means greater than 0.01 moles dissolve in 1 L of solution 1. All nitrates, acetates, ammonium and Group 1 salts are soluble 2. Solubility of chlorides, bromides and iodides (all soluble except Ag+ Pb2+ and Hg22+) 3. Hydroxides (all insoluble except rule 1, Ca, Sr, Ba) ...
Synthesis, Structure, Magnetic Properties and Phase Diagram of a
... ferrocene (Fc) was added as internal reference. The potential of Fc+/Fc couple was taken to +460 mV vs SCE.5 The reversibility of the first oxidation process is evidenced by the dependence of peak currents with the square-root of the scan rate. For electrolysis, the preparating electrode was a Pt gr ...
... ferrocene (Fc) was added as internal reference. The potential of Fc+/Fc couple was taken to +460 mV vs SCE.5 The reversibility of the first oxidation process is evidenced by the dependence of peak currents with the square-root of the scan rate. For electrolysis, the preparating electrode was a Pt gr ...
ZnSo4 CuSo4 Zn Cu
... Name the above purification of Nickel. (1) (b)Semiconductor grade silicon is obtained by zone refining. Describe the process. (2) 7. (a) Account for the following . ...
... Name the above purification of Nickel. (1) (b)Semiconductor grade silicon is obtained by zone refining. Describe the process. (2) 7. (a) Account for the following . ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... Vast quantity of dyes are annually produced and consumed in many different industries all over the world, which include pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, leather, paper, and textiles [1]. Dyes are coloured compounds, they absorbed light in the visible region of the spectrum (400-700nm) and posses at ...
... Vast quantity of dyes are annually produced and consumed in many different industries all over the world, which include pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, food, leather, paper, and textiles [1]. Dyes are coloured compounds, they absorbed light in the visible region of the spectrum (400-700nm) and posses at ...
Syllabus - Chemistry
... VSEPR: Shape of molecules and ions; limitations Hydrogen bond: Detection, theories, effect on properties and π- hydrogen bonding. Odd electron bonds: Types, properties and molecular orbital treatment. Metal Clusters. Introduction to metal clusters; Dinuclear species; trinuclear clusters; metal-metal ...
... VSEPR: Shape of molecules and ions; limitations Hydrogen bond: Detection, theories, effect on properties and π- hydrogen bonding. Odd electron bonds: Types, properties and molecular orbital treatment. Metal Clusters. Introduction to metal clusters; Dinuclear species; trinuclear clusters; metal-metal ...
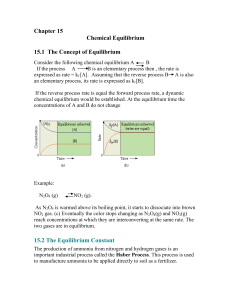
Consider the following chemical equilibrium A B
... where n is the change in the number of moles of gas in the balance equation The numerical value of the equilibrium constant tells us something about the nature of the reaction. When K (Kc or Kp) is a very large number, we say that the equilibrium lies to the right. That means that products predomina ...
... where n is the change in the number of moles of gas in the balance equation The numerical value of the equilibrium constant tells us something about the nature of the reaction. When K (Kc or Kp) is a very large number, we say that the equilibrium lies to the right. That means that products predomina ...
Conductometric and Potentiometric Determination of the Solubility
... determined at 25̊C and corrected for the dilution effect. About 0.5 g portion of each ionassociates Ds3PM2, Ds3PT2, Ds2SM, Ds2ST, DsTPB2, DsRein2, and DsPi2 was added to 50 ml distilled water. The solutions were shaken for about 24 h at 25˚C and left to stand for a week to attain a stable equilibriu ...
... determined at 25̊C and corrected for the dilution effect. About 0.5 g portion of each ionassociates Ds3PM2, Ds3PT2, Ds2SM, Ds2ST, DsTPB2, DsRein2, and DsPi2 was added to 50 ml distilled water. The solutions were shaken for about 24 h at 25˚C and left to stand for a week to attain a stable equilibriu ...
Chemistry - University of Kashmir
... VSEPR: Shape of molecules and ions; limitations Hydrogen bond: Detection, theories, effect on properties and π- hydrogen bonding. Odd electron bonds: Types, properties and molecular orbital treatment. Metal Clusters. Introduction to metal clusters; Dinuclear species; trinuclear clusters; metal-metal ...
... VSEPR: Shape of molecules and ions; limitations Hydrogen bond: Detection, theories, effect on properties and π- hydrogen bonding. Odd electron bonds: Types, properties and molecular orbital treatment. Metal Clusters. Introduction to metal clusters; Dinuclear species; trinuclear clusters; metal-metal ...
Document
... water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...
... water, results in a solution that can conduct electricity. A nonelectrolyte is a substance that, when dissolved, results in a solution that does not conduct electricity. ...