VALIDITY OF HENRY`S LAW IN DILUTE SOLUTIONS (l)
... refers to the solvent and L is the Henry-Dalton absorption coefficient) the absorption cocfficient can be approximately constant even in such concentration intervals where the activity coefficient of the gas dissolved is not constant. This is equivalent to the original interpretation of Henry's Law. ...
... refers to the solvent and L is the Henry-Dalton absorption coefficient) the absorption cocfficient can be approximately constant even in such concentration intervals where the activity coefficient of the gas dissolved is not constant. This is equivalent to the original interpretation of Henry's Law. ...
Module 3 -- Lesson 4
... When the volume of the container holding a gaseous system is reduced, the system responds by reducing its own volume. This is done by decreasing the total number of gaseous molecules in the system. Example: In the reaction H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2HCl(g), all substances are gases. Pressure would not shift ...
... When the volume of the container holding a gaseous system is reduced, the system responds by reducing its own volume. This is done by decreasing the total number of gaseous molecules in the system. Example: In the reaction H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2HCl(g), all substances are gases. Pressure would not shift ...
Soluble salts
... ions. A good example is sodium chloride dissolved in water. NaCl(s) + H2O(l) ---> NaCl(aq) How sodium chloride exists in solution. ____________________________________________ ________ electrolyte are solutes that exist in solution predominantly in the form of hydrated (solvated) molecules. A good e ...
... ions. A good example is sodium chloride dissolved in water. NaCl(s) + H2O(l) ---> NaCl(aq) How sodium chloride exists in solution. ____________________________________________ ________ electrolyte are solutes that exist in solution predominantly in the form of hydrated (solvated) molecules. A good e ...
EXPERIMENT III PREPARATION AND IDENTIFICATION OF
... OF COBALT(III)-IMINODIACETATE Compounds with the same formula, but different structures are called isomers, of which two types can be classified. These include structural isomer and stereoisomer. One type of structural isomerism that may arise when a ligand has more than one chemically distinct dono ...
... OF COBALT(III)-IMINODIACETATE Compounds with the same formula, but different structures are called isomers, of which two types can be classified. These include structural isomer and stereoisomer. One type of structural isomerism that may arise when a ligand has more than one chemically distinct dono ...
Oxidation of benzoin with anchored vanadyl and
... carried out in the absence of catalyst, was very slow and low yields of benzil were obtained even when the reaction was allowed to proceed for a longer time (up to 32 h). Experiments were carried out using (i) the organic polymer without ligand and metal complex and (ii) the organic polymer function ...
... carried out in the absence of catalyst, was very slow and low yields of benzil were obtained even when the reaction was allowed to proceed for a longer time (up to 32 h). Experiments were carried out using (i) the organic polymer without ligand and metal complex and (ii) the organic polymer function ...
SURP Physical Sciences 5
... One strategy for developing transition metal complexes capable of mediating multielectron bond activation reactions is to design redox activity into both the metal center and the auxiliary ligand set. In this program, systems of the type MII(isq)2 (M = Ni, Pd, Pt; isq– = 4,6-ditert-butyl-2-arylimino ...
... One strategy for developing transition metal complexes capable of mediating multielectron bond activation reactions is to design redox activity into both the metal center and the auxiliary ligand set. In this program, systems of the type MII(isq)2 (M = Ni, Pd, Pt; isq– = 4,6-ditert-butyl-2-arylimino ...
The origin and status of the Arrhenius equation
... the kinetics of reactions in solution an awareness of a more general shortcomine of the Arrhenius eouation in that experimental data, obiained with improved'precision and over wider ranaes of temperature. showed that in certain cases ~rrheniusblotswere -&deniably curved. Ironically, one of the first ...
... the kinetics of reactions in solution an awareness of a more general shortcomine of the Arrhenius eouation in that experimental data, obiained with improved'precision and over wider ranaes of temperature. showed that in certain cases ~rrheniusblotswere -&deniably curved. Ironically, one of the first ...
Chemical Equation Reactions
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
... 2. Solid calcium reacts with oxygen gas. 3. Solutions of aluminum chloride & sodium carbonate are mixed. 4. Liquid magnesium bromide is decomposed at high temperature. 5. Solid nickel is reacted with aqueous magnesium sulfate. 6. Chlorine gas is reacted with aqueous potassium bromide. 7. Solid magne ...
as a PDF
... correspond to ionization from the orbitals of mainly metal d-character of t2 and e symmetry. The remaining i.p.s have counterparts in the free ligands, that at 13.2 eV in the nickel and at 14.5 eV in the platinum complex correspond to ionization from orbitals that correlate with the phosphorous lone ...
... correspond to ionization from the orbitals of mainly metal d-character of t2 and e symmetry. The remaining i.p.s have counterparts in the free ligands, that at 13.2 eV in the nickel and at 14.5 eV in the platinum complex correspond to ionization from orbitals that correlate with the phosphorous lone ...
CHAPTER 4: AQUEOUS REACTIONS AND SOLUTION
... The substance present in the greatest quantity is called the solvent. Water is considered the universal solvent because of its ability to dissolve many substances. The other dissolved substances are called the solutes. A solvent dissolves a solute. ...
... The substance present in the greatest quantity is called the solvent. Water is considered the universal solvent because of its ability to dissolve many substances. The other dissolved substances are called the solutes. A solvent dissolves a solute. ...
Document
... As stated above, a buffer solution resists changes in pH by consuming and countering the effects of strong acids and bases. A brief overview of how a buffer is made and how it serves to counteract changes in pH can be seen at the link below. (If this link does not open, just double-click on the Powe ...
... As stated above, a buffer solution resists changes in pH by consuming and countering the effects of strong acids and bases. A brief overview of how a buffer is made and how it serves to counteract changes in pH can be seen at the link below. (If this link does not open, just double-click on the Powe ...
template - Communications in Inorganic Synthesis
... SCHEMES. Groups of reactions that show action are called schemes. Schemes may have brief titles describing their contents. The title should follow the format "Scheme 1. Schemes may also have footnotes. To insert the scheme into the template, be sure it is already sized appropriately and paste after ...
... SCHEMES. Groups of reactions that show action are called schemes. Schemes may have brief titles describing their contents. The title should follow the format "Scheme 1. Schemes may also have footnotes. To insert the scheme into the template, be sure it is already sized appropriately and paste after ...
IB Chemistry Summer Assignment Summer 2013
... Memorize the names, formulas and charges of common ions (see separate sheet) Be able to name the three basic sub-atomic particles, their mass, charge and general location within the atom. Know the difference between an atom and an ion. Given the name of an ionic compound, write its chemical formula ...
... Memorize the names, formulas and charges of common ions (see separate sheet) Be able to name the three basic sub-atomic particles, their mass, charge and general location within the atom. Know the difference between an atom and an ion. Given the name of an ionic compound, write its chemical formula ...
Document
... Standard enthalpy of formation of a compound, Hof, is the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of compound with all substances in their standard ...
... Standard enthalpy of formation of a compound, Hof, is the enthalpy change for the formation of 1 mol of compound with all substances in their standard ...
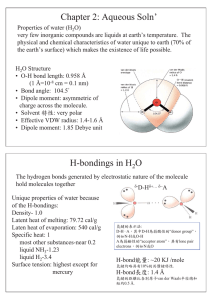
Chapter 2: Aqueous Soln` H
... The Lewis definition encompasses the Bronsted-Lowry definition: In the reaction of H+ and OH-, H+ is a Lewis acid because it accepts an electron pair from the OH-. Since the OH- donates an electron pair we call it a Lewis base. As an example not described by the Bronsted-Lowry definition, Al3+ in wa ...
... The Lewis definition encompasses the Bronsted-Lowry definition: In the reaction of H+ and OH-, H+ is a Lewis acid because it accepts an electron pair from the OH-. Since the OH- donates an electron pair we call it a Lewis base. As an example not described by the Bronsted-Lowry definition, Al3+ in wa ...
Mercury Complexes Derived From Some Acetone
... coordination process. The bands centered nearly at 1600 and 1550 cm-1 were assigned to uC=N and uC=C; they displayed positive shift upon complexation. This result may be due to the summation of two effects, which could be summarized in the following equation: Total shift in uC=N = [shift due to the ...
... coordination process. The bands centered nearly at 1600 and 1550 cm-1 were assigned to uC=N and uC=C; they displayed positive shift upon complexation. This result may be due to the summation of two effects, which could be summarized in the following equation: Total shift in uC=N = [shift due to the ...
handout 4
... 1. Salts containing Group I elements are soluble (Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, Rb+). Exceptions to this rule are rare. Salts containing the ammonium ion (NH4+) are also soluble. 2. Salts containing nitrate ion (NO3-) are generally soluble. 3. Salts containing Cl -, Br -, I - are generally soluble. Important e ...
... 1. Salts containing Group I elements are soluble (Li+, Na+, K+, Cs+, Rb+). Exceptions to this rule are rare. Salts containing the ammonium ion (NH4+) are also soluble. 2. Salts containing nitrate ion (NO3-) are generally soluble. 3. Salts containing Cl -, Br -, I - are generally soluble. Important e ...
20-2 Chemistry of Acyl Halides and Anhydrides(PPT)
... Alkanoyl chlorides are reduced to alcohols when sodium borohydride or lithium aluminum hydride are used directly. The reaction stops at the aldehyde if LiAlH4 is first reacted with three molecules of 2-methyl-2-propanol (tert-butyl alcohol), which reduces the nucleophilicity of the remaining hydride ...
... Alkanoyl chlorides are reduced to alcohols when sodium borohydride or lithium aluminum hydride are used directly. The reaction stops at the aldehyde if LiAlH4 is first reacted with three molecules of 2-methyl-2-propanol (tert-butyl alcohol), which reduces the nucleophilicity of the remaining hydride ...
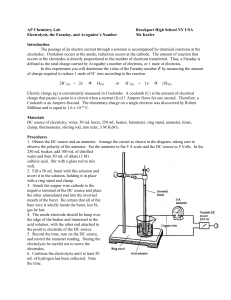
Electrolysis, the Faraday, and Avogadro`s Number
... 1. Determine the exact moles of H2 produced (PV = nRT) under your conditions. 2. Using the elapsed time, determine the amount of charge q in Coulombs that were transferred. 3. Determine the Faraday number F and calculate a percent error. 4. Determine a value for Avogadro’s number using your Faraday ...
... 1. Determine the exact moles of H2 produced (PV = nRT) under your conditions. 2. Using the elapsed time, determine the amount of charge q in Coulombs that were transferred. 3. Determine the Faraday number F and calculate a percent error. 4. Determine a value for Avogadro’s number using your Faraday ...
Mechanisms 3
... Free radical substitution reactions are quite random, generally any of the C-H bonds can become a C-Cl bond. Products containing more than one halogen atom can be formed by further substitution on molecules that already contain a halogen atom. ...
... Free radical substitution reactions are quite random, generally any of the C-H bonds can become a C-Cl bond. Products containing more than one halogen atom can be formed by further substitution on molecules that already contain a halogen atom. ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC) e-ISSN: 2278-5736.
... physical and chemical properties of transition metal complexes are greatly influenced by their structures and the coordination geometries by the ligand design. Transition metal complexes and Schiff bases derived from the reaction of aromatic aldehyde and aliphatic or aromatic amines represents an im ...
... physical and chemical properties of transition metal complexes are greatly influenced by their structures and the coordination geometries by the ligand design. Transition metal complexes and Schiff bases derived from the reaction of aromatic aldehyde and aliphatic or aromatic amines represents an im ...
File
... gaseous hydrogen bromide. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is 4 x 1018. 1. Calculate the free energy change at 200°C 2. Calculate the free energy change if the partial pressure of HBr is 1.50 atm and hydrogen is 0.500 atm at 298 K. The standard free energy change is 106.4 kJ/mol -2 x 105 J/ ...
... gaseous hydrogen bromide. The equilibrium constant for the reaction is 4 x 1018. 1. Calculate the free energy change at 200°C 2. Calculate the free energy change if the partial pressure of HBr is 1.50 atm and hydrogen is 0.500 atm at 298 K. The standard free energy change is 106.4 kJ/mol -2 x 105 J/ ...