System International Base Units
... Lewis dot structure for period 2 elements Notice dots equal their number of valence electrons and do not pair up until after all four quadrants have at least one dot ...
... Lewis dot structure for period 2 elements Notice dots equal their number of valence electrons and do not pair up until after all four quadrants have at least one dot ...
Presentation 3
... This is almost the case when either pH = 6.4 or pH = 10.3 because at either pH, {106.4 10-pH + 1 + 10-10.3 10pH} is only slightly greater than 2, e.g., ...
... This is almost the case when either pH = 6.4 or pH = 10.3 because at either pH, {106.4 10-pH + 1 + 10-10.3 10pH} is only slightly greater than 2, e.g., ...
3 -or - IONiC / VIPEr
... over a larger region of space) can be considered to have low electron densities. Do not confuse electron density with electronegativity or how electron-rich or poor an atom is classified. Electron-rich: Atoms that are willing to readily donate electrons or electron pairs to other atoms are considere ...
... over a larger region of space) can be considered to have low electron densities. Do not confuse electron density with electronegativity or how electron-rich or poor an atom is classified. Electron-rich: Atoms that are willing to readily donate electrons or electron pairs to other atoms are considere ...
ch 5 notes
... Section Focus Transparency What are the names of some useful ionic compounds? Binary Ionic Compounds Contain only two elements, but may contain more than one ion of each element! **Subscripts NaCl AlCl3 Naming: 1. Write the name of the + ion (usually a metal) 2. Write the name of the – ion (usually ...
... Section Focus Transparency What are the names of some useful ionic compounds? Binary Ionic Compounds Contain only two elements, but may contain more than one ion of each element! **Subscripts NaCl AlCl3 Naming: 1. Write the name of the + ion (usually a metal) 2. Write the name of the – ion (usually ...
Lecture 11 – Reaction Types and Mechanisms for Inorganic
... Each of these mechanisms involves a reaction to give a reactive intermediate with a different coordination number (5 or 7). When M = Co(III) (low-spin d6), considerable crystal field stabilization is lost because the CFSE is so much greater for octahedral coordination than the CFSE than any possible ...
... Each of these mechanisms involves a reaction to give a reactive intermediate with a different coordination number (5 or 7). When M = Co(III) (low-spin d6), considerable crystal field stabilization is lost because the CFSE is so much greater for octahedral coordination than the CFSE than any possible ...
Synthesis, spectroscopy, and electrochemistry of copper(II
... liquid–crystalline polymers [5], as catalytically active materials to develop surface-modified electrodes [6,7]. The Msalen type chelates have attracted considerable interest due to their ability to bind reversibly O2 and CO2 [1,3,8], and because of that they can be used as “metalloligands” ...
... liquid–crystalline polymers [5], as catalytically active materials to develop surface-modified electrodes [6,7]. The Msalen type chelates have attracted considerable interest due to their ability to bind reversibly O2 and CO2 [1,3,8], and because of that they can be used as “metalloligands” ...
111 Exam III OUTLINE TRO 1-3-11
... at 1000. °C, Kp is 0.403. If CO(g), at a pressure of 1.000 atm, and excess FeO(s) are placed in a container at 1000°C, what are the pressures of CO(g) and CO2(g) when equilibrium is attained? ...
... at 1000. °C, Kp is 0.403. If CO(g), at a pressure of 1.000 atm, and excess FeO(s) are placed in a container at 1000°C, what are the pressures of CO(g) and CO2(g) when equilibrium is attained? ...
AP Chemistry: Chapter 13 Gaseous Equilibrium Section 1: Multiple
... 2 H2S(g) 2 H2(g) + S2(g) When heated, hydrogen sulfide gas decomposes according to the equation above. A 3.40 g sample of H2S(g) is introduced into an evacuated rigid 1.25 L container. The sealed container is heated to 483 K, and 3.72×10–2 mol of S2(g) is present at equilibrium. (a) Write the expr ...
... 2 H2S(g) 2 H2(g) + S2(g) When heated, hydrogen sulfide gas decomposes according to the equation above. A 3.40 g sample of H2S(g) is introduced into an evacuated rigid 1.25 L container. The sealed container is heated to 483 K, and 3.72×10–2 mol of S2(g) is present at equilibrium. (a) Write the expr ...
Photochemistry of tetrasulfido complexes of molybdenum (VI
... states of the metal, the bonding in these complexes must have large covalent contributions. I t follows that some of the MO's are strongly delocalized between metal and ligands. L M C T transitions may then not be associated with the transfer of much charge from the ligand to the metal. The absorpti ...
... states of the metal, the bonding in these complexes must have large covalent contributions. I t follows that some of the MO's are strongly delocalized between metal and ligands. L M C T transitions may then not be associated with the transfer of much charge from the ligand to the metal. The absorpti ...
Matter - tompkinsmath
... The formula unit is Ca(NO3)2(s) Binary ionic compound → an ionic compound composed of two monatomic ions. Two kinds of ...
... The formula unit is Ca(NO3)2(s) Binary ionic compound → an ionic compound composed of two monatomic ions. Two kinds of ...
coordination chemistry
... (iii) Coordination number: The total number of ligands (either neutral molecules or negative ions) that get attached to the central metal atom in the coordination sphere is called the coordination number of the central metal atom. It is also referred to as its ligancy. For example: (a) In the comple ...
... (iii) Coordination number: The total number of ligands (either neutral molecules or negative ions) that get attached to the central metal atom in the coordination sphere is called the coordination number of the central metal atom. It is also referred to as its ligancy. For example: (a) In the comple ...
Appendix 1
... Note that we could have also arrived at this picture using LFT by considering how the ligand orbitals transform in C3v symmetry, then considering the symmetry allowed interactions (combinations) with the orbitals on Mo (s, p, and d). The orbital labels above are symmetry designations derived from LF ...
... Note that we could have also arrived at this picture using LFT by considering how the ligand orbitals transform in C3v symmetry, then considering the symmetry allowed interactions (combinations) with the orbitals on Mo (s, p, and d). The orbital labels above are symmetry designations derived from LF ...
CHEMISTRY 1000 - U of L Class Index
... In base, follow the above steps then add enough OH-(aq) to exactly cancel all H+(aq). By definition, a basic solution never has a significant concentration of H+(aq). In neutral conditions, H+(aq) is acceptable as a product; however, OH-(aq) should be added to neutralize any H+(aq) on the reactant s ...
... In base, follow the above steps then add enough OH-(aq) to exactly cancel all H+(aq). By definition, a basic solution never has a significant concentration of H+(aq). In neutral conditions, H+(aq) is acceptable as a product; however, OH-(aq) should be added to neutralize any H+(aq) on the reactant s ...
Chapter 8 and 9 homework
... 14. Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction. Aqueous iron(III) sulfate is added to aqueous sodium sulfide to produce solid iron(III) sulfide and aqueous sodium sulfate. 15. What mass of Li3PO4 is needed to prepare 500.0 mL of a solution having a lithium ion concentration of 0.175 M? ...
... 14. Write the net ionic equation for the following reaction. Aqueous iron(III) sulfate is added to aqueous sodium sulfide to produce solid iron(III) sulfide and aqueous sodium sulfate. 15. What mass of Li3PO4 is needed to prepare 500.0 mL of a solution having a lithium ion concentration of 0.175 M? ...
Solution
... Two moles of an element are added to a vessel of volume approximately 20 L containing oxygen gas at a pressure of 2 atm at 0°C. All of the element reacts, yielding 1 mole of an oxide and ½ atm of oxygen gas. Which of the following could be the oxide? A.) Na2O ...
... Two moles of an element are added to a vessel of volume approximately 20 L containing oxygen gas at a pressure of 2 atm at 0°C. All of the element reacts, yielding 1 mole of an oxide and ½ atm of oxygen gas. Which of the following could be the oxide? A.) Na2O ...
Examples of anions
... numbers. The coordination number is often twice the oxidation number of the metallic ion. Ligands are joined one at a time and have a formation constant for each reaction that joins a single ligand. This means that it would take six reactions to form Cr(H2O)63+, each successive reaction joining anot ...
... numbers. The coordination number is often twice the oxidation number of the metallic ion. Ligands are joined one at a time and have a formation constant for each reaction that joins a single ligand. This means that it would take six reactions to form Cr(H2O)63+, each successive reaction joining anot ...
Spectrophotometry Copper Sulfate
... Per the pre-lab readings we note that UV-VIS spectroscopy is an effective tool for solutions containing transition metal complexes, due to the color of the transition metal ion, in water. From where does this color originate? We know now, that most transition metal ions do not exist as monatomic ion ...
... Per the pre-lab readings we note that UV-VIS spectroscopy is an effective tool for solutions containing transition metal complexes, due to the color of the transition metal ion, in water. From where does this color originate? We know now, that most transition metal ions do not exist as monatomic ion ...
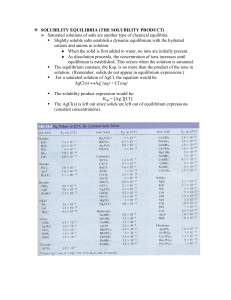
SOLUBILITY EQUILIBRIA
... Ksp AND THE REACTION QUOTIENT, Q With some knowledge of the reaction quotient, we can decide whether a ppt will form AND what concentrations of ions are required to begin the ppt. of an insoluble salt. 1. Q < Ksp, the system is not at equil. (unsaturated) 2. Q = Ksp, the system is at equil. ...
... Ksp AND THE REACTION QUOTIENT, Q With some knowledge of the reaction quotient, we can decide whether a ppt will form AND what concentrations of ions are required to begin the ppt. of an insoluble salt. 1. Q < Ksp, the system is not at equil. (unsaturated) 2. Q = Ksp, the system is at equil. ...
Intro to Titrimetry
... Precipitation Titration – forms insoluble salts which also serves as a monitor of reaction completion. Ex: Volhard Methods and Fajans Method RedOx Titrations – involves species which undergo redox reactions. The reaction is monitored by RedOx indicators or ...
... Precipitation Titration – forms insoluble salts which also serves as a monitor of reaction completion. Ex: Volhard Methods and Fajans Method RedOx Titrations – involves species which undergo redox reactions. The reaction is monitored by RedOx indicators or ...