L-12 Spontaneity of chemical reactions
... 12.7 Standard Gibbs Energy Change (Gº) and Equilibrium Constant (K) The standard Gibbs energy change is defined as the change in Gibbs energy for the process in which the reactants in their standard states are converted into the products in their standard states. It is denoted by the symbol rG°. T ...
... 12.7 Standard Gibbs Energy Change (Gº) and Equilibrium Constant (K) The standard Gibbs energy change is defined as the change in Gibbs energy for the process in which the reactants in their standard states are converted into the products in their standard states. It is denoted by the symbol rG°. T ...
Slide 1
... •The benzene ring is not neutral. Rather, it carries a charge close to -2, as there is transfer of uranium 5f electron density into the benzene e2u C-C π* molecular orbitals. The benzene ring is thus no longer Hückel aromatic, and is significantly non-planar as a result. W.J. Evans, S.A. Kozimor, J. ...
... •The benzene ring is not neutral. Rather, it carries a charge close to -2, as there is transfer of uranium 5f electron density into the benzene e2u C-C π* molecular orbitals. The benzene ring is thus no longer Hückel aromatic, and is significantly non-planar as a result. W.J. Evans, S.A. Kozimor, J. ...
Document
... What we see is coupling of the unpaired electron to the copper nucleus (I = 3/2) to give a four line pattern with a large hyperfine coupling constant (A Cu on coupling tree on the diagram above). Each line is then further split into a quintet by interaction with the two nitrogen nuclei (14N: I = 1, ...
... What we see is coupling of the unpaired electron to the copper nucleus (I = 3/2) to give a four line pattern with a large hyperfine coupling constant (A Cu on coupling tree on the diagram above). Each line is then further split into a quintet by interaction with the two nitrogen nuclei (14N: I = 1, ...
Metal Ions in Biological Systems
... 2. The kinetic problem Oxygen has two unpaired electrons in its ground state and forms therefore a triplet state. The overwhelming majority of organic molecules (such as glucose or n-hexane) have all electrons paired and occur therefore in the singlet state. The products of oxidation of organic mole ...
... 2. The kinetic problem Oxygen has two unpaired electrons in its ground state and forms therefore a triplet state. The overwhelming majority of organic molecules (such as glucose or n-hexane) have all electrons paired and occur therefore in the singlet state. The products of oxidation of organic mole ...
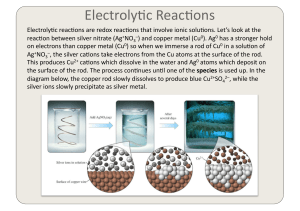
Electrochemistry 2
... Note the func)on of the salt bridge. If we have no salt bridge, the Cu half cell anode will start to lose electrons and generate Cu2+ ca)ons but it will not have enough nega)ve counter ions. ...
... Note the func)on of the salt bridge. If we have no salt bridge, the Cu half cell anode will start to lose electrons and generate Cu2+ ca)ons but it will not have enough nega)ve counter ions. ...
Chapter 17 lecture notes on Chemical Equilibria
... energy of the system, ∆Go, under standard conditions. ∆Go describes the free energy change in the system that accompanies the conversion of all reactants in their standard states (1M, 1 atm) to products in their standard states (1M, 1 atm). We now define the free energy, ∆G, which is the free energy ...
... energy of the system, ∆Go, under standard conditions. ∆Go describes the free energy change in the system that accompanies the conversion of all reactants in their standard states (1M, 1 atm) to products in their standard states (1M, 1 atm). We now define the free energy, ∆G, which is the free energy ...
Chemistry Lab 2010
... • Second order = concentration doubles, rate quadruples Remember that rate is change in concentration divided by time. Just looking at time changes can lead to wrong answer! When two experiments are being compared, remember to make sure only one reactant has a change of initial concentration ...
... • Second order = concentration doubles, rate quadruples Remember that rate is change in concentration divided by time. Just looking at time changes can lead to wrong answer! When two experiments are being compared, remember to make sure only one reactant has a change of initial concentration ...
Exam 3, Fall 2013 - Mattson Creighton
... [Co(NH3)5X]2+ à [Co(NH3)5]3+ + X- slow [Co(NH3)5]3+ + H2O à [Co(NH3)5H2O]3+ 10B. rate = k1[[Co(NH3)5X]2+]1 10C. k should: stay the same; K should: increase 11. The first one is faster because the first step (dissociation) has a larger entropy factor. 12. (4 pts) Square planar complexes often under ...
... [Co(NH3)5X]2+ à [Co(NH3)5]3+ + X- slow [Co(NH3)5]3+ + H2O à [Co(NH3)5H2O]3+ 10B. rate = k1[[Co(NH3)5X]2+]1 10C. k should: stay the same; K should: increase 11. The first one is faster because the first step (dissociation) has a larger entropy factor. 12. (4 pts) Square planar complexes often under ...
Solubility and Complex-ion Equilibria
... determine whether precipitation will occur. • One form of kidney stones is calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2, which has a Ksp of 1.0 × 10−26. A sample of urine contains 1.0 × 10−3 M Ca2+ and 1.0 × 10−8 M PO43− ion. • Calculate Qc and predict whether Ca3(PO4)2 will precipitate. ...
... determine whether precipitation will occur. • One form of kidney stones is calcium phosphate, Ca3(PO4)2, which has a Ksp of 1.0 × 10−26. A sample of urine contains 1.0 × 10−3 M Ca2+ and 1.0 × 10−8 M PO43− ion. • Calculate Qc and predict whether Ca3(PO4)2 will precipitate. ...
Chapter 8. Chiral Catalysts
... multiple. If the metal is not in zero oxidation state, it will require the presence of an anion that would act as a ligand in the case of coordinating anions (chloride for example) or not in the case of non-coordinating anions (perchlorate for example). If chiral ligand and substrate are not able to ...
... multiple. If the metal is not in zero oxidation state, it will require the presence of an anion that would act as a ligand in the case of coordinating anions (chloride for example) or not in the case of non-coordinating anions (perchlorate for example). If chiral ligand and substrate are not able to ...
Fractional Composition
... and B, instead of HA and A• Equation 3 gives the fraction in the form BH+ • Equation 4 gives the fraction in the form B • Ka is then the acid dissociation constant for BH+ (which is Kw/Kb) ...
... and B, instead of HA and A• Equation 3 gives the fraction in the form BH+ • Equation 4 gives the fraction in the form B • Ka is then the acid dissociation constant for BH+ (which is Kw/Kb) ...
APEF – Equilibrium and Reaction Rate Multiple Choice Answers
... 33. Analysis of a sample of HCl gas showed that when equilibrium was reached at a certain temperature, one half of the HCl molecules had dissociated into H2 and Cl2 molecules: 2HCl(g) ' H2(g) + Cl2(g) What is numerical value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature? A. 0.25 B. 0.50 C. 1.0 D. ...
... 33. Analysis of a sample of HCl gas showed that when equilibrium was reached at a certain temperature, one half of the HCl molecules had dissociated into H2 and Cl2 molecules: 2HCl(g) ' H2(g) + Cl2(g) What is numerical value of the equilibrium constant at this temperature? A. 0.25 B. 0.50 C. 1.0 D. ...
Enantioselective Homogeneous Hydrogenation of Monosubstituted
... homogeneous Rh complexes of ferrocenyl diphosphine ligands, whereas the corresponding methyl ester only gave 4% ee. All other efforts to hydrogenate aromatic rings enantioselectively have resulted in ees below 6% [7±9]. A few cases of a diastereoselective hydrogenation of aromatic rings with chiral ...
... homogeneous Rh complexes of ferrocenyl diphosphine ligands, whereas the corresponding methyl ester only gave 4% ee. All other efforts to hydrogenate aromatic rings enantioselectively have resulted in ees below 6% [7±9]. A few cases of a diastereoselective hydrogenation of aromatic rings with chiral ...
Ligand to Ligand Charge Transfer in
... electronegativities, has been developed,1 but the most common descriptions are based on HOMO-LUMO separations calculated by molecular orbital theory. An uncommon type of charge-transfer transition is ligand to ligand (LLCT) or interligand charge transfer. In comparison to the vast literature on MLCT ...
... electronegativities, has been developed,1 but the most common descriptions are based on HOMO-LUMO separations calculated by molecular orbital theory. An uncommon type of charge-transfer transition is ligand to ligand (LLCT) or interligand charge transfer. In comparison to the vast literature on MLCT ...
Chapter 13 Notes Types of Solutions Saturated Solution: contains
... Saturated Solution: contains the maximum amount of a solute that will dissolve in a given solvent at a specific temperature. Unsaturated Solution: contains less solute than it has the capacity to dissolve. Supersaturated Solution: contains more solute than is present in a saturated solution (very un ...
... Saturated Solution: contains the maximum amount of a solute that will dissolve in a given solvent at a specific temperature. Unsaturated Solution: contains less solute than it has the capacity to dissolve. Supersaturated Solution: contains more solute than is present in a saturated solution (very un ...
Section 4.8: Acid-Base Reactions
... react with an accurately and precisely weighed sample of primary standard. Primary standards are ultra-pure solid compounds with high molecular weights and reliable stability. Once a solution is standardized, it may be used as a secondary standard for determining the concentration of other solutions ...
... react with an accurately and precisely weighed sample of primary standard. Primary standards are ultra-pure solid compounds with high molecular weights and reliable stability. Once a solution is standardized, it may be used as a secondary standard for determining the concentration of other solutions ...
acids, bases and solution equilibria
... For Mg2+ in water the order of stability of MXn is: F > Cl > Br > IThis behaviour is referred to as 'Class A'. However, for Hg2+ in water the order of stability of MXn is: I > Br > Cl > F. This behaviour is referred to as 'Class B'. More generally, we use the terms ‘Hard’ and ‘Soft’ acids ...
... For Mg2+ in water the order of stability of MXn is: F > Cl > Br > IThis behaviour is referred to as 'Class A'. However, for Hg2+ in water the order of stability of MXn is: I > Br > Cl > F. This behaviour is referred to as 'Class B'. More generally, we use the terms ‘Hard’ and ‘Soft’ acids ...
General Chemistry I
... • Air is a solution which is a mixture of various gases. • Carbonated water (soda) is a mixture of a gas (CO2) dissolved in a liquid (H2O). • Even alloys such as gold-silver alloys are solutions containing two solids. A true solution is a solution which has only one solvent with one or more solutes. ...
... • Air is a solution which is a mixture of various gases. • Carbonated water (soda) is a mixture of a gas (CO2) dissolved in a liquid (H2O). • Even alloys such as gold-silver alloys are solutions containing two solids. A true solution is a solution which has only one solvent with one or more solutes. ...