Objectives - Dixie State University
... 8. Explain the difference between an exothermic and an endothermic reaction, including how their energy diagrams differ, whether their enthalpy is positive or negative, and what causes a reaction to be endothermic or exothermic. 9. Explain the relationship between G, H, and S. II. Kinetics of Reacti ...
... 8. Explain the difference between an exothermic and an endothermic reaction, including how their energy diagrams differ, whether their enthalpy is positive or negative, and what causes a reaction to be endothermic or exothermic. 9. Explain the relationship between G, H, and S. II. Kinetics of Reacti ...
〈541〉 TITRIMETRY
... back titration, due allowance being made for the respective normality or molarity factors of the two solutions, and the equivalence factor for the substance given in the individual monograph. Complexometric Titrations—Successful complexometric titrations depend on several factors. The equilibrium co ...
... back titration, due allowance being made for the respective normality or molarity factors of the two solutions, and the equivalence factor for the substance given in the individual monograph. Complexometric Titrations—Successful complexometric titrations depend on several factors. The equilibrium co ...
Review Session Handout from 10/6
... 36. (from last spring’s exam) Margarine can be made from natural oils such as coconut oil by hydrogenation: C57H104O6 (l) + 3 H2 (g) → C57H110O6 (s) If an industrial hydrogenator with a volume of 2.50 x 102 L is filled with 12.0 kg of oil (C57H104O6) and 7.00 atm of H2 at 473 K, how many kilograms o ...
... 36. (from last spring’s exam) Margarine can be made from natural oils such as coconut oil by hydrogenation: C57H104O6 (l) + 3 H2 (g) → C57H110O6 (s) If an industrial hydrogenator with a volume of 2.50 x 102 L is filled with 12.0 kg of oil (C57H104O6) and 7.00 atm of H2 at 473 K, how many kilograms o ...
Equilibrium a.k.a. The Up Hill Climb
... C. Set up RICE diagram. R = write a balanced reaction for the predominant reacting species I = fill in the initial concentrations C = what change is taking in place E = equilibrium concentrations D. Fill in initial concentrations. E. Calculate change in concentration using coefficients or informatio ...
... C. Set up RICE diagram. R = write a balanced reaction for the predominant reacting species I = fill in the initial concentrations C = what change is taking in place E = equilibrium concentrations D. Fill in initial concentrations. E. Calculate change in concentration using coefficients or informatio ...
Slide 1
... In other words, Surrounding can be defined as a large constant-temperature heat source that can supply heat to system (or heat sink if the heat flows from the system to the surroundings). Thus, the change in entropy of the surroundings depends on how much heat is absorbed or given off by the system. ...
... In other words, Surrounding can be defined as a large constant-temperature heat source that can supply heat to system (or heat sink if the heat flows from the system to the surroundings). Thus, the change in entropy of the surroundings depends on how much heat is absorbed or given off by the system. ...
Principles of Reactivity: Chemical Equilibria
... products are omitted from the equilibrium constant expression. The molar concentration of water (or of any liquid reactant or product) is omitted from the equilibrium constant expression. ...
... products are omitted from the equilibrium constant expression. The molar concentration of water (or of any liquid reactant or product) is omitted from the equilibrium constant expression. ...
Equilibrium 5
... 5. At a certain temperature, a 1.00-L flask initially contained 0.298 moles of PCl3 (g) and 8.7 x 10-3 moles of PCl5 (g). After the system had reached equilibrium, 2.00 x 10-3 moles of Cl2 (g) was found in the flask. Gaseous PCl5 decomposes according to the reaction: PCl5 (g) ...
... 5. At a certain temperature, a 1.00-L flask initially contained 0.298 moles of PCl3 (g) and 8.7 x 10-3 moles of PCl5 (g). After the system had reached equilibrium, 2.00 x 10-3 moles of Cl2 (g) was found in the flask. Gaseous PCl5 decomposes according to the reaction: PCl5 (g) ...
Synthesis, Characterization, and Luminescent Properties of
... addition of about half of the CS2, the solution becomes light yellow. After the addition of more than 0.65 mL of CS2, the clear yellow solution turns cloudy. The cloudy yellow solution is then left to stir for 1 h, after which a yellow precipitate starts to form. After stirring of the mixture for an ...
... addition of about half of the CS2, the solution becomes light yellow. After the addition of more than 0.65 mL of CS2, the clear yellow solution turns cloudy. The cloudy yellow solution is then left to stir for 1 h, after which a yellow precipitate starts to form. After stirring of the mixture for an ...
Ksp Problem Sets 1 and 2
... 4. The solubility product constant for lead (II) chloride is 1.7 x 10 . How many moles of lead nitrate can dissolve in 1.00 L of a 0.1 M solution of sodium chloride? (Hint: One of the ions found in PbCl2, the chloride ion, is already present in the solution. That can be taken to be its equilibrium ...
... 4. The solubility product constant for lead (II) chloride is 1.7 x 10 . How many moles of lead nitrate can dissolve in 1.00 L of a 0.1 M solution of sodium chloride? (Hint: One of the ions found in PbCl2, the chloride ion, is already present in the solution. That can be taken to be its equilibrium ...
Solution of the 1st Major Exam, Term 061, Version 000, all correct
... of lithium sulfide and copper (II) nitrate are mixed. A) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) B) 2Li+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → CuSO4(s) + 2Li+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) C) Li+ (aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq) D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq ...
... of lithium sulfide and copper (II) nitrate are mixed. A) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + 2 Li+(aq) + 2 NO3-(aq) B) 2Li+(aq) + SO42-(aq) + Cu2+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) → CuSO4(s) + 2Li+(aq) + 2NO3-(aq) C) Li+ (aq) + S-(aq) + Cu+(aq) + NO3-(aq) → CuS(s) + LiNO3(aq) D) 2 Li+(aq) + S2-(aq ...
$doc.title
... species and subsequent quenching with the alkylating agent, three products were afforded i.e. the orange monocarbene complex 22, the purple biscarbene complex 23 as well as the pink orange decomposition product, complex 24. Three analogous compounds were yielded upon reaction with tungsten hexacarb ...
... species and subsequent quenching with the alkylating agent, three products were afforded i.e. the orange monocarbene complex 22, the purple biscarbene complex 23 as well as the pink orange decomposition product, complex 24. Three analogous compounds were yielded upon reaction with tungsten hexacarb ...
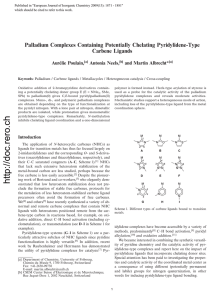
Imidazole-Based [2 + 1] Re(I)/99mTc(I
... yield at 40 °C (Scheme 1). The retention time of the product matched that of the Re complex 5a, which was prepared according to a literature method in 72% yield.41 It was also possible to prepare the complex at room temperature using a reaction time of just 5 min. Building on the success using N-met ...
... yield at 40 °C (Scheme 1). The retention time of the product matched that of the Re complex 5a, which was prepared according to a literature method in 72% yield.41 It was also possible to prepare the complex at room temperature using a reaction time of just 5 min. Building on the success using N-met ...
5.04 Principles of Inorganic Chemistry II
... on the σ-axis, hence ¼ eσ. The δ component of the transformation comes from the 2z2–(x2+y2) orbital functional form. Thus if L2 has an orbital of δ symmetry, then it will have an energy of ¾ eδ. The transformation properties of the other d-orbitals, as they pertain to L2 orbital overlap, may be asce ...
... on the σ-axis, hence ¼ eσ. The δ component of the transformation comes from the 2z2–(x2+y2) orbital functional form. Thus if L2 has an orbital of δ symmetry, then it will have an energy of ¾ eδ. The transformation properties of the other d-orbitals, as they pertain to L2 orbital overlap, may be asce ...
chemistry 2.1
... © ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd – ISBN 978-0-908340-10-1 – Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is limited to 3% under the NZ Copyright Act. ...
... © ESA Publications (NZ) Ltd – ISBN 978-0-908340-10-1 – Copying or scanning from ESA workbooks is limited to 3% under the NZ Copyright Act. ...
Open Access
... of selectivity and reactivity by ligand design. Manipulating the steric and electronic properties of the ligands on the metal cluster makes it possible to achieve size selectivity, e.g. branched or linear products and the selective preparation of one enantiomer, the latter being called asymmetric sy ...
... of selectivity and reactivity by ligand design. Manipulating the steric and electronic properties of the ligands on the metal cluster makes it possible to achieve size selectivity, e.g. branched or linear products and the selective preparation of one enantiomer, the latter being called asymmetric sy ...
An assessment of excess carbon dioxide partial pressures in natural
... chemical activity-concentration difference using the Davies equation within the calculations and the methodology is presented in Appendix B. 2.6. Comparisons between direct measurements and case 1 to case 5 methodologies In order to provide a validation of the theoretical methods developed in this p ...
... chemical activity-concentration difference using the Davies equation within the calculations and the methodology is presented in Appendix B. 2.6. Comparisons between direct measurements and case 1 to case 5 methodologies In order to provide a validation of the theoretical methods developed in this p ...
Notes - Text
... • If Q = K, then the system is at equilibrium. • If Q < K, then the forward reaction must occur to reach equilibrium. • If Q > K, then the reverse reaction must occur to reach equilibrium. • Products are consumed and reactants are formed. • Q decreases until it equals K. ...
... • If Q = K, then the system is at equilibrium. • If Q < K, then the forward reaction must occur to reach equilibrium. • If Q > K, then the reverse reaction must occur to reach equilibrium. • Products are consumed and reactants are formed. • Q decreases until it equals K. ...
Chapter 19 - public.asu.edu
... Second Law of Thermodynamics 2nd Law: In any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases. ∆Suniv = ∆Ssys + ∆Ssurr: the change in entropy of the universe is the sum of the change in entropy of the system and the change in entropy of the surroundings. Entropy is not conserved: ∆Suniv is ...
... Second Law of Thermodynamics 2nd Law: In any spontaneous process, the entropy of the universe increases. ∆Suniv = ∆Ssys + ∆Ssurr: the change in entropy of the universe is the sum of the change in entropy of the system and the change in entropy of the surroundings. Entropy is not conserved: ∆Suniv is ...
Ch 17 Equilibrium
... considered as a reactant. • For an exothermic reaction, H < 0 and heat can be considered as a product. • Adding heat (i.e. heating the vessel) favors away from the increase: – if H > 0, adding heat favors the forward reaction, – if H < 0, adding heat favors the reverse reaction. ...
... considered as a reactant. • For an exothermic reaction, H < 0 and heat can be considered as a product. • Adding heat (i.e. heating the vessel) favors away from the increase: – if H > 0, adding heat favors the forward reaction, – if H < 0, adding heat favors the reverse reaction. ...
as a PDF
... yields higher than 100% (based on Pd) were obtained and precipitation of metallic palladium occurred under these conditions. The best solvents for carrying out the oxidation of terminal olefins by PPT were anhydrous chlorinated solvents (e.g., methylene chloride, 1,2-dichloroethane, chlorobenzene), ...
... yields higher than 100% (based on Pd) were obtained and precipitation of metallic palladium occurred under these conditions. The best solvents for carrying out the oxidation of terminal olefins by PPT were anhydrous chlorinated solvents (e.g., methylene chloride, 1,2-dichloroethane, chlorobenzene), ...












![Imidazole-Based [2 + 1] Re(I)/99mTc(I](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016453198_1-7284afe0756f420c3d5e168652a9a305-300x300.png)