nuclear chemistry - La Salle High School
... state; the excited state is unstable and goes to a lower-energy state by releasing energ y in the form of gamma rays. ...
... state; the excited state is unstable and goes to a lower-energy state by releasing energ y in the form of gamma rays. ...
NUCLEAR CHEMISTRY
... Spend a decade or more in tank Limited time for plant operation due to contamination ...
... Spend a decade or more in tank Limited time for plant operation due to contamination ...
Radioactivity - Miami Beach Senior High School
... • The nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei, which are radioactive. • More neutrons are released. • The additional neutrons released may also hit other uranium nuclei and cause them to split. Even more neutrons are then released, which in turn can split more uranium nuclei. This is called a chain r ...
... • The nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei, which are radioactive. • More neutrons are released. • The additional neutrons released may also hit other uranium nuclei and cause them to split. Even more neutrons are then released, which in turn can split more uranium nuclei. This is called a chain r ...
Life of a star
... volume. Compression continues until the electrons are able to assume energetic configurations that distinguish them. When all possible combinations have run out, according to Pauli's exclusion principle no other electrons can enter that given volume; thus a barrier is formed which prevents matter fr ...
... volume. Compression continues until the electrons are able to assume energetic configurations that distinguish them. When all possible combinations have run out, according to Pauli's exclusion principle no other electrons can enter that given volume; thus a barrier is formed which prevents matter fr ...
nuclear chemistry notes 1
... same number of protons and neutrons. This is when they are the most stable. Large atoms with around 83 protons or more are so large that they too are unstable. If atoms are too unstable, they will decompose, or radioactively decay, releasing different types of particles in order to become more stabl ...
... same number of protons and neutrons. This is when they are the most stable. Large atoms with around 83 protons or more are so large that they too are unstable. If atoms are too unstable, they will decompose, or radioactively decay, releasing different types of particles in order to become more stabl ...
Test 4
... 1. Suppose you have 1.00L of an aqueous buffer containing 55.0 mmol of acetic acid (pKa=4.67) and 45 mmol acetate Calculate the pH of this buffer. ...
... 1. Suppose you have 1.00L of an aqueous buffer containing 55.0 mmol of acetic acid (pKa=4.67) and 45 mmol acetate Calculate the pH of this buffer. ...
FUSION AND FISSION
... • The fusion of two nuclei lighter than iron or nickel generally releases energy. • The fusion of nuclei heavier than them absorbs energy. Result: gain or loss of energy ...
... • The fusion of two nuclei lighter than iron or nickel generally releases energy. • The fusion of nuclei heavier than them absorbs energy. Result: gain or loss of energy ...
Workshop module 4 - Physics 114, Spring 2003
... from the battery. The separation between the plates is then doubled. How does the electric field change? The potential difference? The total energy? Explain your reasoning. 2) The source of a star’s energy is thermonuclear fusion taking place in the core of the star. Estimate the temperature at the ...
... from the battery. The separation between the plates is then doubled. How does the electric field change? The potential difference? The total energy? Explain your reasoning. 2) The source of a star’s energy is thermonuclear fusion taking place in the core of the star. Estimate the temperature at the ...
Masses in Atomic Units - proton 1.007 u 938.28 MeV
... in a process called fusion - large nuclei can lower their energy by breaking up into smaller nuclei in a process called fission - the most stable nucleus is an isotope of iron (Fe) - the binding energy of nucleons is extremely large compared to other atomic energy scales ...
... in a process called fusion - large nuclei can lower their energy by breaking up into smaller nuclei in a process called fission - the most stable nucleus is an isotope of iron (Fe) - the binding energy of nucleons is extremely large compared to other atomic energy scales ...
Nuclear Fission sim
... • Some fissionable materials have the property that, while they require one neutron to fission, they produce more than one neutron. This means that, if you have enough atoms (a CRITICAL MASS), the one neutron you started with quickly produces more neutrons which cause more and more atoms to fission, ...
... • Some fissionable materials have the property that, while they require one neutron to fission, they produce more than one neutron. This means that, if you have enough atoms (a CRITICAL MASS), the one neutron you started with quickly produces more neutrons which cause more and more atoms to fission, ...
PHY 491: Atomic, Molecular, and Condensed Matter Physics
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T , t ...
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T , t ...
File
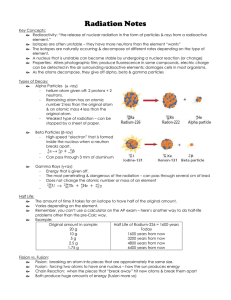
... Radioactivity: “the release of nuclear radiation in the form of particles & rays from a radioactive element.” Isotopes are often unstable – they have more neutrons than the element “wants” The isotopes are naturally occurring & decompose at different rates depending on the type of element. A ...
... Radioactivity: “the release of nuclear radiation in the form of particles & rays from a radioactive element.” Isotopes are often unstable – they have more neutrons than the element “wants” The isotopes are naturally occurring & decompose at different rates depending on the type of element. A ...
PHY801: Survey of Atomic and Condensed Matter Physics
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of the Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T ...
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of the Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T ...
Radioactivity - Williamstown Independent Schools
... materials that can be safely placed in the body to track movement of materials. • Radiation can also be used to kill cancerous ...
... materials that can be safely placed in the body to track movement of materials. • Radiation can also be used to kill cancerous ...
Adobe Acrobat file ()
... An iron nucleus (in hemoglobin) has a few more neutrons than protons, but in a typical water molecule there are eight neutrons and ten protons. So protons and neutrons are nearly equally numerous in your body, each contributing 35 kg out of a total body mass of 70 kg. ...
... An iron nucleus (in hemoglobin) has a few more neutrons than protons, but in a typical water molecule there are eight neutrons and ten protons. So protons and neutrons are nearly equally numerous in your body, each contributing 35 kg out of a total body mass of 70 kg. ...
Nuclear Decay
... Fusion is a process where nuclei collide and join together to form a heavier atom, usually deuterium and tritium. When this happens a considerable amount of energy gets released at extremely high temperatures: nearly 150 million degrees Celsius. At extreme temperatures, electrons are separated from ...
... Fusion is a process where nuclei collide and join together to form a heavier atom, usually deuterium and tritium. When this happens a considerable amount of energy gets released at extremely high temperatures: nearly 150 million degrees Celsius. At extreme temperatures, electrons are separated from ...
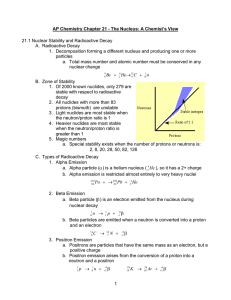
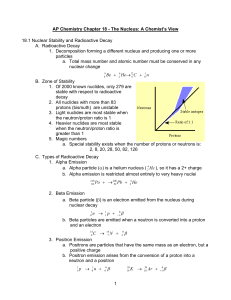
1 AP Chemistry Chapter 21 - The Nucleus: A Chemist`s View 21.1
... b. Carbon-14 decays, with a half-life of 5730 years C → 147 N + −10 β (1) Living things take in carbon-12 and carbon-14, in a fixed ratio (2) When a living thing dies, the amount of carbon-12 does not change, but carbon-14 begins to decrease through decay ...
... b. Carbon-14 decays, with a half-life of 5730 years C → 147 N + −10 β (1) Living things take in carbon-12 and carbon-14, in a fixed ratio (2) When a living thing dies, the amount of carbon-12 does not change, but carbon-14 begins to decrease through decay ...
Chapter 18 Notes
... b. Carbon-14 decays, with a half-life of 5730 years C → 147 N + −10 β (1) Living things take in carbon-12 and carbon-14, in a fixed ratio (2) When a living thing dies, the amount of carbon-12 does not change, but carbon-14 begins to decrease through decay ...
... b. Carbon-14 decays, with a half-life of 5730 years C → 147 N + −10 β (1) Living things take in carbon-12 and carbon-14, in a fixed ratio (2) When a living thing dies, the amount of carbon-12 does not change, but carbon-14 begins to decrease through decay ...
Review & Closure - Little Shop of Physics
... assumption), how many fusion reactions are requir get the ship up to speed? c. How many kilograms of 21H and of 32He are required to duce the required number of reactions? A muon is a lepton that is a higher-mass (rest 105 MeV/c 2) sibling to the electron. Muons are produc the upper atmosphere when ...
... assumption), how many fusion reactions are requir get the ship up to speed? c. How many kilograms of 21H and of 32He are required to duce the required number of reactions? A muon is a lepton that is a higher-mass (rest 105 MeV/c 2) sibling to the electron. Muons are produc the upper atmosphere when ...
Atomic/Nuclear
... The binding energy per nucleon versus atomic number graph peaks at iron. Smaller and larger nuclei have less binding energy per nucleon than iron. If a nucleus with an even atomic number 92 or greater and an odd mass number absorbs a neutron, it can be split into two smaller nuclei with about 3 neut ...
... The binding energy per nucleon versus atomic number graph peaks at iron. Smaller and larger nuclei have less binding energy per nucleon than iron. If a nucleus with an even atomic number 92 or greater and an odd mass number absorbs a neutron, it can be split into two smaller nuclei with about 3 neut ...
Unit 14 Notes - shscience.net
... U-235 and Po-239 are the only fissionable isotopes chain reaction Can release enormous amounts of energy: 1 kg U-235 --> explosion of 20,000 tons of dynamite ...
... U-235 and Po-239 are the only fissionable isotopes chain reaction Can release enormous amounts of energy: 1 kg U-235 --> explosion of 20,000 tons of dynamite ...
Nuclear Fission and Fusion
... Nuclear Fission and Energy: The splitting of atoms produces a large amount of energy. This energy is produced in nuclear power plants Problems with nuclear power: The waste produced has to be safely stored for thousands of years. ...
... Nuclear Fission and Energy: The splitting of atoms produces a large amount of energy. This energy is produced in nuclear power plants Problems with nuclear power: The waste produced has to be safely stored for thousands of years. ...
first lecture - الدكتورة / زينب بنت زكي الفل
... system and hence can exist in different quantum states characterized by their energies ,angular momenta etc. the lowest energy state is known as as the ground state and the nuclei normally exist in this state , the properties of the nuclei which will be discussed in this chapter correspond to their ...
... system and hence can exist in different quantum states characterized by their energies ,angular momenta etc. the lowest energy state is known as as the ground state and the nuclei normally exist in this state , the properties of the nuclei which will be discussed in this chapter correspond to their ...
Nuclear Chemistry Test Topics
... broken nucleus bombard other unstable nuclei in the sample of material causing them to break apart. This chain of one nucleus splitting and causing others to split is called a chain reaction. At the end of fission stable nuclei will result and the energy released will be great! Uranium235 is commonl ...
... broken nucleus bombard other unstable nuclei in the sample of material causing them to break apart. This chain of one nucleus splitting and causing others to split is called a chain reaction. At the end of fission stable nuclei will result and the energy released will be great! Uranium235 is commonl ...
Nuclear fusion

In nuclear physics, nuclear fusion is a nuclear reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei come very close and then collide at a very high speed and join to form a new nucleus. During this process, matter is not conserved because some of the matter of the fusing nuclei is converted to photons (energy). Fusion is the process that powers active or ""main sequence"" stars.The fusion of two nuclei with lower masses than Iron-56 (which, along with Nickel-62, has the largest binding energy per nucleon) generally releases energy, while the fusion of nuclei heavier than iron absorbs energy. The opposite is true for the reverse process, nuclear fission. This means that fusion generally occurs for lighter elements only, and likewise, that fission normally occurs only for heavier elements. There are extreme astrophysical events that can lead to short periods of fusion with heavier nuclei. This is the process that gives rise to nucleosynthesis, the creation of the heavy elements during events such as supernova.Following the discovery of quantum tunneling by Friedrich Hund, in 1929 Robert Atkinson and Fritz Houtermans used the measured masses of light elements to predict that large amounts of energy could be released by fusing small nuclei. Building upon the nuclear transmutation experiments by Ernest Rutherford, carried out several years earlier, the laboratory fusion of hydrogen isotopes was first accomplished by Mark Oliphant in 1932. During the remainder of that decade the steps of the main cycle of nuclear fusion in stars were worked out by Hans Bethe. Research into fusion for military purposes began in the early 1940s as part of the Manhattan Project. Fusion was accomplished in 1951 with the Greenhouse Item nuclear test. Nuclear fusion on a large scale in an explosion was first carried out on November 1, 1952, in the Ivy Mike hydrogen bomb test.Research into developing controlled thermonuclear fusion for civil purposes also began in earnest in the 1950s, and it continues to this day. The present article is about the theory of fusion. For details of the quest for controlled fusion and its history, see the article Fusion power.