The Brain, Biology, and Behavior Neuron
... production. If damaged, person knows what s/he wants to say but can’t say the words Wernicke’s Area: Related to language comprehension. If damaged, person has problems with meanings of words, NOT pronunciation Agnosia: Inability to identify seen objects Facial agnosia: Inability to perceive fami ...
... production. If damaged, person knows what s/he wants to say but can’t say the words Wernicke’s Area: Related to language comprehension. If damaged, person has problems with meanings of words, NOT pronunciation Agnosia: Inability to identify seen objects Facial agnosia: Inability to perceive fami ...
Text S1.
... weights is used, In the conventional mean field approach, a set of fixed synaptic which establish the strength of the different connections between all the subpopulations. These weights are normally obtained in accordance with the hypothesis of Hebbian associative plasticity, i.e. synaptic effica ...
... weights is used, In the conventional mean field approach, a set of fixed synaptic which establish the strength of the different connections between all the subpopulations. These weights are normally obtained in accordance with the hypothesis of Hebbian associative plasticity, i.e. synaptic effica ...
Biol 155 Human Physiology - University of British Columbia
... These channels have two voltage sensitive gates. At resting Em, one gate is closed and the other is open. When the membrane becomes depolarized enough, the second gate will open. After a short time, the second gate will then shut. ...
... These channels have two voltage sensitive gates. At resting Em, one gate is closed and the other is open. When the membrane becomes depolarized enough, the second gate will open. After a short time, the second gate will then shut. ...
The human brain
... The secret of the brain lies in the vast number of neurons (tens of billions) and the complicated way they are connected. ...
... The secret of the brain lies in the vast number of neurons (tens of billions) and the complicated way they are connected. ...
Neuroscience 14c – The Limbic System and Drugs of Abuse
... of anger and aggression. Defects can result in “sham rage” – easy aggregation by provocation. 5-HT (serotonin) in raphe nuclei are also associated with anger. ...
... of anger and aggression. Defects can result in “sham rage” – easy aggregation by provocation. 5-HT (serotonin) in raphe nuclei are also associated with anger. ...
AP Psychology Test Review
... A four year old boy was involved in a terrible accident that damaged his brain. Though most of his left hemisphere was removed, three years later he was nearly normal. What term best explains the ability of the brain to recover from injury by rewiring itself? ...
... A four year old boy was involved in a terrible accident that damaged his brain. Though most of his left hemisphere was removed, three years later he was nearly normal. What term best explains the ability of the brain to recover from injury by rewiring itself? ...
BIOLOGY AND BEHAVIOR
... Deteriorates with Alzheimers. • Dopamine – bodily movements – lack of causes Parkinson’s disease. Too much may cause schizophrenic episodes. • Endorphins: relieve pain and increase our sense of well-being. • Serotonin: our feel good NT ...
... Deteriorates with Alzheimers. • Dopamine – bodily movements – lack of causes Parkinson’s disease. Too much may cause schizophrenic episodes. • Endorphins: relieve pain and increase our sense of well-being. • Serotonin: our feel good NT ...
29 - IWS2.collin.edu
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural transmission ...
... Neurotransmitter must be released, diffuse across the synapse, and bind to receptors Synaptic delay – time needed to do this Synaptic delay is the rate-limiting step of neural transmission ...
THE VISUAL SYSTEM: EYE TO CORTEX Outline
... like simple cells in that they respond best to straight-line stimuli in a particular orientation unlike simple cells in that the position of the stimulus within the receptive field does not matter ...
... like simple cells in that they respond best to straight-line stimuli in a particular orientation unlike simple cells in that the position of the stimulus within the receptive field does not matter ...
Nervous Dia rams
... 5. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. 6. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. ...
... 5. A rapid automatic response to a stimulus. 6. The covering of fatty material that speeds up the passage of nerve impulses. ...
Action Representation in Mirror Neurons
... strongest vision-only and motor responses. In conclusion, area F5 contains a population of neurons—audio-visual mirror neurons—that discharge not just to the execution or observation of a specific action but also when this action can only be heard. Multimodal neurons have been described in several c ...
... strongest vision-only and motor responses. In conclusion, area F5 contains a population of neurons—audio-visual mirror neurons—that discharge not just to the execution or observation of a specific action but also when this action can only be heard. Multimodal neurons have been described in several c ...
Brain Presentation1
... •GHB can increase acetylcholine levels. •GHB can increase serotonin levels. •GHB can reduce dopamine activity, especially in the basal ganglia. This action is probably the result of the inhibition of the release of dopamine from synaptic terminals. Some studies show that GHB first inhibits the relea ...
... •GHB can increase acetylcholine levels. •GHB can increase serotonin levels. •GHB can reduce dopamine activity, especially in the basal ganglia. This action is probably the result of the inhibition of the release of dopamine from synaptic terminals. Some studies show that GHB first inhibits the relea ...
8Neurotrophins PCD
... • The transcription of genes for CNS neurotrophins is regulated by various forms of neuronal activity. • It has been observed that levels of BDNF mRNA in hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum can be changed by: - depolarization and Ca2+ influx - excitatory neurotransmission (glu, kainate increase; GAB ...
... • The transcription of genes for CNS neurotrophins is regulated by various forms of neuronal activity. • It has been observed that levels of BDNF mRNA in hippocampus, cortex, and cerebellum can be changed by: - depolarization and Ca2+ influx - excitatory neurotransmission (glu, kainate increase; GAB ...
Questions and Answers
... there are other ways of storing information. However, these other ways were not discussed. What other ways of storing information are there in the brain? A: 1. geometry of neurons 2. short term information may be stored in the temporal differences in the oscillation of neurons, 3. 4. How do synapses ...
... there are other ways of storing information. However, these other ways were not discussed. What other ways of storing information are there in the brain? A: 1. geometry of neurons 2. short term information may be stored in the temporal differences in the oscillation of neurons, 3. 4. How do synapses ...
Cell body
... Gray Matter – Cerebral cortex & Basal nuclei White Matter – Myelinated fiber tracts (axons) ...
... Gray Matter – Cerebral cortex & Basal nuclei White Matter – Myelinated fiber tracts (axons) ...
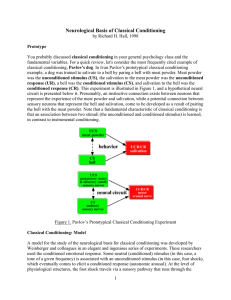
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
Neuro Physiology 1
... A synapse is the anatomical site where nerve cells communicate with other nerves, muscle and glands. There are two types which have been identified, either a chemical or electrical synapse. In electrical synapses, the membranes of the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons come close together, and gap ...
... A synapse is the anatomical site where nerve cells communicate with other nerves, muscle and glands. There are two types which have been identified, either a chemical or electrical synapse. In electrical synapses, the membranes of the presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons come close together, and gap ...
ANPS 019 Black 10-28
... This lecture will introduce you to the terms we will discuss throughout the rest of the semester ORGANIZEATION OF THE CNS How neurons and glia arranged? How does the CNS get its adult shape? How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Glial cells are smaller than neuro ...
... This lecture will introduce you to the terms we will discuss throughout the rest of the semester ORGANIZEATION OF THE CNS How neurons and glia arranged? How does the CNS get its adult shape? How do we tell one part from another? What does each part of the brain do? Glial cells are smaller than neuro ...
Human Nervous System Central nervous system
... A synapse is a region where neurons nearly touch Small gap between neurons is the synaptic cleft Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter molec ...
... A synapse is a region where neurons nearly touch Small gap between neurons is the synaptic cleft Transmission across a synapse is carried out by neurotransmitters Sudden rise in calcium at end of one neuron Stimulates synaptic vesicles to merge with the presynaptic membrane Neurotransmitter molec ...
bio 342 human physiology
... e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
... e) Axons of first order neurons ascend in the dorsal columns and synapse onto second order neurons in the dorsal column nuclei. ...
Computational vision --- a window to our brain
... One degree of visual angle = 0.3 mm on the retina Number of cones in each retina: 5x106 Number of rods in each retina: 108 ...
... One degree of visual angle = 0.3 mm on the retina Number of cones in each retina: 5x106 Number of rods in each retina: 108 ...
Computational vision --- a window to our brain
... One degree of visual angle = 0.3 mm on the retina Number of cones in each retina: 5x106 Number of rods in each retina: 108 ...
... One degree of visual angle = 0.3 mm on the retina Number of cones in each retina: 5x106 Number of rods in each retina: 108 ...
Neural pathways
... envelopes cell body – endbulb of Held Allows for ‘one-to-one’ transmission of action potentials ...
... envelopes cell body – endbulb of Held Allows for ‘one-to-one’ transmission of action potentials ...
Neuron Anatomy
... bind their receptors on the postsynaptic cell. • This supplements the uptake mechanisms and degradation mechanisms that neurons already have in place. • Such supplementation may be particularly important for high [neurotransmitters]s (e.g., glutamate, whether naturally or drug-induced). ...
... bind their receptors on the postsynaptic cell. • This supplements the uptake mechanisms and degradation mechanisms that neurons already have in place. • Such supplementation may be particularly important for high [neurotransmitters]s (e.g., glutamate, whether naturally or drug-induced). ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.