C8003 Psychobiology sample paper 2016-17
... Generation of an action potential at the axon hillock Depolarisation of and calcium entry into presynaptic terminals Neurotransmitter release and diffusion across the synaptic cleft Binding of neurotransmitter to receptor ion channels ...
... Generation of an action potential at the axon hillock Depolarisation of and calcium entry into presynaptic terminals Neurotransmitter release and diffusion across the synaptic cleft Binding of neurotransmitter to receptor ion channels ...
Griggs_Chapter_02_Neuroscience
... The auditory cortex is in the temporal lobes These primary areas pass the results of their analyses on to areas in the other lobes to complete the brain’s interpretation of the incoming visual or auditory information ...
... The auditory cortex is in the temporal lobes These primary areas pass the results of their analyses on to areas in the other lobes to complete the brain’s interpretation of the incoming visual or auditory information ...
Pathology - Med4just
... • Cause is unknown • Most are sporadic, 5-10% familial AD • Several gene mutations implicated, ...
... • Cause is unknown • Most are sporadic, 5-10% familial AD • Several gene mutations implicated, ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... 4. The interaction between neurotransmitters and receptors is very specific, like a lock and key. A specific receptor (a “lock”) can only be stimulated by a specific neurotransmitter (a “key”). 5. This interaction creates a signal called a postsynaptic potential (PSP) that might make action potentia ...
... 4. The interaction between neurotransmitters and receptors is very specific, like a lock and key. A specific receptor (a “lock”) can only be stimulated by a specific neurotransmitter (a “key”). 5. This interaction creates a signal called a postsynaptic potential (PSP) that might make action potentia ...
Sleep Brain Labelling
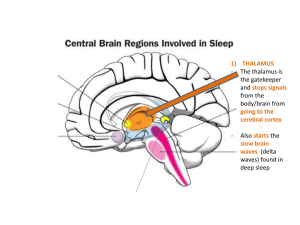
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
... 1) THALAMUS - The thalamus is the gatekeeper and stops signals from the body/brain from going to the cerebral cortex ...
13.1- neurons
... The areas between the sections of myelin sheath are known as the nodes of Ranvier. All nerve fibres found within the peripheral nervous system have a thin outer membrane called the neurilemma, which surrounds the ...
... The areas between the sections of myelin sheath are known as the nodes of Ranvier. All nerve fibres found within the peripheral nervous system have a thin outer membrane called the neurilemma, which surrounds the ...
The yin and yang of cortical layer 1
... of the authors had established that the active intrinsic properties of L5 pyramidal neurons allow them to couple inputs arriving at the tuft and basal dendrites simultaneously10. This mechanism has been hypothesized to facilitate the association of top-down and bottom-up processes in the cortex10,11 ...
... of the authors had established that the active intrinsic properties of L5 pyramidal neurons allow them to couple inputs arriving at the tuft and basal dendrites simultaneously10. This mechanism has been hypothesized to facilitate the association of top-down and bottom-up processes in the cortex10,11 ...
DESIRED RESULTS (STAGE 1) - Anoka
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
... The Difference between the two hemispheres somatic nervous system autonomic nervous system The structure of the nervous system hormone limbic system How neurons communicate To understand, students will need to DO... REASONING ...
Unit Two: Biological Bases of Behavior
... – Sends messages from brain muscles, organs, glands ...
... – Sends messages from brain muscles, organs, glands ...
Brain calculus: neural integration and persistent activity
... changes in firing rate induced with the intracellular injection of current. This supports the network hypothesis, because if the step changes were generated through mechanisms intrinsic to the cell recorded, such as through the activation of a persistent depolarizing current, then hyperpolarization ...
... changes in firing rate induced with the intracellular injection of current. This supports the network hypothesis, because if the step changes were generated through mechanisms intrinsic to the cell recorded, such as through the activation of a persistent depolarizing current, then hyperpolarization ...
Chapter 16: Basal Ganglia
... the posterior parietal cortex clearly plays a role in voluntary movements, by assessing the context in which they are being made. The parietal cortex receives somatosensory, proprioreceptive, and visual inputs, then uses them to determine such things as the positions of the body and the target in sp ...
... the posterior parietal cortex clearly plays a role in voluntary movements, by assessing the context in which they are being made. The parietal cortex receives somatosensory, proprioreceptive, and visual inputs, then uses them to determine such things as the positions of the body and the target in sp ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... Figure 3 Retrograde labeling of the perforant pathway to evaluate neuronal loss, axonal atrophy and terminal degeneration in the aged DKI mouse. A–D Fluorogold accumulation is depicted in the perforant pathway neurons of origin in layer II of the dorsal entorhinal cortex A-wild type, B-DKI and ventr ...
... Figure 3 Retrograde labeling of the perforant pathway to evaluate neuronal loss, axonal atrophy and terminal degeneration in the aged DKI mouse. A–D Fluorogold accumulation is depicted in the perforant pathway neurons of origin in layer II of the dorsal entorhinal cortex A-wild type, B-DKI and ventr ...
Nervous Regulation
... specific receptor that it will “fit” – Certain drugs mimic the effects of neurotransmitters by binding to these receptor molecules ...
... specific receptor that it will “fit” – Certain drugs mimic the effects of neurotransmitters by binding to these receptor molecules ...
Neural Network of C. elegans is a Small
... • The hermaphrodite version has a simple nervous system comprising about 302 neurons. • It’s neural network is completely mapped. • The pattern of connectivity portrays smallworld network characteristics. ...
... • The hermaphrodite version has a simple nervous system comprising about 302 neurons. • It’s neural network is completely mapped. • The pattern of connectivity portrays smallworld network characteristics. ...
Central Nervous System - Home Page of Ken Jones
... Substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors A nerve fiber; conducts impulse away from a neuro ...
... Substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into brain or spinal cord from receptors A nerve fiber; conducts impulse away from a neuro ...
Nervous System Intro
... with cranial and spinal nerves. • There are ganglia which are somatic, autonomic, and enteric (that is, they contain those types of neurons.) ...
... with cranial and spinal nerves. • There are ganglia which are somatic, autonomic, and enteric (that is, they contain those types of neurons.) ...
structure of the brain (cont.)
... – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA • GABA Keys – alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – when GABA neurons are excited, the ...
... – GABA neurons have chemical locks that can be opened by chemical keys in the form of the neurotransmitter GABA • GABA Keys – alcohol molecules so closely resemble those of the GABA neurotransmitter that alcohol can function like GABA keys and open GABA receptors – when GABA neurons are excited, the ...
ben_slides1
... Odor receptor changes shape and binds/activates an “olfactory-type” G protein G protein activates the lyase adenylate cyclase (LAC) LAC converts ATP into cAMP cAMP opens cyclic nucleotidegated ion channels Calcium and sodium ions to enter into the cell, depolarizing the ORN Calcium-dependent Chlorin ...
... Odor receptor changes shape and binds/activates an “olfactory-type” G protein G protein activates the lyase adenylate cyclase (LAC) LAC converts ATP into cAMP cAMP opens cyclic nucleotidegated ion channels Calcium and sodium ions to enter into the cell, depolarizing the ORN Calcium-dependent Chlorin ...
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Welcome to SBI4U with Ms. Taman!
... brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
... brain and spinal cord. • The sensory and motor neurons that connect to the CNS – Function = to carry info between organs of the body and the CNS ...
File
... Soma: The cell body with a nucleus and other structures for cellular life. Axon: a long slender tube covered in myelin that carries information from the cell body to the terminal buttons. Terminal Buttons: Structures which produce chemicals called neurotransmitters when excited by the actions potent ...
... Soma: The cell body with a nucleus and other structures for cellular life. Axon: a long slender tube covered in myelin that carries information from the cell body to the terminal buttons. Terminal Buttons: Structures which produce chemicals called neurotransmitters when excited by the actions potent ...
Types of Neuron and their function - Click here
... be interconnected. When a nerve signal, or impulse reaches the ends of its axon, it has travelled as an action potential, or a pulse of electricity. However, there is no cellular continuity between one neuron and the next; there is a gap called synapse. The membranes of the sending and receiving cel ...
... be interconnected. When a nerve signal, or impulse reaches the ends of its axon, it has travelled as an action potential, or a pulse of electricity. However, there is no cellular continuity between one neuron and the next; there is a gap called synapse. The membranes of the sending and receiving cel ...
Biology and Behavior
... (list in order that the neuron receives the message) 2. Inside the neuron is a _____ charge, until an action potential occurs, making the charge _____. 3. Neurons can have excitatory and _____ effects on each other causing an action potential to occur or not occur. 4. The communication within a neur ...
... (list in order that the neuron receives the message) 2. Inside the neuron is a _____ charge, until an action potential occurs, making the charge _____. 3. Neurons can have excitatory and _____ effects on each other causing an action potential to occur or not occur. 4. The communication within a neur ...
nervous system 2012 - Junction Hill C
... have about 100 billion neurons in their brain alone! While variable in size and shape, all neurons have three parts. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. The cell body contains the nucleus. The axon conducts messages away from the cell body. ...
... have about 100 billion neurons in their brain alone! While variable in size and shape, all neurons have three parts. Dendrites receive information from another cell and transmit the message to the cell body. The cell body contains the nucleus. The axon conducts messages away from the cell body. ...
Symbolic Reasoning in Spiking Neurons:
... without any random variation to changes in their inputs. We thus adapt their model, replacing individual idealized neurons with groups of realistic leaky-integrate-and-fire (LIF) spiking neurons. For our neurons, the membrane time constant (τRC; controlling the amount of current leaking out of the n ...
... without any random variation to changes in their inputs. We thus adapt their model, replacing individual idealized neurons with groups of realistic leaky-integrate-and-fire (LIF) spiking neurons. For our neurons, the membrane time constant (τRC; controlling the amount of current leaking out of the n ...
Synaptic gating

Synaptic gating is the ability of neural circuits to gate inputs by either suppressing or facilitating specific synaptic activity. Selective inhibition of certain synapses has been studied thoroughly (see Gate theory of pain), and recent studies have supported the existence of permissively gated synaptic transmission. In general, synaptic gating involves a mechanism of central control over neuronal output. It includes a sort of gatekeeper neuron, which has the ability to influence transmission of information to selected targets independently of the parts of the synapse upon which it exerts its action (see also neuromodulation).Bistable neurons have the ability to oscillate between a hyperpolarized (down state) and a depolarized (up state) resting membrane potential without firing an action potential. These neurons can thus be referred to as up/down neurons. According to one model, this ability is linked to the presence of NMDA and AMPA glutamate receptors. External stimulation of the NMDA receptors is responsible for moving the neuron from the down state to the up state, while the stimulation of AMPA receptors allows the neuron to reach and surpass the threshold potential. Neurons that have this bistable ability have the potential to be gated because outside gatekeeper neurons can modulate the membrane potential of the gated neuron by selectively shifting them from the up state to the down state. Such mechanisms have been observed in the nucleus accumbens, with gatekeepers originating in the cortex, thalamus and basal ganglia.