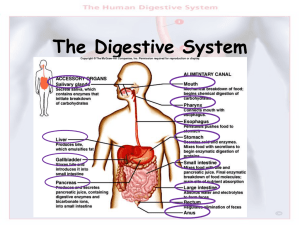
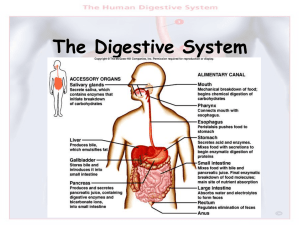
File
... • Large Intestine – Final section of the canal. • 5 feet in length, 2 inch diameter • Absorption of H20 & any remaining nutrients; storage of indigestible materials before elimination; absorption of some vitamins; and transportation of waste out of the body. • Cecum – First part of the large intesti ...
... • Large Intestine – Final section of the canal. • 5 feet in length, 2 inch diameter • Absorption of H20 & any remaining nutrients; storage of indigestible materials before elimination; absorption of some vitamins; and transportation of waste out of the body. • Cecum – First part of the large intesti ...
2 division Digestive system parts –GI
... . Mylase (break down starch) Deglutition (tongue sends bolus to pharynx) Swallowing occurs by involuntary process. Uvula and soft palate raise to protect the nose from up-flow of food; Tongue is raised to seal of back of mouth. Epiglottis descends to cover the opening of the larynx. Bolus is moved t ...
... . Mylase (break down starch) Deglutition (tongue sends bolus to pharynx) Swallowing occurs by involuntary process. Uvula and soft palate raise to protect the nose from up-flow of food; Tongue is raised to seal of back of mouth. Epiglottis descends to cover the opening of the larynx. Bolus is moved t ...
The Digestive System - Curriculum for Excellence Science
... • Beakers of water – labelled saliva • Large sandwich bags – stomach • Beaker of vinegar + colouring – labelled stomach acid • Leg of a tight (both ends cut off) – intestines • Cut off bottle with lid on – rectum and anus Best to do the squeezing over a sink ...
... • Beakers of water – labelled saliva • Large sandwich bags – stomach • Beaker of vinegar + colouring – labelled stomach acid • Leg of a tight (both ends cut off) – intestines • Cut off bottle with lid on – rectum and anus Best to do the squeezing over a sink ...
Stages of Digestion
... into the small intestine. • The first metre is called the duodenum. Digestion is complete after foods leaves. • Within the first 30 cm are ducts that connect to other organs. • Pancreas: produces enzymes • Liver: produces bile. ...
... into the small intestine. • The first metre is called the duodenum. Digestion is complete after foods leaves. • Within the first 30 cm are ducts that connect to other organs. • Pancreas: produces enzymes • Liver: produces bile. ...
Day 2: Digestive and Excretory System
... 2. Locate the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity. Find the most obvious structure in the abdominal cavity, the brownishcolored liver. Count the number of lobes. 3. Locate the soft, sac-like stomach beneath the liver. With scissors/scalpel, cut a ...
... 2. Locate the diaphragm, a sheet of muscle that separates the abdominal cavity from the thoracic cavity. Find the most obvious structure in the abdominal cavity, the brownishcolored liver. Count the number of lobes. 3. Locate the soft, sac-like stomach beneath the liver. With scissors/scalpel, cut a ...
Microbiology: A Systems Approach, 2nd ed.
... and has been linked to a variety of gastrointestinal ailments Gastritis: sharp or burning pain emanating from the abdomen Gastric ulcers are actual lesions in the mucosa of the stomach Duodenal ulcer: lesion in the uppermost portion of the small intestine Severe ulcers can be accompanied by bloody s ...
... and has been linked to a variety of gastrointestinal ailments Gastritis: sharp or burning pain emanating from the abdomen Gastric ulcers are actual lesions in the mucosa of the stomach Duodenal ulcer: lesion in the uppermost portion of the small intestine Severe ulcers can be accompanied by bloody s ...
The Digestive and Nervous Systems - CGW-Life-Science
... The final digestive and absorption process 1. Almost all chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients takes place in the small intestine. 2. Liver - bile - break up fats. 3. Pancreas - enzymes - breaks down starches, proteins and fats. 4. In the large intestine, water is absorbed into the bloods ...
... The final digestive and absorption process 1. Almost all chemical digestion and absorption of nutrients takes place in the small intestine. 2. Liver - bile - break up fats. 3. Pancreas - enzymes - breaks down starches, proteins and fats. 4. In the large intestine, water is absorbed into the bloods ...
PowerPoint Presentation - The Human Digestive System
... Mixes food with digestive juices Acid in the stomach kills bacteria ...
... Mixes food with digestive juices Acid in the stomach kills bacteria ...
THE DIGESTIVE SYSTEM
... juices, ex. the hormone gastrin stimulate gastric juice release before food gets to stomach ...
... juices, ex. the hormone gastrin stimulate gastric juice release before food gets to stomach ...
Diseases in theDigestive System
... Gastric Hormones • Gastrin: peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid • Incretin: Incretins are a group of gastrointestinal hormones that cause an increase in the amount of insulin released. They also slow the rate of absorption of nutrients into the blood stream by reducing gastric ...
... Gastric Hormones • Gastrin: peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid • Incretin: Incretins are a group of gastrointestinal hormones that cause an increase in the amount of insulin released. They also slow the rate of absorption of nutrients into the blood stream by reducing gastric ...
The Digestive System
... excessive use of alcohol or medications like asprin bacteria, Helicobacter Pylori anemia, infections, bile reflux (bile released from bile tract into stomach) ...
... excessive use of alcohol or medications like asprin bacteria, Helicobacter Pylori anemia, infections, bile reflux (bile released from bile tract into stomach) ...
Gastrointestinal System Unit 44
... Cancers are very common. Symptoms depend on location of malignancy and may include obstruction, indigestion, vomiting, constipation, flatus, blood in the stool. Treatment may include: Esophagectomy, subtotal gastrectomy, colectomy(bowel resection), colostomy, ileostomy. ...
... Cancers are very common. Symptoms depend on location of malignancy and may include obstruction, indigestion, vomiting, constipation, flatus, blood in the stool. Treatment may include: Esophagectomy, subtotal gastrectomy, colectomy(bowel resection), colostomy, ileostomy. ...
The Digestive System The Digestive System
... • Guard openings to stomach – Cardiac - esophagus to stomach – Pyloric - lower portion of stomach to small intestine. • Pylorospasm - muscle will not relax to allow passage of bolus = vomiting ...
... • Guard openings to stomach – Cardiac - esophagus to stomach – Pyloric - lower portion of stomach to small intestine. • Pylorospasm - muscle will not relax to allow passage of bolus = vomiting ...
The Upper Alimentary System
... • Rugae- folds of tissue that allow the stomach to expand when full with food • Mechanical digestion •Lined with three layers of muscles to churn food, continue chopping after the teeth ...
... • Rugae- folds of tissue that allow the stomach to expand when full with food • Mechanical digestion •Lined with three layers of muscles to churn food, continue chopping after the teeth ...
Slide 1
... •A loss of only 10% of the body’s water is a serious health risk •Loss of 15% or more is life threatening •Up to two thirds of the body is water •Provides shape to cells •Helps transport nutrients, wastes, and hormones in blood •Controls body temperature ...
... •A loss of only 10% of the body’s water is a serious health risk •Loss of 15% or more is life threatening •Up to two thirds of the body is water •Provides shape to cells •Helps transport nutrients, wastes, and hormones in blood •Controls body temperature ...
The Digestive System The Digestive System: Function
... • Guard openings to stomach – Cardiac - esophagus to stomach – Pyloric - lower portion of stomach to small intestine. • Pylorospasm - muscle will not relax to allow passage of bolus = vomiting ...
... • Guard openings to stomach – Cardiac - esophagus to stomach – Pyloric - lower portion of stomach to small intestine. • Pylorospasm - muscle will not relax to allow passage of bolus = vomiting ...
Chapter 14: Study Guide 1. What is peristalsis? 2. What are papillae
... 2. What are papillae and where are they located? 3. What is the roof of the oral cavity called (2 parts): Where is the uvula? 4. What are the three salivary glands and where are they located? 5. What are the two types of movements within the alimentary canal? 6. What are the three main functions of ...
... 2. What are papillae and where are they located? 3. What is the roof of the oral cavity called (2 parts): Where is the uvula? 4. What are the three salivary glands and where are they located? 5. What are the two types of movements within the alimentary canal? 6. What are the three main functions of ...