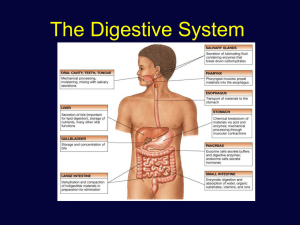
Chapter 24 The Digestive System Lecture Outline
... Functions to secrete mucus, digestive enzymes, and hormones, to absorb end products of digestion, and provide protection from pathogens A. Epithelium (continuously renewed, surface cells last only 2-6 days) Stratified squamous: oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, anus Simple columnar: stomach, intestin ...
... Functions to secrete mucus, digestive enzymes, and hormones, to absorb end products of digestion, and provide protection from pathogens A. Epithelium (continuously renewed, surface cells last only 2-6 days) Stratified squamous: oral cavity, pharynx, esophagus, anus Simple columnar: stomach, intestin ...
Human Digestive System
... 1) Fruits, vegetables, grains and other “natural” foods that come from plants are good sources 2) “Processed” foods from plant sources often have little or no roughage ...
... 1) Fruits, vegetables, grains and other “natural” foods that come from plants are good sources 2) “Processed” foods from plant sources often have little or no roughage ...
16 DIGESTION Presentation
... Jaundice: The liver is affected, skin and eyes turn yellow due to the deposit of bile pigments. ...
... Jaundice: The liver is affected, skin and eyes turn yellow due to the deposit of bile pigments. ...
Digestion and Absorption Review
... Achlorhydria, gastrectomy, GI dysfunction or disease ↑ risk of bacterial overgrowth in the intestines Protein digestion begins with pepsinogen which is converted to active pepsin in acidic stomach environment Chief cells secrete acid-stable gastric lipase, which has minor effect on shorter-chain tri ...
... Achlorhydria, gastrectomy, GI dysfunction or disease ↑ risk of bacterial overgrowth in the intestines Protein digestion begins with pepsinogen which is converted to active pepsin in acidic stomach environment Chief cells secrete acid-stable gastric lipase, which has minor effect on shorter-chain tri ...
Perspectives in Nutrition, 8th Edition
... Common bile duct and pancreatic duct empty into the duodenum at the sphincter of Oddi ...
... Common bile duct and pancreatic duct empty into the duodenum at the sphincter of Oddi ...
6.1 activity worksheet
... Three sphincter muscles are mentioned in the video: the cardiac sphincter -controls entry into the stomach from the esophagus pyloric sphincter – controls entry from the stomach into the small intestine iliocecal sphincter – controls entry from the small to the large intestine ...
... Three sphincter muscles are mentioned in the video: the cardiac sphincter -controls entry into the stomach from the esophagus pyloric sphincter – controls entry from the stomach into the small intestine iliocecal sphincter – controls entry from the small to the large intestine ...
a&p2-Ch24.ppt
... molecules to disacharides. Disaccharides are broken down by enzymes (disaccharideases) on intestinal microvilli in the lining of the small intestine. these enzymes convert the disaccharides into monosaccharides Disaccharides include: lactose, sucrose, maltose, isomaltose enzymes that digest these ar ...
... molecules to disacharides. Disaccharides are broken down by enzymes (disaccharideases) on intestinal microvilli in the lining of the small intestine. these enzymes convert the disaccharides into monosaccharides Disaccharides include: lactose, sucrose, maltose, isomaltose enzymes that digest these ar ...
Name: Date:
... Your task is to design a t-shirt with the digestive tract on it. You can use an old t-shirt or any similar material, (for example an old bed sheet), as long as it fits over the head and can be worn. You must use a variety of materials with different colors to represent each part of the digestive tra ...
... Your task is to design a t-shirt with the digestive tract on it. You can use an old t-shirt or any similar material, (for example an old bed sheet), as long as it fits over the head and can be worn. You must use a variety of materials with different colors to represent each part of the digestive tra ...
The Digestive System - Anatomy and Physiology Course Anatomy
... This is caused by a reflux of the stomach acids back up into the oesophagus. As was said, the stomach produces mucus to protect itself from these acids, but the oesophagus has no such protection, so it is burned. This results in oesophagitis, or heart burn, experienced as retrosternal pain. If this ...
... This is caused by a reflux of the stomach acids back up into the oesophagus. As was said, the stomach produces mucus to protect itself from these acids, but the oesophagus has no such protection, so it is burned. This results in oesophagitis, or heart burn, experienced as retrosternal pain. If this ...
BIO_ALL IN1_StGd_tese_ch38
... the mouth and ending with the large intestine. They should also indicate which nutrients are broken down in each organ. ...
... the mouth and ending with the large intestine. They should also indicate which nutrients are broken down in each organ. ...
Digestive System - Fall River Public Schools
... • Bile dissolves and disperses droplets of fat found in foods – Makes it easier for enzymes to reach and break down fats ...
... • Bile dissolves and disperses droplets of fat found in foods – Makes it easier for enzymes to reach and break down fats ...
Digestive System
... An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric or peptic ulcer The partially digested food in the stomach is changed into a semi-liquid state called chyme in 3 to 5 hours Liquids will pass through the stomach in minutes When the consistency of the chyme is right, the pyloric sphincter, at the end of th ...
... An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric or peptic ulcer The partially digested food in the stomach is changed into a semi-liquid state called chyme in 3 to 5 hours Liquids will pass through the stomach in minutes When the consistency of the chyme is right, the pyloric sphincter, at the end of th ...
Digestive System - Petal School District
... Treatment- rest, diet high in protein and calories but low in fat. If severe, liver transplant. ...
... Treatment- rest, diet high in protein and calories but low in fat. If severe, liver transplant. ...
Digestive System - Fall River Public Schools
... down food into small molecules that can be passed to the cells that need them • The human digestive system is built around an alimentary canala one-way tube that passes through the body • Also called the Gastrointestinal Tract Digestive System ...
... down food into small molecules that can be passed to the cells that need them • The human digestive system is built around an alimentary canala one-way tube that passes through the body • Also called the Gastrointestinal Tract Digestive System ...
Duodenal Ulcer / Duodenitis - Royal Surrey – County Hospital
... cases of duodenal ulcers. More than a quarter of people in the UK become infected with H. pylori at some stage in their life. Once you are infected, unless treated, the infection usually stays for the rest of your life. In many people it causes no problems and a number of these bacteria just live ha ...
... cases of duodenal ulcers. More than a quarter of people in the UK become infected with H. pylori at some stage in their life. Once you are infected, unless treated, the infection usually stays for the rest of your life. In many people it causes no problems and a number of these bacteria just live ha ...
Digestive System
... several times a day in cecum and entire colon. Reverse peristalsis = orally directed which gives more time to the fecal matter to be expose of water absorption. ...
... several times a day in cecum and entire colon. Reverse peristalsis = orally directed which gives more time to the fecal matter to be expose of water absorption. ...
Unfolding the Diagnosis - Case Western Reserve University
... of anti-CMV IgG antibodies favors the former. However, false positive results for anti-CMV IgM antibodies have been reported in cases of cancer or systemic inflammation, causing some doubt about this diagnosis. The absence of clinically significant proteinuria rules out protein loss through the urin ...
... of anti-CMV IgG antibodies favors the former. However, false positive results for anti-CMV IgM antibodies have been reported in cases of cancer or systemic inflammation, causing some doubt about this diagnosis. The absence of clinically significant proteinuria rules out protein loss through the urin ...
Digestion System & Nutrition
... Nutrition is the process by which the body takes in and uses nutrients Essential nutrients are those that cannot be synthesized by human cells Carbohydrates, such as sugars and starches, are organic compounds used for sources of energy in the diet. Carbohydrates can be consumed in a variety of ways: ...
... Nutrition is the process by which the body takes in and uses nutrients Essential nutrients are those that cannot be synthesized by human cells Carbohydrates, such as sugars and starches, are organic compounds used for sources of energy in the diet. Carbohydrates can be consumed in a variety of ways: ...
Study Guide Digestive System
... intestine formed of flesh can digest meat without any harm to them. 18. Fat soluble substances like Alcohol and Aspirin easily pass into blood in stomach and can easily cause gastric irritation. ...
... intestine formed of flesh can digest meat without any harm to them. 18. Fat soluble substances like Alcohol and Aspirin easily pass into blood in stomach and can easily cause gastric irritation. ...
Human Organ Systems
... ____________ of nutrients occur here. After food leaves the stomach, it enters the first part of the small intestine called the _________. At this stage, the partially digested food is called ________. When chyme reaches the duodenum, it stimulates the production of enzymes from the ________ and ___ ...
... ____________ of nutrients occur here. After food leaves the stomach, it enters the first part of the small intestine called the _________. At this stage, the partially digested food is called ________. When chyme reaches the duodenum, it stimulates the production of enzymes from the ________ and ___ ...
Digestion - Belle Vernon Area School District
... l. Kupffer cells – Phagocytic cells that remove bacteria from the blood that came from the digestive tract. m. Bile Canaliculi- Secrete bile. n. right hepatic duct o. cystic duct p. Common bile duct q. Duodenal papilla opening in small intestines from the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct. ...
... l. Kupffer cells – Phagocytic cells that remove bacteria from the blood that came from the digestive tract. m. Bile Canaliculi- Secrete bile. n. right hepatic duct o. cystic duct p. Common bile duct q. Duodenal papilla opening in small intestines from the common bile duct and the pancreatic duct. ...
File digestive system
... Bile is a yellow-green watery solution containing bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, and other substances. It is made in the liver but is stored in the gall bladder. It does not contain enzymes but the bile salts help to emulsify fat, breaking it down from large fat globules into smaller fat drople ...
... Bile is a yellow-green watery solution containing bile salts, bilirubin, cholesterol, and other substances. It is made in the liver but is stored in the gall bladder. It does not contain enzymes but the bile salts help to emulsify fat, breaking it down from large fat globules into smaller fat drople ...
The Digestive System
... Submucosa - layer of dense irregular connective tissue, vascularized (blood and lymphatic), innervated – nerve plexus, submucosal glands Muscularis externa - smooth muscle arranged in circular and longitudinal layers Adventitia or Serosa - serous membrane made of areolar connective tissue with colla ...
... Submucosa - layer of dense irregular connective tissue, vascularized (blood and lymphatic), innervated – nerve plexus, submucosal glands Muscularis externa - smooth muscle arranged in circular and longitudinal layers Adventitia or Serosa - serous membrane made of areolar connective tissue with colla ...