
C H A P T E R 6 3
... These intense peristaltic contractions often create 50 to 70cm of water pressure, which is about six times as powerful as the usual mixing type of ...
... These intense peristaltic contractions often create 50 to 70cm of water pressure, which is about six times as powerful as the usual mixing type of ...
stomach
... • Tight junctions between epithelial cells • Damaged epithelial cells are quickly replaced by division of stem cells ...
... • Tight junctions between epithelial cells • Damaged epithelial cells are quickly replaced by division of stem cells ...
Digestive System Notes
... – involves: chewing, grinding, churning • CHEMICAL digestion – Breaking down of food into simpler substances ...
... – involves: chewing, grinding, churning • CHEMICAL digestion – Breaking down of food into simpler substances ...
Digestion
... involves: chewing, grinding, churning CHEMICAL digestion Breaking down of food into simpler substances ...
... involves: chewing, grinding, churning CHEMICAL digestion Breaking down of food into simpler substances ...
Digestion
... wall muscles keep the feed mixing through strong contractions. The rumen provides a host site for bacteria, anaerobic fungi, and protozoa that carry out a symbiotic relationship. The symbiosis exists when both the ruminant and the microorganisms benefit. In this case, the rumen provides food for the ...
... wall muscles keep the feed mixing through strong contractions. The rumen provides a host site for bacteria, anaerobic fungi, and protozoa that carry out a symbiotic relationship. The symbiosis exists when both the ruminant and the microorganisms benefit. In this case, the rumen provides food for the ...
Small Intestine - Human Digestive System
... Structure Of Small Intestine o Tube-like structure winds compactly back and forth within the abdominal cavity for about 7 m o Consist of #1 Duodenum #2 Jejunum #3 Ileum o Have finger-like projections known as villi (increase surface area for absorption of nutrients). ...
... Structure Of Small Intestine o Tube-like structure winds compactly back and forth within the abdominal cavity for about 7 m o Consist of #1 Duodenum #2 Jejunum #3 Ileum o Have finger-like projections known as villi (increase surface area for absorption of nutrients). ...
Animal Digestion
... hemicellulose) and soluble carbohydrates that escape digestion in small intestine to VFA’s. ...
... hemicellulose) and soluble carbohydrates that escape digestion in small intestine to VFA’s. ...
Chapters 22-24
... 9. Know the three phases of gastric activity and what happens at each phase. 10. Know what types of digestion and absorption occur in the stomach. 11. Know the general features of the small intestine. What is the key function of the small intestine? Know what features are unique to each of the secti ...
... 9. Know the three phases of gastric activity and what happens at each phase. 10. Know what types of digestion and absorption occur in the stomach. 11. Know the general features of the small intestine. What is the key function of the small intestine? Know what features are unique to each of the secti ...
Digestive system
... Chyme with H+, fats, peptides, irritating substances inhibition-tightening of pyloric sphincter - no more food entry to small intestine. If small intestine is forced to accept more chyme it causes dumping syndrome-(nausea and vomiting). ...
... Chyme with H+, fats, peptides, irritating substances inhibition-tightening of pyloric sphincter - no more food entry to small intestine. If small intestine is forced to accept more chyme it causes dumping syndrome-(nausea and vomiting). ...
63a-AP-Digestive
... Gastrin Hormone secreted by the stomach that initiates the production and secretion of gastric juices and stimulates bile and pancreatic enzyme emissions into the small intestines." ...
... Gastrin Hormone secreted by the stomach that initiates the production and secretion of gastric juices and stimulates bile and pancreatic enzyme emissions into the small intestines." ...
Ch23.Digestive.System_1
... The Gut Flora • 10X as many microbes as there are cells of the human body!!! • Perform many metabolic activities “forgotten organ” • Bacteria most of the flora, also fungi & protozoa • Makes up 60% of the dry mass of feces! • About 500 species in gut (small & large intestines) • 99% of bacteria ...
... The Gut Flora • 10X as many microbes as there are cells of the human body!!! • Perform many metabolic activities “forgotten organ” • Bacteria most of the flora, also fungi & protozoa • Makes up 60% of the dry mass of feces! • About 500 species in gut (small & large intestines) • 99% of bacteria ...
Livestock Nutrition
... • Feed in proventriculus are secreted by the glandular stomach and mixed with feed. The feed next moves to the gizzard. • Epithelium breaks the feed into smaller particles, further mixing of proventricular digestive juices with the feed in the gizzard.The end of the digestive system is the vent. ...
... • Feed in proventriculus are secreted by the glandular stomach and mixed with feed. The feed next moves to the gizzard. • Epithelium breaks the feed into smaller particles, further mixing of proventricular digestive juices with the feed in the gizzard.The end of the digestive system is the vent. ...
File
... 21.10 The small intestine is the major organ of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption The first 25 cm of the small intestine is the duodenum, where chyme squirted from the stomach mixes with digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, and gland cells in the intestinal wall. – The ...
... 21.10 The small intestine is the major organ of chemical digestion and nutrient absorption The first 25 cm of the small intestine is the duodenum, where chyme squirted from the stomach mixes with digestive juices from the pancreas, liver, gallbladder, and gland cells in the intestinal wall. – The ...
The Digestive System
... primarily responsible for water reabsorption. Peristalsis: Repeated involuntary waves of muscular movement that serve to move ingested matter through the intestines during digestion. Proton pump inhibitor: A group of medications that reduce the secretion of stomach acids. Rebound tenderness: Pain fe ...
... primarily responsible for water reabsorption. Peristalsis: Repeated involuntary waves of muscular movement that serve to move ingested matter through the intestines during digestion. Proton pump inhibitor: A group of medications that reduce the secretion of stomach acids. Rebound tenderness: Pain fe ...
The Obesity Hypoventilation Syndrome
... and chest-wall (including diaphragm) elastance. Compliance is the inverse of elastance and measures the change in volume from an applied pressure. Naimark and Cherniack found the compliance of the respiratory system (Crs) to be 119 mL/cm H2O in seated lean subjects, and 52 mL/cm H2O in seated obese ...
... and chest-wall (including diaphragm) elastance. Compliance is the inverse of elastance and measures the change in volume from an applied pressure. Naimark and Cherniack found the compliance of the respiratory system (Crs) to be 119 mL/cm H2O in seated lean subjects, and 52 mL/cm H2O in seated obese ...
Human Digestive System
... human digestive system, the system used in the human body for the process of digestion. The human digestive system consists primarily of the digestive tract, or the series of structures and organs through which food and liquids pass during their processing into forms absorbable into the bloodstream. ...
... human digestive system, the system used in the human body for the process of digestion. The human digestive system consists primarily of the digestive tract, or the series of structures and organs through which food and liquids pass during their processing into forms absorbable into the bloodstream. ...
Indigestion and Ulcers - Family Doctor Publications
... infective agent called Helicobacter pylori – you’ll find out more about this later (see page 64). The third common cause of indigestion, called nonulcer dyspepsia, is something of a puzzle. This is the diagnosis given to people who have persistent symptoms of indigestion but in whom the tests for ga ...
... infective agent called Helicobacter pylori – you’ll find out more about this later (see page 64). The third common cause of indigestion, called nonulcer dyspepsia, is something of a puzzle. This is the diagnosis given to people who have persistent symptoms of indigestion but in whom the tests for ga ...
Tour Guide - TangHua2012-2013
... face (I am sure that you all know about that). They are soft, movable, and was used to help holding food in our mouth. Our lips can feel cold and hot, in another word, it is an organ which allows to use sense to know what we are eating. It also help to direct food onto our teeth. ...
... face (I am sure that you all know about that). They are soft, movable, and was used to help holding food in our mouth. Our lips can feel cold and hot, in another word, it is an organ which allows to use sense to know what we are eating. It also help to direct food onto our teeth. ...
PPT23Chapter23DigestiveSystem
... open allowing passage of food into the stomach When contracted LES closes the base of the esophagus preventing reflux or regurgitation ...
... open allowing passage of food into the stomach When contracted LES closes the base of the esophagus preventing reflux or regurgitation ...
Duodenal Ulcer
... clear this infection. If this infection is not cleared, the ulcer is likely to return once you stop taking acidsuppressing medication. Two antibiotics are needed. In addition, you need to take an acid-suppressing medicine to reduce the acid in the stomach. This is needed to allow the antibiotics to ...
... clear this infection. If this infection is not cleared, the ulcer is likely to return once you stop taking acidsuppressing medication. Two antibiotics are needed. In addition, you need to take an acid-suppressing medicine to reduce the acid in the stomach. This is needed to allow the antibiotics to ...
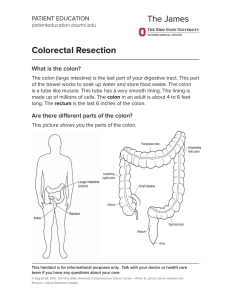
Colorectal Resection - OSU Patient Education Materials
... called resection. Some normal tissue and lymph nodes may also be removed. The healthy sections of the bowel are then sewn together. This is called anastomosis. ...
... called resection. Some normal tissue and lymph nodes may also be removed. The healthy sections of the bowel are then sewn together. This is called anastomosis. ...
digestion.pps [Compatibility Mode]
... the stomach by the pylorus • shorter in carnivores, longer in herbivores – dynamic changes • in tadpoles longer than in frogs relative to body size • duodenum: production of mucus and fluids + receives secretions from liver and pancreas – neutralization of stomach acid and digestion • jejunum: secre ...
... the stomach by the pylorus • shorter in carnivores, longer in herbivores – dynamic changes • in tadpoles longer than in frogs relative to body size • duodenum: production of mucus and fluids + receives secretions from liver and pancreas – neutralization of stomach acid and digestion • jejunum: secre ...





















![digestion.pps [Compatibility Mode]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003729047_1-76eb6cb06dc9687dff1e2f59bf530546-300x300.png)