Abnormal Psychology - University of Toronto
... • Learning refers to an enduring change in the way an organism responds based on its experience – Distinct from • Drug effects (caffeine-induced jitters are not learning) • Fatigue or illness ...
... • Learning refers to an enduring change in the way an organism responds based on its experience – Distinct from • Drug effects (caffeine-induced jitters are not learning) • Fatigue or illness ...
PSY100-learning10
... • Learning refers to an enduring change in the way an organism responds based on its experience – Distinct from • Drug effects (caffeine-induced jitters are not learning) • Fatigue or illness ...
... • Learning refers to an enduring change in the way an organism responds based on its experience – Distinct from • Drug effects (caffeine-induced jitters are not learning) • Fatigue or illness ...
Examples of Learning Psychology
... of learning. You may use Comic Life, PowerPoint, Prezi or any other type of electronic media of your choice. Each of the different types of learning needs to be clearly labeled and explained. Personal experiences need to be applied for all the concepts that have a star next to them. Topics should ma ...
... of learning. You may use Comic Life, PowerPoint, Prezi or any other type of electronic media of your choice. Each of the different types of learning needs to be clearly labeled and explained. Personal experiences need to be applied for all the concepts that have a star next to them. Topics should ma ...
Learning - abbydelman
... Conditioned response (CR) A response that is elicited by the conditioned stimulus Occurs after the CS has been associated with the US Is usually similar to the US ...
... Conditioned response (CR) A response that is elicited by the conditioned stimulus Occurs after the CS has been associated with the US Is usually similar to the US ...
Chapter 6 - learning
... stimulus that has come to elicit a CR because it has been associated with the UCS Conditioned response (CR) - a learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral, or meaningless ...
... stimulus that has come to elicit a CR because it has been associated with the UCS Conditioned response (CR) - a learned response to a stimulus that was previously neutral, or meaningless ...
Innate/Learned Behavior Powerpoint
... Soon, the rat pressed the lever far more often than he would just by chance. But with each instance of lever pressing, the operant is reinforced by reward with food. The rat learns that pressing the lever is associated with food, and so he will increasingly press it. ...
... Soon, the rat pressed the lever far more often than he would just by chance. But with each instance of lever pressing, the operant is reinforced by reward with food. The rat learns that pressing the lever is associated with food, and so he will increasingly press it. ...
Chapter 5: Learning - MDC Faculty Home Pages
... He determined that a cats’ learning is based on a trial and error bases Law of Effect—learning principle proposed by Thorndike that proposes that responses followed by a satisfying effect become strengthened and are more likely to recur, while responses followed by a dissatisfying effect are weakene ...
... He determined that a cats’ learning is based on a trial and error bases Law of Effect—learning principle proposed by Thorndike that proposes that responses followed by a satisfying effect become strengthened and are more likely to recur, while responses followed by a dissatisfying effect are weakene ...
Midterm Review File
... 8. A senior in high school took the SAT two extra times to try and avoid receiving a rejection letter from the last series of universities to which he had applied. Which operant conditioning term applies to his action in trying to avoid another rejection letter? _____________________________________ ...
... 8. A senior in high school took the SAT two extra times to try and avoid receiving a rejection letter from the last series of universities to which he had applied. Which operant conditioning term applies to his action in trying to avoid another rejection letter? _____________________________________ ...
Outcome 2 Classical Conditioning Notes week 8
... with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) to elicit a response. The UCS causes a reflex response called the unconditioned response (UCR). If the NS is consistently paired with the UCS, it becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) capable of producing a response by itself. This response is a conditioned (learnt ...
... with an unconditioned stimulus (UCS) to elicit a response. The UCS causes a reflex response called the unconditioned response (UCR). If the NS is consistently paired with the UCS, it becomes a conditioned stimulus (CS) capable of producing a response by itself. This response is a conditioned (learnt ...
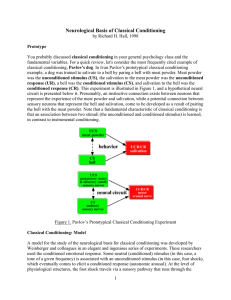
Neurological Basis of Classical Conditioning
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
... In order to test the viability of the neurological model presented above, Weinberger and colleagues began by establishing the tonotopic frequency of a set of neurons within the auditory system, in particular the auditory cortex. Many cells in the auditory system are "tuned" to a given frequency, tha ...
Prenatal “experience” and the phylogenesis and ontogenesis of music
... a) environmental sounds and movements b) perception c) classical conditioning d) communication with mother ...
... a) environmental sounds and movements b) perception c) classical conditioning d) communication with mother ...
Learning
... Learning in which an organism comes to associate stimuli also called Pavlovian or respondent conditioning Conditioned = learned Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (US) ...
... Learning in which an organism comes to associate stimuli also called Pavlovian or respondent conditioning Conditioned = learned Classical Conditioning Unconditioned Stimulus (US) ...
Theories of Human Behavior Objectives
... superego; secondary process thinking (logical, mature, delays gratification); functions include the defenses ...
... superego; secondary process thinking (logical, mature, delays gratification); functions include the defenses ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide What is learning? What is associative
... 6. Describe the Little Albert Study. Who conducted it? What was Little Albert conditioned to fear? ...
... 6. Describe the Little Albert Study. Who conducted it? What was Little Albert conditioned to fear? ...
theories of learning
... ●Stimulus Generalization: once the dog has learned to salivate at the sound of the bell, it will salivate at other similar sounds. ●Extinction: if you stop pairing the bell with the food, salivation will eventually cease in response to the bell. ●Spontaneous recovery: Extinguished responses can be “ ...
... ●Stimulus Generalization: once the dog has learned to salivate at the sound of the bell, it will salivate at other similar sounds. ●Extinction: if you stop pairing the bell with the food, salivation will eventually cease in response to the bell. ●Spontaneous recovery: Extinguished responses can be “ ...
Psychology210 Lab Report - St. Francis Xavier University
... Classical conditioning involves the presentation of a conditioned stimulus (CS), which was initially a neutral event such as a light or a tone and does not create a response in any manner from the individual or individuals which are being tested. In these tests or instances the CR is paired with an ...
... Classical conditioning involves the presentation of a conditioned stimulus (CS), which was initially a neutral event such as a light or a tone and does not create a response in any manner from the individual or individuals which are being tested. In these tests or instances the CR is paired with an ...
Conditioned Learning
... a period of training in which it has been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. ...
... a period of training in which it has been paired with an unconditioned stimulus. ...
PSYC 305
... Concepts addressed: Learning, Motivation and Emotion: Classical conditioning: applications of classical conditioning, reinforcement, extinction spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Learning ...
... Concepts addressed: Learning, Motivation and Emotion: Classical conditioning: applications of classical conditioning, reinforcement, extinction spontaneous recovery, generalization, and discrimination. Learning ...
FREE Sample Here
... decides that he needs to eat something to keep up his strength, so he gets out of bed, puts on a heavy sweater to keep himself warm, heats up a bowl of leftover chili, and settles down in an easy chair to watch a television game show while he eats. A few days later, after Jacob has recovered from th ...
... decides that he needs to eat something to keep up his strength, so he gets out of bed, puts on a heavy sweater to keep himself warm, heats up a bowl of leftover chili, and settles down in an easy chair to watch a television game show while he eats. A few days later, after Jacob has recovered from th ...
PsychSim: Learning - Socialscientist.us
... How would you interpret these graphs? Did your subject show evidence of stimulus generalization, or stimulus discrimination, or both? Extinction Trials How would you interpret these results? Has the conditioned response been extinguished in your subject? What would happen if we continued immedia ...
... How would you interpret these graphs? Did your subject show evidence of stimulus generalization, or stimulus discrimination, or both? Extinction Trials How would you interpret these results? Has the conditioned response been extinguished in your subject? What would happen if we continued immedia ...
Print › AP Psychology
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
... stimulus in one conditioning experience is paired with a new neutral stimulus, creating a second (often weaker) conditioned stimulus. For example, an animal that has learned that a tone predicts food might then learn that a light predicts the tone and begin responding to the light alone. (Also calle ...
Classical conditioning

Classical conditioning (also known as Pavlovian or respondent conditioning) is a learning process in which an innate response to a potent stimulus comes to be elicited in response to a previously neutral stimulus; this is achieved by repeated pairings of the neutral stimulus with the potent stimulus. The basic facts about classical conditioning were discovered by Ivan Pavlov through his famous experiments with dogs. Together with operant conditioning, classical conditioning became the foundation of Behaviorism, a school of psychology that dominated psychology in the mid-20th century and is still an important influence on the practice of psychological therapy and the study of animal behaviour (ethology). Classical conditioning is now the best understood of the basic learning processes, and its neural substrates are beginning to be understood.