DOC - World bank documents
... Individuals have self-control and time inconsistency problems. They can give into shortrun temptations and later regret it. They can have strong feelings about others that drive them to commit both generous acts and spiteful ones. They often passively accept defaults, rather than making active choic ...
... Individuals have self-control and time inconsistency problems. They can give into shortrun temptations and later regret it. They can have strong feelings about others that drive them to commit both generous acts and spiteful ones. They often passively accept defaults, rather than making active choic ...
Evolution and Human Nature Arthur J. Robson The Journal of
... Another evolutionary argument bearing on impatience concerns whether, when other things are equal, an individual would prefer to have children earlier or later. Given that each individual has more than one offspring on average (so that positive population growth occurs), a faster rate of growth can ...
... Another evolutionary argument bearing on impatience concerns whether, when other things are equal, an individual would prefer to have children earlier or later. Given that each individual has more than one offspring on average (so that positive population growth occurs), a faster rate of growth can ...
Evolutionary rescue under environmental change?
... such as through phenotypic plasticity, maternal effects, or various other non-genetic phenotypic alterations (Bonduriansky and Day 2009; Pigluicci 2001, see also Chapter 11). Although these developmental changes (henceforth just ‘plasticity’) can be a particularly rapid way to recover fitness follow ...
... such as through phenotypic plasticity, maternal effects, or various other non-genetic phenotypic alterations (Bonduriansky and Day 2009; Pigluicci 2001, see also Chapter 11). Although these developmental changes (henceforth just ‘plasticity’) can be a particularly rapid way to recover fitness follow ...
Keverne et al (2001)
... from the paternal allele. Both male and female Peg1 offspring from normal mothers (i.e., inheriting the mutated allele from !/" fathers) are smaller and weigh less than wild-type littermates (i.e., inheriting the normal allele from fathers) (Lefebvre et al., 1998). Mutant embryos and placental weigh ...
... from the paternal allele. Both male and female Peg1 offspring from normal mothers (i.e., inheriting the mutated allele from !/" fathers) are smaller and weigh less than wild-type littermates (i.e., inheriting the normal allele from fathers) (Lefebvre et al., 1998). Mutant embryos and placental weigh ...
Second-order conditioning
... be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be ...
... be more firmly connected with the situation, so that, when it recurs, they will be more likely to recur; those which are accompanied or closely followed by discomfort to the animal will, other things being equal, have their connections to the situation weakened, so that, when it recurs, they will be ...
BEHAVIOUR MODIFICATION: Strategies for Everyday Use
... Owner opens gate Dog’s behaviour is (+) reinforced Owner’s behaviour is (-) reinforced ...
... Owner opens gate Dog’s behaviour is (+) reinforced Owner’s behaviour is (-) reinforced ...
Fisheries-induced evolution of maturation reaction norms
... consequences on the target species, but may also induce adaptive changes in their life history because fishing is by essence selective (Stokes et al. 1993, Palumbi 2001, Ashley et al. 2003 ). ∎ Adaptive changes can have two different origins (Rijnsdorp 1993, Law 2000): Phenotypic plasticity: most ...
... consequences on the target species, but may also induce adaptive changes in their life history because fishing is by essence selective (Stokes et al. 1993, Palumbi 2001, Ashley et al. 2003 ). ∎ Adaptive changes can have two different origins (Rijnsdorp 1993, Law 2000): Phenotypic plasticity: most ...
FIGURE 1-1 Figure text here.
... through congruent communication” approach, and Glasser’s “Cooperation through individual and group problem solving” approach. Gary D. Borich Effective Teaching Methods, 6e ...
... through congruent communication” approach, and Glasser’s “Cooperation through individual and group problem solving” approach. Gary D. Borich Effective Teaching Methods, 6e ...
Classical v. Operant Conditioning
... Classical Conditioning • The classical conditioning process is particularly important in understanding how we learn emotional behavior. – When we develop a new fear, for example, we learn to fear a stimulus that has been combined with some other frightening stimulus. – Studies of classical conditio ...
... Classical Conditioning • The classical conditioning process is particularly important in understanding how we learn emotional behavior. – When we develop a new fear, for example, we learn to fear a stimulus that has been combined with some other frightening stimulus. – Studies of classical conditio ...
slide show - Psycholosphere
... 3b. What is Attribution Theory Attribution theory is concerned with answering the question, “Why do people do what they do?” It is a theory concerned with how people formulate explanations about the causes of their own behavior and that of others. The causal explanations assume that behavior ...
... 3b. What is Attribution Theory Attribution theory is concerned with answering the question, “Why do people do what they do?” It is a theory concerned with how people formulate explanations about the causes of their own behavior and that of others. The causal explanations assume that behavior ...
Unit 6 Learning Classical Conditioning Please keep in mind that
... Primary Reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need (e.g., food or water). Secondary (or Conditioned) Reinforcer: a stimulus that gains it reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer (e.g., money). **Remember: Immediate reinforce ...
... Primary Reinforcer: an innately reinforcing stimulus, such as one that satisfies a biological need (e.g., food or water). Secondary (or Conditioned) Reinforcer: a stimulus that gains it reinforcing power through its association with a primary reinforcer (e.g., money). **Remember: Immediate reinforce ...
Psy 331.03 Advanced Laboratory in Operant Behavior
... Any cheating will not be tolerated. Cheating or plagiarism will result in an F in the course and referral to the Student Code Enforcement Review Board (SCERB) for disciplinary action. Cheating INCLUDES (but is not limited to): plagiarism of both published and unpublished written work, having another ...
... Any cheating will not be tolerated. Cheating or plagiarism will result in an F in the course and referral to the Student Code Enforcement Review Board (SCERB) for disciplinary action. Cheating INCLUDES (but is not limited to): plagiarism of both published and unpublished written work, having another ...
Exploring 9e - Forensic Consultation
... Discrimination: the ability to become more and more specific in what situations trigger a response. Shaping can increase discrimination, if reinforcement only comes for certain discriminative stimuli. For examples, dogs, rats, and even spiders can be trained to search for very specific smells, from ...
... Discrimination: the ability to become more and more specific in what situations trigger a response. Shaping can increase discrimination, if reinforcement only comes for certain discriminative stimuli. For examples, dogs, rats, and even spiders can be trained to search for very specific smells, from ...
How Evolution Works - The Teacher-Friendly Guide™ to Evolution
... give them an advantage within their environment; these individuals will survive to reproduce and pass on those traits to their offspring. 6. Genetic composition: In subsequent generations, there will be a higher percentage of individuals that possess advantageous traits. Therefore, the advantageous ...
... give them an advantage within their environment; these individuals will survive to reproduce and pass on those traits to their offspring. 6. Genetic composition: In subsequent generations, there will be a higher percentage of individuals that possess advantageous traits. Therefore, the advantageous ...
How Does Evolution Explain Blindness in Cavefish?
... drift. All too often textbooks use the terms “evolution” and “natural selection” interchangeably, ignoring the importance of genetic drift. Genetic drift is “the process of change in the genetic composition of a population due to chance or random events rather than to natural selection, resulting in ...
... drift. All too often textbooks use the terms “evolution” and “natural selection” interchangeably, ignoring the importance of genetic drift. Genetic drift is “the process of change in the genetic composition of a population due to chance or random events rather than to natural selection, resulting in ...
Learning Chapter (Myers Text) Presentation
... The term behaviorism was used by John B. Watson (1878‐1958), a proponent of classical conditioning, as well as by B.F. Skinner (1904‐1990), a leader in research about operant conditioning. Both scientists believed the mental life was much less important than behavior as a foundation for psy ...
... The term behaviorism was used by John B. Watson (1878‐1958), a proponent of classical conditioning, as well as by B.F. Skinner (1904‐1990), a leader in research about operant conditioning. Both scientists believed the mental life was much less important than behavior as a foundation for psy ...
No Slide Title
... – no food at end, their speed through the maze did not increase muchat all Group B: – food at end daily, they ran the maze a little faster each day Group C: (actually a sub-group of A) – no food till day 11, then they immediately ran the maze as fast as group B ...
... – no food at end, their speed through the maze did not increase muchat all Group B: – food at end daily, they ran the maze a little faster each day Group C: (actually a sub-group of A) – no food till day 11, then they immediately ran the maze as fast as group B ...
A “Sudden Appearance” model for the Evolution of Human
... the first stone tools that appeared in the record 500,000 years earlier (Tattersall, 1997). This suggests that although this early H. erectus population was larger in physical size and cranial capacity than H. habilis, it had not developed any increase in cognitive ability. Noble and Davidson (1997) ...
... the first stone tools that appeared in the record 500,000 years earlier (Tattersall, 1997). This suggests that although this early H. erectus population was larger in physical size and cranial capacity than H. habilis, it had not developed any increase in cognitive ability. Noble and Davidson (1997) ...
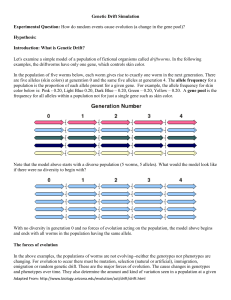
Genetic Drift Simulation Experimental Question: How do random
... In the above examples, the populations of worms are not evolving--neither the genotypes nor phenotypes are changing. For evolution to occur there must be mutation, selection (natural or artificial), immigration, emigration or random genetic drift. These are the major forces of evolution. The cause c ...
... In the above examples, the populations of worms are not evolving--neither the genotypes nor phenotypes are changing. For evolution to occur there must be mutation, selection (natural or artificial), immigration, emigration or random genetic drift. These are the major forces of evolution. The cause c ...
Evolution on purpose: how behaviour has shaped the evolutionary
... although he did recognize Lamarck’s role in championing the then unpopular view that life on Earth had gradually evolved. Lamarck is best-known, even infamous, for his thesis that the course of evolution has also been shaped by ‘habits acquired by conditions’ (i.e. the direct inheritance of traits d ...
... although he did recognize Lamarck’s role in championing the then unpopular view that life on Earth had gradually evolved. Lamarck is best-known, even infamous, for his thesis that the course of evolution has also been shaped by ‘habits acquired by conditions’ (i.e. the direct inheritance of traits d ...
quantity or quality of the reinforcer
... Degree response variability along three dimensions of drawing a rectangle (size, shape, and location) for human participants who were reinforced for varying the type of rectangles they drew (VARY) or received reinforcement on the same trials but without any requirement to vary the nature of their dr ...
... Degree response variability along three dimensions of drawing a rectangle (size, shape, and location) for human participants who were reinforced for varying the type of rectangles they drew (VARY) or received reinforcement on the same trials but without any requirement to vary the nature of their dr ...
AP Ch. 5 Operant
... • Spanking is a common form of discipline used in the U.S. – Some researchers believe that mild and effective spanking is not necessarily harmful. – Other research demonstrates that physical punishment is associated with increased child aggressiveness, delinquency, and antisocial behavior. Additiona ...
... • Spanking is a common form of discipline used in the U.S. – Some researchers believe that mild and effective spanking is not necessarily harmful. – Other research demonstrates that physical punishment is associated with increased child aggressiveness, delinquency, and antisocial behavior. Additiona ...
Operant Conditioning - PV
... followed by reinforcement or occurs less frequently if followed by punishment. ...
... followed by reinforcement or occurs less frequently if followed by punishment. ...
The Social Cognitive Approach (AKA Social Learning Theory)
... Attention of any kind reinforces childrens behavior Boys encouraged to be aggressive, loud, boisterous Girls- encouraged to be- submissive dependent, passive Problem when parents are rejecting, punishing, sarcastic, humiliating, neglectful, their children, become hostileHostile personality causes- ...
... Attention of any kind reinforces childrens behavior Boys encouraged to be aggressive, loud, boisterous Girls- encouraged to be- submissive dependent, passive Problem when parents are rejecting, punishing, sarcastic, humiliating, neglectful, their children, become hostileHostile personality causes- ...