Chapter 22 Powerpoint
... probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals. ...
... probability of surviving and reproducing in a given environment tend to leave more offspring than other individuals. ...
Evolution and Natural Selection PowerPoint
... that survive will pass on their traits. Natural selection occurs through “Survival of the fittest” Fitness: the ability to survive and reproduce Not all individuals survive to adulthood ...
... that survive will pass on their traits. Natural selection occurs through “Survival of the fittest” Fitness: the ability to survive and reproduce Not all individuals survive to adulthood ...
Theories of Evolution - Mr. Schultz Biology Page
... generations and can therefore be detected in living populations. ...
... generations and can therefore be detected in living populations. ...
Final Exam
... A multiple choice test may bring out knowledge you might not be able to show on an essay test due to the process of ...
... A multiple choice test may bring out knowledge you might not be able to show on an essay test due to the process of ...
Are the fit the survivors? How does the environment cause
... produce more offspring than a stronger, dull male. The tiny bird has higher evolutionary fitness than their stronger, larger counterpart. ...
... produce more offspring than a stronger, dull male. The tiny bird has higher evolutionary fitness than their stronger, larger counterpart. ...
Darwin`s Last Laugh
... that there is “no fundamental difference between man and the higher mammals in their neural substrate seems to be involved3. Similarly, mental faculties”. Attempts to identify human- bonobos, golden monkeys and a variety of social like cognition in other animals has invariably mammals kiss, embrace, ...
... that there is “no fundamental difference between man and the higher mammals in their neural substrate seems to be involved3. Similarly, mental faculties”. Attempts to identify human- bonobos, golden monkeys and a variety of social like cognition in other animals has invariably mammals kiss, embrace, ...
Homologous structures
... Science aims to understand the natural world through observation and reasoning. Science begins with observations, therefore, much of science is purely descriptive. Science uses both deductive and inductive ...
... Science aims to understand the natural world through observation and reasoning. Science begins with observations, therefore, much of science is purely descriptive. Science uses both deductive and inductive ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... 3. Selection= traits that allow organisms to survive are “selected” for and will become more common in the next generations of offspring 4. Adaptation= an inherited trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment ...
... 3. Selection= traits that allow organisms to survive are “selected” for and will become more common in the next generations of offspring 4. Adaptation= an inherited trait that helps an organism survive and reproduce in its environment ...
Chpt. 15.1- Darwin`s Theory of Evolution by Natural Selection
... or act like another animal to fool predators into thinking it is poisonous or dangerous. ...
... or act like another animal to fool predators into thinking it is poisonous or dangerous. ...
Unit 7 Test with answers
... environment to hide from predators they are more likely to survive and reproduce. 20. How does mimicry help increase an organism’s chance of survival? If an organism can mimic another organism to keep predators away, it’s more likely to survive and reproduce. 21. When you are sick with a bacterial i ...
... environment to hide from predators they are more likely to survive and reproduce. 20. How does mimicry help increase an organism’s chance of survival? If an organism can mimic another organism to keep predators away, it’s more likely to survive and reproduce. 21. When you are sick with a bacterial i ...
Assessing how ecology influences evolutionary transitions to
... individuals and species interact. For example, complex social interactions are unlikely to evolve in species where ecological pressures promote a solitary existence. Simillarly, when food resources are abundant there is little to be gained by coordinated foraging efforts (e.g., hunting in packs) amo ...
... individuals and species interact. For example, complex social interactions are unlikely to evolve in species where ecological pressures promote a solitary existence. Simillarly, when food resources are abundant there is little to be gained by coordinated foraging efforts (e.g., hunting in packs) amo ...
Wilson_1975_Wilson_1975_Sociobiology The Abridged Edition, p
... members of the society. Some authors make a distinction between socialization, regarded as the development of social behavior basic to every normal human being, and enculturation, the act of learning one culture in all its uniqueness and particularity (see for example Mead, 1963). However, in this w ...
... members of the society. Some authors make a distinction between socialization, regarded as the development of social behavior basic to every normal human being, and enculturation, the act of learning one culture in all its uniqueness and particularity (see for example Mead, 1963). However, in this w ...
Evolution Notes
... – Need traits that will help them survive • predators • disease • competition for food • competition for territory – Traits that help individuals reproduce • so they can attract a mate • compete for nesting sites • successfully raise young ...
... – Need traits that will help them survive • predators • disease • competition for food • competition for territory – Traits that help individuals reproduce • so they can attract a mate • compete for nesting sites • successfully raise young ...
Unit Plan Template
... cause an allele to become more or less common in a population. The Hardy-Weinberg principle predicts that five conditions can disturb genetic equilibrium and cause evolution to occur: (1) nonrandom mating, (2) small population size, (3) immigration or emigration, (4) mutations, or (5) natural selec ...
... cause an allele to become more or less common in a population. The Hardy-Weinberg principle predicts that five conditions can disturb genetic equilibrium and cause evolution to occur: (1) nonrandom mating, (2) small population size, (3) immigration or emigration, (4) mutations, or (5) natural selec ...
Name Crash Course-Psychology #11
... Crash Course-Psychology #11-How to Train a Brain Directions: As you view/listen to the crash course video, listen for information to complete each of the following statements. 1) For scholars of psychology, we can define _______________________________ as the process of acquiring, through experience ...
... Crash Course-Psychology #11-How to Train a Brain Directions: As you view/listen to the crash course video, listen for information to complete each of the following statements. 1) For scholars of psychology, we can define _______________________________ as the process of acquiring, through experience ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. Since the 1960s, Americans have
... A) genes; home environment B) home environment; genes C) genes; peer influence D) home environments; peer influence ...
... A) genes; home environment B) home environment; genes C) genes; peer influence D) home environments; peer influence ...
Theories of Evolution
... When individual organisms move in or out of a population their genes go with them! ...
... When individual organisms move in or out of a population their genes go with them! ...
Animal Behavior Final Review Sheet
... Classify the following. Identify the type of aggression. 22) At a major corporation, everyone knows his or her place and to whom he or she must always be respectful as well as whom he or she can boss around. A person who errs is severely reprimanded. ...
... Classify the following. Identify the type of aggression. 22) At a major corporation, everyone knows his or her place and to whom he or she must always be respectful as well as whom he or she can boss around. A person who errs is severely reprimanded. ...
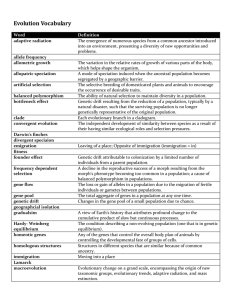
Evolution Vocabulary
... A special case of polymorphism based on the distinction between the secondary sex characteristics of males and females. An evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade. A homology common to a taxon more inclusive than the one being defined. Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by ...
... A special case of polymorphism based on the distinction between the secondary sex characteristics of males and females. An evolutionary novelty unique to a particular clade. A homology common to a taxon more inclusive than the one being defined. Natural selection that favors intermediate variants by ...
Theory of Evolution
... Individuals that have physical or behavioral traits that better suite their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
... Individuals that have physical or behavioral traits that better suite their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce. ...
File
... Why did the population of killer whales off the coast of South Africa retain it’s genetic ...
... Why did the population of killer whales off the coast of South Africa retain it’s genetic ...
evidence for evolution
... 3. Analogous Features(not a piece of evidence for evolution): serve similar function and they look similar, but the organisms don’t share a common ancestor ex. Wings in insects and birds ...
... 3. Analogous Features(not a piece of evidence for evolution): serve similar function and they look similar, but the organisms don’t share a common ancestor ex. Wings in insects and birds ...
Natural Selection - Teacher **DRAFT
... exists in a population. Natural selection leads to evolutionary adaptions in organisms—heritable traits that confer an advantage in the current environment. This advantage is increased genetic fitness—how productive a particular genotype is in a population, i.e., the number of offspring with that ge ...
... exists in a population. Natural selection leads to evolutionary adaptions in organisms—heritable traits that confer an advantage in the current environment. This advantage is increased genetic fitness—how productive a particular genotype is in a population, i.e., the number of offspring with that ge ...