Chapter 9: Learning: Principles and Applications
... John Garcia and R.A. Koelling (1966) first demonstrated this phenomenon with rats. The animals were placed in a cage with a tube containing flavored water. Whenever a rat took a drink, lights flashed and clicks sounded. Then, some of the rats were given an electric shock after they drank. All these ...
... John Garcia and R.A. Koelling (1966) first demonstrated this phenomenon with rats. The animals were placed in a cage with a tube containing flavored water. Whenever a rat took a drink, lights flashed and clicks sounded. Then, some of the rats were given an electric shock after they drank. All these ...
Operant Conditioning
... psychology should instead study how organisms respond to stimuli in their environments, said Watson. 41 lts theoretical goal is the prediction and control of behavior. Introspection forms no essential part of its methods." Simply said, psychology should be an objective science based on observable be ...
... psychology should instead study how organisms respond to stimuli in their environments, said Watson. 41 lts theoretical goal is the prediction and control of behavior. Introspection forms no essential part of its methods." Simply said, psychology should be an objective science based on observable be ...
LEARNING
... Schedules of reinforcement 1. Continuous reinforcement – correct response is reinforced every time it is given 2. Partial reinforcement – when only some responses are reinforced a)Fixed interval schedule – reinforcement delivered after a fixed time (10 seconds) b)Fixed ratio schedule - reinforcement ...
... Schedules of reinforcement 1. Continuous reinforcement – correct response is reinforced every time it is given 2. Partial reinforcement – when only some responses are reinforced a)Fixed interval schedule – reinforcement delivered after a fixed time (10 seconds) b)Fixed ratio schedule - reinforcement ...
Intro to Psychological Disorders
... trained nurses for the mentally ill and helped to change public attitudes regarding their treatment. 3. In the United States, Benjamin Rush (17451813), the founder of American psychiatry, encouraged humane treatment of the mentally ill and the establishment of hospitals for their care. ...
... trained nurses for the mentally ill and helped to change public attitudes regarding their treatment. 3. In the United States, Benjamin Rush (17451813), the founder of American psychiatry, encouraged humane treatment of the mentally ill and the establishment of hospitals for their care. ...
Ability - WordPress.com
... other way, moving from specific observations to broader generalizations and theories. Informally, we sometimes call this a "bottom up" approach (please note that it's "bottom up" and not "bottoms up" which is the kind of thing the bartender says to customers when he's trying to close for the night!) ...
... other way, moving from specific observations to broader generalizations and theories. Informally, we sometimes call this a "bottom up" approach (please note that it's "bottom up" and not "bottoms up" which is the kind of thing the bartender says to customers when he's trying to close for the night!) ...
Classical Conditioning - District 196 e
... Learning) ► Observational Learning ► Latent Learning ...
... Learning) ► Observational Learning ► Latent Learning ...
OpenStax_Psychology_CH01_use this onefall2016
... Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. (credit "background": modification of work by Nattachai Noogure; credit "top left": modification of work by U.S. Navy; credit "top middle-left": modification of work by Peter Shanks; credit "top middle-right": modification of work by "devinf"/ ...
... Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. (credit "background": modification of work by Nattachai Noogure; credit "top left": modification of work by U.S. Navy; credit "top middle-left": modification of work by Peter Shanks; credit "top middle-right": modification of work by "devinf"/ ...
n e w s a n d ...
... each can inform and motivate future directions in motor control. In psychology, reward and punishment have long been recognized as instrumental for learning. As early as 1898, Edward Thorndike’s law of effect stated that if a response leads to a “satisfying state of affairs” it will be strengthened ...
... each can inform and motivate future directions in motor control. In psychology, reward and punishment have long been recognized as instrumental for learning. As early as 1898, Edward Thorndike’s law of effect stated that if a response leads to a “satisfying state of affairs” it will be strengthened ...
here
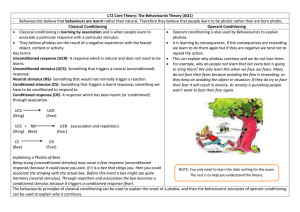
... - Behaviourists believe that behaviours are learnt rather than natural. Therefore they believe that people learn to be phobic rather than are born phobic. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Classical conditioning is learning by association and is when people learn to Operant conditionin ...
... - Behaviourists believe that behaviours are learnt rather than natural. Therefore they believe that people learn to be phobic rather than are born phobic. Classical Conditioning Operant Conditioning Classical conditioning is learning by association and is when people learn to Operant conditionin ...
GCSE Psychology Learning - Greenacre Academy Trust
... In Skinners box the rat would sometimes explore its environment and push a button. This button would cause an electric shock from the floor. What do you think happened? .... the rat learned very quickly not to do that again! Punishment should not be confused with negative reinforcement – it is quite ...
... In Skinners box the rat would sometimes explore its environment and push a button. This button would cause an electric shock from the floor. What do you think happened? .... the rat learned very quickly not to do that again! Punishment should not be confused with negative reinforcement – it is quite ...
phe1idh notes - Amazon Web Services
... → Response cost – involves the removal of a positive event after a response that decreases the probability of the behaviour occurring again → Something good is taken away → Everyday Example: use of fines for speeding, withdrawal of affection when child throws tantrum → Health Related Example: certai ...
... → Response cost – involves the removal of a positive event after a response that decreases the probability of the behaviour occurring again → Something good is taken away → Everyday Example: use of fines for speeding, withdrawal of affection when child throws tantrum → Health Related Example: certai ...
LT2Ch4c
... More crowded classes and higher student-to-faculty ratios (harder to see your advisor) Cuts in services ...
... More crowded classes and higher student-to-faculty ratios (harder to see your advisor) Cuts in services ...
Chapter 6: Motivating Effectively
... because of company policy or threat of reprisal. • Punishment may engender resentment. • Punishment may lead to revenge and retaliation. • Punishment leads to adherence only when the person administering the punishment is present or monitoring • Others may misinterpret the reasons for punishment. • ...
... because of company policy or threat of reprisal. • Punishment may engender resentment. • Punishment may lead to revenge and retaliation. • Punishment leads to adherence only when the person administering the punishment is present or monitoring • Others may misinterpret the reasons for punishment. • ...
Introducing Psychology
... • Very controversial ideas • “Psychoanalytic theory” – Theory explaining personality, motives and disorders via “dynamic unconscious processes” ...
... • Very controversial ideas • “Psychoanalytic theory” – Theory explaining personality, motives and disorders via “dynamic unconscious processes” ...
האוניברסיטה העברית בירושלי - Center for the Study of Rationality
... recency [10] and primacy [2]. Moreover, model-free RL has been proven useful in the field of computational psychiatry as a way of diagnosing and characterizing different pathologies [11–14]. However, there is also evidence that the correspondence between dopaminergic neurons and the RPE is more comp ...
... recency [10] and primacy [2]. Moreover, model-free RL has been proven useful in the field of computational psychiatry as a way of diagnosing and characterizing different pathologies [11–14]. However, there is also evidence that the correspondence between dopaminergic neurons and the RPE is more comp ...
Canine Learning - Session 3
... A secondary reinforcer is paired to a primary and starts to become as reinforcing as a primary. A primary reinforcer must always follow a ...
... A secondary reinforcer is paired to a primary and starts to become as reinforcing as a primary. A primary reinforcer must always follow a ...
Artificial Consciousness
... itself or upon observing others with the same behavior Primary representation equivalent to mirror neuron ...
... itself or upon observing others with the same behavior Primary representation equivalent to mirror neuron ...
GCSE Psychology Learning
... In Skinners box the rat would sometimes explore its environment and push a button. This button would cause an electric shock from the floor. What do you think happened? .... the rat learned very quickly not to do that again! Punishment should not be confused with negative reinforcement – it is qu ...
... In Skinners box the rat would sometimes explore its environment and push a button. This button would cause an electric shock from the floor. What do you think happened? .... the rat learned very quickly not to do that again! Punishment should not be confused with negative reinforcement – it is qu ...
Learning Theory and Development of Social
... theorists are firmly in the nurture camp. They believe that people are not born with certain capabilities (apart from basic reflexes), they have to learn everything. Bandura (1977) says "Except for elementary reflexes, people are not equipped with inborn repertoires of behaviour. They must learn the ...
... theorists are firmly in the nurture camp. They believe that people are not born with certain capabilities (apart from basic reflexes), they have to learn everything. Bandura (1977) says "Except for elementary reflexes, people are not equipped with inborn repertoires of behaviour. They must learn the ...
Number 3 • April 1997 - Institute for Applied Behavior Analysis
... Desmond’s communication problems had led to a degree of social isolation in class. In his attempts to gain peer approval and acceptance Desmond was beginning to copy the disruptive behavior of other children. The teacher’s attempts to manage him at these times ran the risk of further treatment and f ...
... Desmond’s communication problems had led to a degree of social isolation in class. In his attempts to gain peer approval and acceptance Desmond was beginning to copy the disruptive behavior of other children. The teacher’s attempts to manage him at these times ran the risk of further treatment and f ...
a PowerPoint presentation of Module 52
... Sometimes, insight is not helpful to recover from some mental health problems. The client might know the right changes to make, but finds that it’s hard to change actual behavior. Behavior therapy uses the principles of learning, especially classical and operant conditioning, to help reduce unwa ...
... Sometimes, insight is not helpful to recover from some mental health problems. The client might know the right changes to make, but finds that it’s hard to change actual behavior. Behavior therapy uses the principles of learning, especially classical and operant conditioning, to help reduce unwa ...
Pavlov`s Methodological Behaviorism as a Pre
... The differential/experimental distinction that Cronbach specified is important because any adequate account of psychological phenomena requires the recognition of the validity of both approaches, and a meaningful melding of the two. This paper suggests that Pavlov’s work in psychology, based on earl ...
... The differential/experimental distinction that Cronbach specified is important because any adequate account of psychological phenomena requires the recognition of the validity of both approaches, and a meaningful melding of the two. This paper suggests that Pavlov’s work in psychology, based on earl ...
Chapter 1: Introduction and Research Methods I. Introduction: The
... Howard University, which produced more black psychologists than all other American colleges and universities combined. One of his students, Kenneth Bancroft Clark, played an instrumental role in the U.S. Supreme Court’s 1954 decision to end segregated schools. Clark became the first black president ...
... Howard University, which produced more black psychologists than all other American colleges and universities combined. One of his students, Kenneth Bancroft Clark, played an instrumental role in the U.S. Supreme Court’s 1954 decision to end segregated schools. Clark became the first black president ...
Pavlov`s Methodological Behaviorism as a Pre
... The differential/experimental distinction that Cronbach specified is important because any adequate account of psychological phenomena requires the recognition of the validity of both approaches, and a meaningful melding of the two. This paper suggests that Pavlov's work in psychology, based on earl ...
... The differential/experimental distinction that Cronbach specified is important because any adequate account of psychological phenomena requires the recognition of the validity of both approaches, and a meaningful melding of the two. This paper suggests that Pavlov's work in psychology, based on earl ...
PSY402 Theories of Learning
... Discrimination phase -- with training, response to SD increases and response to SΔ declines. Shift back to non-differential reinforcement to show that behavior was caused by reinforcement. ...
... Discrimination phase -- with training, response to SD increases and response to SΔ declines. Shift back to non-differential reinforcement to show that behavior was caused by reinforcement. ...