document1004
... action into the conceptual framework. Thus theory of functional systems, firstly, included the isomorphic system-creating factor into the conceptual apparatus of systemic approach, and, secondly, it radically changed the understanding of the causation of behavior. According to the classic interpreta ...
... action into the conceptual framework. Thus theory of functional systems, firstly, included the isomorphic system-creating factor into the conceptual apparatus of systemic approach, and, secondly, it radically changed the understanding of the causation of behavior. According to the classic interpreta ...
The Influence of Social Norms in Consumer Behavior
... more importantly, an injunctive specification of a norm leads to stronger effects on attitudes but weaker effects on behavior than a descriptive formulation. This implies that an investigation of the effect of social norms which examines only attitudes or only behavior does not provide a complete pi ...
... more importantly, an injunctive specification of a norm leads to stronger effects on attitudes but weaker effects on behavior than a descriptive formulation. This implies that an investigation of the effect of social norms which examines only attitudes or only behavior does not provide a complete pi ...
Neurobiology of Learning and Memory
... 3. Assume that any US can only support a limited amount of conditioning/reinforcement 4. All the CSs compete with echother for the limited amount of conditioning/reinforcement 5. Competition occurs through summation of all the CSs present on a given trial •The US has a certain amount it can conditio ...
... 3. Assume that any US can only support a limited amount of conditioning/reinforcement 4. All the CSs compete with echother for the limited amount of conditioning/reinforcement 5. Competition occurs through summation of all the CSs present on a given trial •The US has a certain amount it can conditio ...
ORGANISATIONAL BEHAVIOUR
... Taylor held that the technique of determining work standards, delimiting wasteful operations and differential piece rate system of wage payment should benefit the worker in form of higher wage payment and the employer in form of higher production and this would result to a “mental revolution” betwee ...
... Taylor held that the technique of determining work standards, delimiting wasteful operations and differential piece rate system of wage payment should benefit the worker in form of higher wage payment and the employer in form of higher production and this would result to a “mental revolution” betwee ...
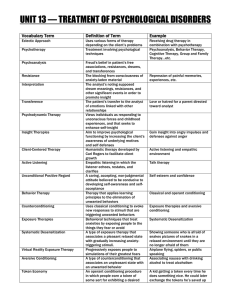
unit 13 — treatment of psychological disorders
... Teaches people new, more adaptive ways of thinking or acting. Integrated therapy that combines cognitive therapy with behavior therapy Treats family as a system; views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by, or directed at, other family members The tendency for extremes of unusual score ...
... Teaches people new, more adaptive ways of thinking or acting. Integrated therapy that combines cognitive therapy with behavior therapy Treats family as a system; views an individual’s unwanted behaviors as influenced by, or directed at, other family members The tendency for extremes of unusual score ...
Chapter 6: Learning - Doral Academy Preparatory
... Q1. A group of ranchers attempts to discourage coyotes from attacking their sheep by placing a substance on the wool of the sheep that makes coyotes violently ill if they eat it.Very quickly, the coyotes avoid the sheep entirely. In this scenario, what are the UCS, CS, and CR, respectively? (A) The ...
... Q1. A group of ranchers attempts to discourage coyotes from attacking their sheep by placing a substance on the wool of the sheep that makes coyotes violently ill if they eat it.Very quickly, the coyotes avoid the sheep entirely. In this scenario, what are the UCS, CS, and CR, respectively? (A) The ...
slide show - Psycholosphere
... “There is a secret tie or union among particular ideas, which causes the mind to conjoin them more frequently together, and makes the one, upon its appearance, introduce the other.” Hume, David (1739). Treatise of Human Nature. Edited by L. A. Selby-Bigge, 2nd Ed.by P.H. Nidditch, Oxford: Clarendon ...
... “There is a secret tie or union among particular ideas, which causes the mind to conjoin them more frequently together, and makes the one, upon its appearance, introduce the other.” Hume, David (1739). Treatise of Human Nature. Edited by L. A. Selby-Bigge, 2nd Ed.by P.H. Nidditch, Oxford: Clarendon ...
Learning
... Pavlov’s Discovery • A conditioned stimulus (CS) – A neutral stimulus (an event) that comes to evoke a classically conditioned (learned) response due to being presented shortly before the US. • In Pavlov’s experiments, the CS was the bell. ...
... Pavlov’s Discovery • A conditioned stimulus (CS) – A neutral stimulus (an event) that comes to evoke a classically conditioned (learned) response due to being presented shortly before the US. • In Pavlov’s experiments, the CS was the bell. ...
Perspectives on Learning
... immediate feedback, and reinforcement, programmed learning can be very effective. (Entwistle, 1994) 2 types: linear model and branched model ...
... immediate feedback, and reinforcement, programmed learning can be very effective. (Entwistle, 1994) 2 types: linear model and branched model ...
PSYC 305
... recovery, generalization, and discrimination The process by which a previously neutral stimulus acquires the capacity to elicit a response through association with a stimulus that already elicits a similar or related response. The response is termed a reflex or a respondent. Development of this revi ...
... recovery, generalization, and discrimination The process by which a previously neutral stimulus acquires the capacity to elicit a response through association with a stimulus that already elicits a similar or related response. The response is termed a reflex or a respondent. Development of this revi ...
VR-DIS
... Agents are computational systems that inhibit some complex dynamic environment, sense and act autonomously in this environment, and by doing so realize a set of goals or tasks for which they are designed (Maes). ...
... Agents are computational systems that inhibit some complex dynamic environment, sense and act autonomously in this environment, and by doing so realize a set of goals or tasks for which they are designed (Maes). ...
PSYC 101 - Study Guide for Mid Term
... A lot of the first "real" scientific Psychology was done in learning Problem Statement Learning cannot be observed directly, but must be inferred that it has occured Draw inference from changes in observable behavior or in measurable capabilities and attitudes Learning does not always result in an o ...
... A lot of the first "real" scientific Psychology was done in learning Problem Statement Learning cannot be observed directly, but must be inferred that it has occured Draw inference from changes in observable behavior or in measurable capabilities and attitudes Learning does not always result in an o ...
Learning
... •Are there different ways to learn? •Why are Pavlov’s dogs so famous? •What is classical conditioning? •Who is Baby Albert? ...
... •Are there different ways to learn? •Why are Pavlov’s dogs so famous? •What is classical conditioning? •Who is Baby Albert? ...
Psychology 10th Edition David Myers
... Sometimes, insight is not helpful to recover from some mental health problems. The client might know the right changes to make, but finds that it’s hard to change actual behavior. Behavior therapy uses the principles of learning, especially classical and operant conditioning, to help reduce unwa ...
... Sometimes, insight is not helpful to recover from some mental health problems. The client might know the right changes to make, but finds that it’s hard to change actual behavior. Behavior therapy uses the principles of learning, especially classical and operant conditioning, to help reduce unwa ...
Chapter 7
... Good job of describing how teachers give rewards and take away rewards to modify behavior Critics argue places too much emphasis on external control of behavior Critics also point out potential ethical problems exist when used inappropriately ...
... Good job of describing how teachers give rewards and take away rewards to modify behavior Critics argue places too much emphasis on external control of behavior Critics also point out potential ethical problems exist when used inappropriately ...
Ethan Frome
... deliberately to weaken the undesirable high error rate behavior when it occurs. Not also, however, that extinction is used inadvertently to weaken the desirable low error rate behavior. Finally, these strategies may be used in combination as well as independently. D. Reinforcement Perspectives: Usag ...
... deliberately to weaken the undesirable high error rate behavior when it occurs. Not also, however, that extinction is used inadvertently to weaken the desirable low error rate behavior. Finally, these strategies may be used in combination as well as independently. D. Reinforcement Perspectives: Usag ...
variable-ratio schedule
... sound, we also tend to jump away from the water spray to avoid being scalded.) ...
... sound, we also tend to jump away from the water spray to avoid being scalded.) ...
A November, 2003 paper on the Pavlovian roots of the approach
... differential and experimental psychological methods to investigate psychological functions.. ...
... differential and experimental psychological methods to investigate psychological functions.. ...
L1 L2 THE CRITICAL PERIOD HYPOTHESIS
... * experiments: smells of food (unconditioned response) sound of bell (neutral stimulus) [repeated stimulus] response (conditioned response: salivation at the sound of the bell) √John B. Watson (1913) + John Locke 1) Human behavior should be studied objectively. 2) No mentalistic notions of inna ...
... * experiments: smells of food (unconditioned response) sound of bell (neutral stimulus) [repeated stimulus] response (conditioned response: salivation at the sound of the bell) √John B. Watson (1913) + John Locke 1) Human behavior should be studied objectively. 2) No mentalistic notions of inna ...
131 Psychology: Does Our Heterogeneous Subject Matter Have Any
... thinks, for instance, of Dollard's Criteria for the Life History (1935), Thurstone's The Vectors of Mind (1935), Miller and Dollard's Social Learning and Imitation (1941), Allport's Personality: A Psychological Interpretation (1937), Murray's Explorations in Personality (1938), Dollard, Doob, Miller ...
... thinks, for instance, of Dollard's Criteria for the Life History (1935), Thurstone's The Vectors of Mind (1935), Miller and Dollard's Social Learning and Imitation (1941), Allport's Personality: A Psychological Interpretation (1937), Murray's Explorations in Personality (1938), Dollard, Doob, Miller ...
LEARNING THEORIES BEHAVIORISM, COGNITIVISM
... • Suggests students learn best as passive receivers of sensory stimuli, as opposed to being active learners • Emotions and motivation not considered important or connected to ...
... • Suggests students learn best as passive receivers of sensory stimuli, as opposed to being active learners • Emotions and motivation not considered important or connected to ...
West Virginia University
... I have concluded that every natural science training program should include a course in comparative analytical epistemology. Different paradigms would be examined for their functional contributions to classes of outcomes deemed important within the communities in which those paradigms respectively p ...
... I have concluded that every natural science training program should include a course in comparative analytical epistemology. Different paradigms would be examined for their functional contributions to classes of outcomes deemed important within the communities in which those paradigms respectively p ...
behaviourist-assumptions-worksheet-nm
... through classical conditioning. This is based on the principle of association. Pavlov showed (through his research with dogs) that if two stimuli are presented at the same time (e.g. food and the sound of a bell) and this happens repeatedly, then they become associated with each other. Through this ...
... through classical conditioning. This is based on the principle of association. Pavlov showed (through his research with dogs) that if two stimuli are presented at the same time (e.g. food and the sound of a bell) and this happens repeatedly, then they become associated with each other. Through this ...
Approach 1: The Behaviourist Approach: Assumptions of the
... through classical conditioning. This is based on the principle of association. Pavlov showed (through his research with dogs) that if two stimuli are presented at the same time (e.g. food and the sound of a bell) and this happens repeatedly, then they become associated with each other. Through this ...
... through classical conditioning. This is based on the principle of association. Pavlov showed (through his research with dogs) that if two stimuli are presented at the same time (e.g. food and the sound of a bell) and this happens repeatedly, then they become associated with each other. Through this ...