L6 Proteins of cereals and legumes - e
... bonds. A minor component of gliadins. Gliadins may associate with one another or with glutenins through hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds. ...
... bonds. A minor component of gliadins. Gliadins may associate with one another or with glutenins through hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonds. ...
Metabolism Fact Sheet - Barth Syndrome Foundation
... production. Summarizing: a gene named TAZ encodes a protein called tafazzin that probably functions as an enzyme to help make mature cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is made first with one kind of fatty acids attached to it which are mostly saturated, then the original fatty acids are removed and other fatt ...
... production. Summarizing: a gene named TAZ encodes a protein called tafazzin that probably functions as an enzyme to help make mature cardiolipin. Cardiolipin is made first with one kind of fatty acids attached to it which are mostly saturated, then the original fatty acids are removed and other fatt ...
ppt-4-dna-proteins-binding-and-ligands
... TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS • Transcription factors (TFs) are molecules involved in regulating gene expression. • They are usually proteins, (they can be short, non-coding RNA). ...
... TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS • Transcription factors (TFs) are molecules involved in regulating gene expression. • They are usually proteins, (they can be short, non-coding RNA). ...
Cheng BY 123 Raut – Mock Exam Unit I 09/21/14 1. Which of the
... dehydration reactions; Barney states that because fats are not polymers, they do not require dehydration reactions. Which of the following is true? A) ester linkages are formed through dehydration B) no dehydration reactions occur C) double bonds in fatty acid tails inhibit glycerol’s ability to per ...
... dehydration reactions; Barney states that because fats are not polymers, they do not require dehydration reactions. Which of the following is true? A) ester linkages are formed through dehydration B) no dehydration reactions occur C) double bonds in fatty acid tails inhibit glycerol’s ability to per ...
Experiment 9: The Widely Varying Colors of d
... examples of all of these throughout the term. Sometimes a color change can be subtle and you need instrumentation to notice what is happening (e.g., myoglobin vs. reduced myoglobin). You have now done two experiments using the UV-Vis spectrophotometer and today you will use it again to try and deter ...
... examples of all of these throughout the term. Sometimes a color change can be subtle and you need instrumentation to notice what is happening (e.g., myoglobin vs. reduced myoglobin). You have now done two experiments using the UV-Vis spectrophotometer and today you will use it again to try and deter ...
Chemistry of Life: The Four Macromolecules
... cell processes (act as enzymes) • forming cellular structures • transporting substances into or out of cells • and helping to fight disease. ...
... cell processes (act as enzymes) • forming cellular structures • transporting substances into or out of cells • and helping to fight disease. ...
C8eBookCh05LegendsTables Щ Figure 5.1 Why do scientists study
... held together by hydrogen bonding between every fourth amino acid, shown above. Although transthyretin has only one helix region (see tertiary structure), other globular proteins have multiple stretches of helix separated by nonhelical regions. Some fibrous proteins, such as -keratin, the struc ...
... held together by hydrogen bonding between every fourth amino acid, shown above. Although transthyretin has only one helix region (see tertiary structure), other globular proteins have multiple stretches of helix separated by nonhelical regions. Some fibrous proteins, such as -keratin, the struc ...
Carbon and Macromolecules
... • Proteins are present in the cells in large amounts; they may determine cellular size, shape, and function. • DNA stores in its genes the information to make all the proteins an organism requires for living • A protein is a stretch of an assortment of 20 different amino acids (aa) joined together b ...
... • Proteins are present in the cells in large amounts; they may determine cellular size, shape, and function. • DNA stores in its genes the information to make all the proteins an organism requires for living • A protein is a stretch of an assortment of 20 different amino acids (aa) joined together b ...
DNA
... – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...
... – The junk (parts of the DNA that are noncoding regions) called introns need to be cut out. – Exons (coding regions) are then stuck together. This is the correct concise message. ...
Chapter 5 – Homework
... ½ pt – All are made by the same reaction, dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction. 2. Identify what function group monosaccharides have in abundance. Describe what properties this functional group give these molecules. 1 pt total ½ pt – they have multiple hydroxyl groups ½ pt – the molecules ...
... ½ pt – All are made by the same reaction, dehydration synthesis or condensation reaction. 2. Identify what function group monosaccharides have in abundance. Describe what properties this functional group give these molecules. 1 pt total ½ pt – they have multiple hydroxyl groups ½ pt – the molecules ...
Project Abstract (150 words max): Scientific Inquiry: The protein
... structure of a cell. Mutations associated within the Ig4 domain of palladin have been observed in pancreatic cancer. In the hydrophobic core of the mutated Ig4 domain the amino acid tryptophan has been replaced with the amino acid cysteine, and we hypothesize that the mutation will affect the struct ...
... structure of a cell. Mutations associated within the Ig4 domain of palladin have been observed in pancreatic cancer. In the hydrophobic core of the mutated Ig4 domain the amino acid tryptophan has been replaced with the amino acid cysteine, and we hypothesize that the mutation will affect the struct ...
Advanced Higher Cells and Proteins
... TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS • Transcription factors (TFs) are molecules involved in regulating gene expression. • They are usually proteins, (they can be short, non-coding RNA). ...
... TRANSCRIPTION FACTORS • Transcription factors (TFs) are molecules involved in regulating gene expression. • They are usually proteins, (they can be short, non-coding RNA). ...
Structural vs. nonstructural proteins
... 3. Proteins and crosslinked DNA are immunoprecipitated. Protein‐DNA crosslinks in the IP material are then reversed, and the DNA fragments are purified. If the protein under investigation is associated with a specific genomic region in vivo, DNA fragments of this region should be further enriched ...
... 3. Proteins and crosslinked DNA are immunoprecipitated. Protein‐DNA crosslinks in the IP material are then reversed, and the DNA fragments are purified. If the protein under investigation is associated with a specific genomic region in vivo, DNA fragments of this region should be further enriched ...
Adenylyl Cyclase FUNCTION
... Enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP Interacts with g proteins and receptors 1064-1353 amino acids long 120-150 kilodaltons ...
... Enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP Interacts with g proteins and receptors 1064-1353 amino acids long 120-150 kilodaltons ...
02 Cell. Cell metabolism
... The basic structure of the plasma membrane and some of its functions are determined by its lipids, but many functions of the plasma membrane are determined by its proteins. The modern concept of the plasma membrane, the fluidmosaic model, suggests that the plasma membrane is neither rigid nor static ...
... The basic structure of the plasma membrane and some of its functions are determined by its lipids, but many functions of the plasma membrane are determined by its proteins. The modern concept of the plasma membrane, the fluidmosaic model, suggests that the plasma membrane is neither rigid nor static ...
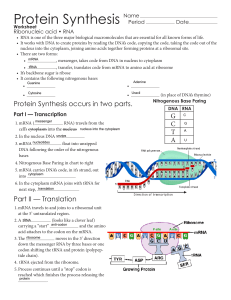
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
... nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ribosomal site. • There are two forms: • mRNA , messenger, takes code from DNA in nucleus to cytoplasm • tRNA , transfer, translates code from mRNA to amino acid at ribosome • It’s backbone sugar is ribose • It conta ...
... nucleus into the cytoplasm, joining amino acids together forming proteins at a ribosomal site. • There are two forms: • mRNA , messenger, takes code from DNA in nucleus to cytoplasm • tRNA , transfer, translates code from mRNA to amino acid at ribosome • It’s backbone sugar is ribose • It conta ...
Power Point Presentation
... The assembler will be capable of holding and positioning reactive compounds in order to control the precise location at which chemical reactions take place. This general approach should allow the construction of large atomically precise objects by a sequence of precisely controlled chemical reaction ...
... The assembler will be capable of holding and positioning reactive compounds in order to control the precise location at which chemical reactions take place. This general approach should allow the construction of large atomically precise objects by a sequence of precisely controlled chemical reaction ...
Probs 2 KEY 240 spr06
... arrange themselves once around one big molecule, proteins fold into a 3 dimensional shape with the nonpolar amino acids clustered inside the structure. The attainment of this energetically favorable condition is what drives protein folding. This process is called the hydrophobic effect. So, proteins ...
... arrange themselves once around one big molecule, proteins fold into a 3 dimensional shape with the nonpolar amino acids clustered inside the structure. The attainment of this energetically favorable condition is what drives protein folding. This process is called the hydrophobic effect. So, proteins ...
Catalog# 786-842 PROTOCOL - G
... through amide bonds. The coupling chemistry used generates a highly stable purification resin that is stable most commonly used buffers and denaturants. Heparin is a linear glycosaminoglycan composed of equimolar quantites of glucosamine and glucuronic acid, alternatively linked by α(1→4) glycosidic ...
... through amide bonds. The coupling chemistry used generates a highly stable purification resin that is stable most commonly used buffers and denaturants. Heparin is a linear glycosaminoglycan composed of equimolar quantites of glucosamine and glucuronic acid, alternatively linked by α(1→4) glycosidic ...
Chapter 5 - Scranton Prep Biology
... Phospholipiils Phospholipids consist of a glycerol linked to two fatty acids and a negatively charged phosphate group, to which other small moleculesmay be attached. The phosphate head of this molecule is hydrophilic and water soluble, whereas the two fatty acid chains are hydrophobic. The unique st ...
... Phospholipiils Phospholipids consist of a glycerol linked to two fatty acids and a negatively charged phosphate group, to which other small moleculesmay be attached. The phosphate head of this molecule is hydrophilic and water soluble, whereas the two fatty acid chains are hydrophobic. The unique st ...
workshops: absences: examinations: textbook
... reveal how these chains can form distinct structural features within a protein, the Secondary Structure, including helices and sheet-like structures. The peptide bond is planar and usually trans in conformation. A chain of amino acids is read N- (amino) terminal to C- (acid 'carboxyl') terminal. A p ...
... reveal how these chains can form distinct structural features within a protein, the Secondary Structure, including helices and sheet-like structures. The peptide bond is planar and usually trans in conformation. A chain of amino acids is read N- (amino) terminal to C- (acid 'carboxyl') terminal. A p ...
29_Metabolism of amino acids. Digestion of proteins
... • Proteins of animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) have high BV because they contain all the essential amino acids. • Proteins from plant sources (wheat, corn, beans) have low BV thus combination of more than one plant protein is required (a vegetarian diet) to increase its BV. ...
... • Proteins of animal sources (meat, milk, eggs) have high BV because they contain all the essential amino acids. • Proteins from plant sources (wheat, corn, beans) have low BV thus combination of more than one plant protein is required (a vegetarian diet) to increase its BV. ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.