DNA - Transcription & Translation
... tRNA complexes bind to mRNA codon by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one ...
... tRNA complexes bind to mRNA codon by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one ...
to get the file - Oxford Brookes University
... rafts may be vectors transporting the 53kDa protein and lipodomains may form the DVs. Such lipid domains may exclude other secretory proteins from DVs thus ensuring an early and precise segregation of proteins destined to the PSV. P. Dupree (Cambridge, UK) introduced PM lipid rafts and suggested tha ...
... rafts may be vectors transporting the 53kDa protein and lipodomains may form the DVs. Such lipid domains may exclude other secretory proteins from DVs thus ensuring an early and precise segregation of proteins destined to the PSV. P. Dupree (Cambridge, UK) introduced PM lipid rafts and suggested tha ...
Gene Section CPEB4 (cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 4)
... CPEB4 has been reported as a master gene involved in the reprogramming of cancer gene expression. The pro-oncogenic functions of CPEB4 originate in the translational activation of mRNAs that are ...
... CPEB4 has been reported as a master gene involved in the reprogramming of cancer gene expression. The pro-oncogenic functions of CPEB4 originate in the translational activation of mRNAs that are ...
slib Human Biochemistry
... – amino acids have no net charge – will not move in an electric field and are least soluble ...
... – amino acids have no net charge – will not move in an electric field and are least soluble ...
Clean Solutions Fuel Affinity Chromatography
... -bacterial systems such as yeast, insect, mammalian or plant cells are also used3. Purification results from the specific interaction between two reaction partners. One reaction partner is the protein tag, the other is a ligand or antibody covalently bound to a matrix. The recombinant protein (or th ...
... -bacterial systems such as yeast, insect, mammalian or plant cells are also used3. Purification results from the specific interaction between two reaction partners. One reaction partner is the protein tag, the other is a ligand or antibody covalently bound to a matrix. The recombinant protein (or th ...
Protein Labeling
... Characteristic positions of intein motifs and numbering. The inserted intein carries the N-terminal extein (left shaded box) and the C-terminal extein (right shaded box). The residues important for the splicing process as well as the conserved segment blocks (A, B, C, D, E, H, F, G) and some intern ...
... Characteristic positions of intein motifs and numbering. The inserted intein carries the N-terminal extein (left shaded box) and the C-terminal extein (right shaded box). The residues important for the splicing process as well as the conserved segment blocks (A, B, C, D, E, H, F, G) and some intern ...
Amino Acids
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins; proteins are made of amino acids. When you ingest a protein your body breaks it down into the individual aminos, reorders them, re-folds them, and turns them into whatever is needed by the body at that time. From only 20 amino acids, the body is able ...
... Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins; proteins are made of amino acids. When you ingest a protein your body breaks it down into the individual aminos, reorders them, re-folds them, and turns them into whatever is needed by the body at that time. From only 20 amino acids, the body is able ...
Membrane Structure and Function
... the plasma membrane freely through water filled pores • No change in protein shape • Most plasma membranes contain specific channel proteins for common ions such as Na+, K+, Cl- ...
... the plasma membrane freely through water filled pores • No change in protein shape • Most plasma membranes contain specific channel proteins for common ions such as Na+, K+, Cl- ...
CHAPTER 6 - Richsingiser.com
... the Higher Levels of Protein Structure? • Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of proteins is formed and stabilized by weak forces • Hydrogen bonds are formed wherever possible • Hydrophobic interactions drive protein folding • Ionic interactions usually occur on the protein ...
... the Higher Levels of Protein Structure? • Secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure of proteins is formed and stabilized by weak forces • Hydrogen bonds are formed wherever possible • Hydrophobic interactions drive protein folding • Ionic interactions usually occur on the protein ...
Enzymes
... • Are one of the most diverse group of macromolecules (polymers). • Contain nitrogen, sulfur, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. • Examples include: (1) Antibodies – fight disease (2) Contractile Proteins – movement - muscles (3) Hormones - messenger proteins which help to regulate bodily activities and ...
... • Are one of the most diverse group of macromolecules (polymers). • Contain nitrogen, sulfur, carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. • Examples include: (1) Antibodies – fight disease (2) Contractile Proteins – movement - muscles (3) Hormones - messenger proteins which help to regulate bodily activities and ...
Carmyle and Kenmuir Mount Vernon Church`s Website article
... for the third and so on for the next 150. This is written as (1/20)150 - that is 1 chance in 20 raised to the power 150 - that is a very small number indeed. Let us simplify this by saying it is (1/2*1/10)150 = (1/2)150 * (1/10)150 or approximately (1/10)50 * (1/10)150 = (1/10)200. In mathematics t ...
... for the third and so on for the next 150. This is written as (1/20)150 - that is 1 chance in 20 raised to the power 150 - that is a very small number indeed. Let us simplify this by saying it is (1/2*1/10)150 = (1/2)150 * (1/10)150 or approximately (1/10)50 * (1/10)150 = (1/10)200. In mathematics t ...
Pre – AP Biology
... proteins and enzymes.) – These are the site of Protein Synthesis. (These are like an actual “construction site” for a building, except they make proteins and not buildings.) • Normal proteins and enzymes are ALL made here. ...
... proteins and enzymes.) – These are the site of Protein Synthesis. (These are like an actual “construction site” for a building, except they make proteins and not buildings.) • Normal proteins and enzymes are ALL made here. ...
All the following is correct about ribosomes EXCEPT
... Which of the following is true about starch and glycogen? a. they are both polymers of glucose b. they are both used for energy storage in plants c. they are both found in humans d. none of them ...
... Which of the following is true about starch and glycogen? a. they are both polymers of glucose b. they are both used for energy storage in plants c. they are both found in humans d. none of them ...
Lecture 5: Major Nutrient Groups
... group of one to the carboxyl group of another this bond is known as the peptide linkage AA found in protein are known as residues protein chains of AA have typically 100200 residues many proteins have more than one chain ...
... group of one to the carboxyl group of another this bond is known as the peptide linkage AA found in protein are known as residues protein chains of AA have typically 100200 residues many proteins have more than one chain ...
Biological Macromolecules and Lipids
... respectively. Collagen and elastin proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues. ...
... respectively. Collagen and elastin proteins provide a fibrous framework in animal connective tissues. ...
Scientist This position will support product
... evaluations and generate application data using current products to demonstrate new or novel functions. We are looking for an enthusiastic, high energy individual looking to play a significant role in creating next generation molecular biology products and learning the product development process in ...
... evaluations and generate application data using current products to demonstrate new or novel functions. We are looking for an enthusiastic, high energy individual looking to play a significant role in creating next generation molecular biology products and learning the product development process in ...
462a Reading and Homework Assignment 3
... (4) Both cis and trans peptide bonds gain about 85 kJ/mol resonance energy when planar (through orbital alignment). Why are cis peptide bonds rarely seen in proteins? Why are cis peptide bonds more common for prolines than for other amino acids? Steric clash limits cis peptide bonds in most amino ...
... (4) Both cis and trans peptide bonds gain about 85 kJ/mol resonance energy when planar (through orbital alignment). Why are cis peptide bonds rarely seen in proteins? Why are cis peptide bonds more common for prolines than for other amino acids? Steric clash limits cis peptide bonds in most amino ...
Diapositivo 1 - Cell Biology Promotion
... Angiogenic activity Promoting cell growth, differentiation and motility ...
... Angiogenic activity Promoting cell growth, differentiation and motility ...
Lecture 4 - ISP 2016
... structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass. Biomacromolecule: Macromolecule (including proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides) formed by living organisms. Biopolymer: Substance compo ...
... structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass. Biomacromolecule: Macromolecule (including proteins, nucleic acids, and polysaccharides) formed by living organisms. Biopolymer: Substance compo ...
Nutrition Nutrition - CENTRAL COAST DRAGON BOAT CLUB
... legumes, nuts, seeds and beans—is beans is low or missing one or more essential amino acid. Complementary proteins are two or more incomplete protein sources that together provide all of the essential amino acids your body needs. For example rice and kidney beans, or chickpeas and corn, orn, are eac ...
... legumes, nuts, seeds and beans—is beans is low or missing one or more essential amino acid. Complementary proteins are two or more incomplete protein sources that together provide all of the essential amino acids your body needs. For example rice and kidney beans, or chickpeas and corn, orn, are eac ...
Cell membrane pp - Valhalla High School
... but not in eukaryotic cells. This fundamentally important advance in biotechnology has led to a vast improvement in human health over the past 80 years. Viruses cannot be treated by antibiotics, since they infect cells directly and grow within the cell, using cellular biosynthetic machinery to repro ...
... but not in eukaryotic cells. This fundamentally important advance in biotechnology has led to a vast improvement in human health over the past 80 years. Viruses cannot be treated by antibiotics, since they infect cells directly and grow within the cell, using cellular biosynthetic machinery to repro ...
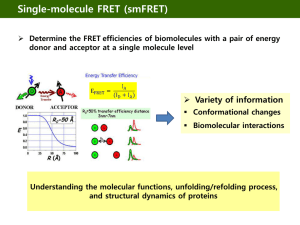
Single molecule analysis - Biomolecular Engineering Laboratory
... manipulate and probe individual molecules Answer many of fundamental biological questions : - Protein functions : Dynamics and recognition - Biomolecular interactions - Biological phenomenon ...
... manipulate and probe individual molecules Answer many of fundamental biological questions : - Protein functions : Dynamics and recognition - Biomolecular interactions - Biological phenomenon ...
12-3 RNA and Protein Synthesis
... Translation Step 2 • mRNA binds to the ribosome. tRNA attaches • Anticodons on the tRNA line up with codons on mRNA The other end of the tRNA is an amino acid ...
... Translation Step 2 • mRNA binds to the ribosome. tRNA attaches • Anticodons on the tRNA line up with codons on mRNA The other end of the tRNA is an amino acid ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.