Chapter 5 Polypeptides Geometry of Peptide Bond
... protein to unfold to an extended structure. The SDS molecules bind to the extended structure at a ratio of about 1 SDS molecule for each amino acid residue, or about 1.4 g SDS per g protein. Rod- like structures are formed, where the charge along the rod is uniformly negative from the sulfate anions ...
... protein to unfold to an extended structure. The SDS molecules bind to the extended structure at a ratio of about 1 SDS molecule for each amino acid residue, or about 1.4 g SDS per g protein. Rod- like structures are formed, where the charge along the rod is uniformly negative from the sulfate anions ...
M6697 - Sigma
... conjugated to KLH. Whole antiserum is purified using protein A immobilized on agarose to provide the IgG fraction of antiserum. Anti-MLKL (58-70) specifically recognizes human MLKL (not tested with other species).The antibody can be used in several immunochemical techniques including immunoblotting. ...
... conjugated to KLH. Whole antiserum is purified using protein A immobilized on agarose to provide the IgG fraction of antiserum. Anti-MLKL (58-70) specifically recognizes human MLKL (not tested with other species).The antibody can be used in several immunochemical techniques including immunoblotting. ...
Protein concentration measurement by UV
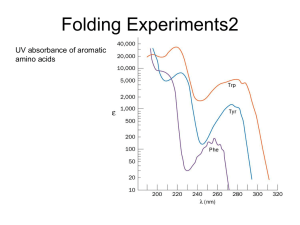
... will expose all aromatic residues to equivalent environment and minimize the effect of the folded protein on their absorbance, but at the same time it will also hide any problems with aggregation of the material as all protein will be denatured and solubilised. Depending on the method, the absorptio ...
... will expose all aromatic residues to equivalent environment and minimize the effect of the folded protein on their absorbance, but at the same time it will also hide any problems with aggregation of the material as all protein will be denatured and solubilised. Depending on the method, the absorptio ...
Multipower Sportsfood launches Fit Protein Lite
... Fit Protein Lite delivers 80% less carbs and sugars than Multipower’s number one selling Fit Protein in the iconic brown bottle. Retailing at just £3.85 a bottle the 500ml drink is available in three delicious flavours of Chocolate, Vanilla and Strawberry. Multipower Nutritionist Drew Price said: “F ...
... Fit Protein Lite delivers 80% less carbs and sugars than Multipower’s number one selling Fit Protein in the iconic brown bottle. Retailing at just £3.85 a bottle the 500ml drink is available in three delicious flavours of Chocolate, Vanilla and Strawberry. Multipower Nutritionist Drew Price said: “F ...
Document
... bond to give mixed disulfide) 2) Protein SH attacks protein-PDI mixed S-S bond to give protein S-S bond 3) Continues until protein in native S-S configuration and PDI cannot bind to exposed hydrophobic patches on the protein ...
... bond to give mixed disulfide) 2) Protein SH attacks protein-PDI mixed S-S bond to give protein S-S bond 3) Continues until protein in native S-S configuration and PDI cannot bind to exposed hydrophobic patches on the protein ...
Principles of Life
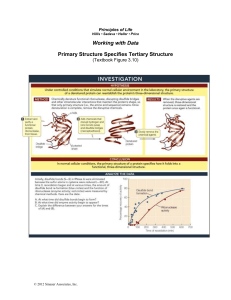
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
... After the tertiary structures of proteins were first shown to be highly specific, the question arose as to how the order of amino acids determined the three-dimensional structure. The second protein whose structure was determined was ribonuclease A, an enzyme from cows that was readily available fro ...
Protein structure homework: FAQ
... Protein structure homework: FAQ Q: Did you tell us not to go to molecule and then information in RasTop to find info on the proteins but for us to open the protein files in notepad. A: I did not tell you not to use the information button -- I warned you that it might be misreading and asked you to v ...
... Protein structure homework: FAQ Q: Did you tell us not to go to molecule and then information in RasTop to find info on the proteins but for us to open the protein files in notepad. A: I did not tell you not to use the information button -- I warned you that it might be misreading and asked you to v ...
powerpoint 22 Aug
... H bonding, sulfide bridges, non-polar/non-polar interactions Quaternary structure More than one peptide chain associated with each other ...
... H bonding, sulfide bridges, non-polar/non-polar interactions Quaternary structure More than one peptide chain associated with each other ...
4. Organic Cmpd
... glycerol and fatty acids made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is different from a carbohydrate because of the ratio and because the smaller units do not link together to form a chemical chain ...
... glycerol and fatty acids made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen. It is different from a carbohydrate because of the ratio and because the smaller units do not link together to form a chemical chain ...
Document
... There are through-bond interactions and through-space interactions. The latter usually being a consequence of the so-called nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE). Experiments of the nuclear-Overhauser variety may establish distances between atoms. • These distances are subjected to a technique called Dist ...
... There are through-bond interactions and through-space interactions. The latter usually being a consequence of the so-called nuclear Overhauser effect (NOE). Experiments of the nuclear-Overhauser variety may establish distances between atoms. • These distances are subjected to a technique called Dist ...
y syste m dreul io
... Proteins that speed up chemical reactions e.g. digestion. Which FACTORS affects enzymes ? Temperature and pH ...
... Proteins that speed up chemical reactions e.g. digestion. Which FACTORS affects enzymes ? Temperature and pH ...
Week 5: Macronutrient Jeopardy
... Q: What is a good source of fat? A: Avocados, cheese, dark chocolate, fish, nuts, coconut oil/extra virgin olive oil, or whole eggs. Q: What is the simplest form of a fat? A: Fatty acids -Q: How much of your daily intake should come from fats? A: 20-35% of one’s daily diet Q: What are the three kind ...
... Q: What is a good source of fat? A: Avocados, cheese, dark chocolate, fish, nuts, coconut oil/extra virgin olive oil, or whole eggs. Q: What is the simplest form of a fat? A: Fatty acids -Q: How much of your daily intake should come from fats? A: 20-35% of one’s daily diet Q: What are the three kind ...
Protein Annotation with GO Codes - dollar
... nomenclature for the description of genes and gene products in organisms. GO consists of three separate ontologies describing molecular functions (F), biological processes (P), and cellular components (C). We classify a subset of SWISS-PROT pertaining to human proteins with all GO codes in the subse ...
... nomenclature for the description of genes and gene products in organisms. GO consists of three separate ontologies describing molecular functions (F), biological processes (P), and cellular components (C). We classify a subset of SWISS-PROT pertaining to human proteins with all GO codes in the subse ...
FARM ANIMAL NUTRITION
... • An essential amino acid is one that can not be synthesized at a rate which would provide normal growth • Nonessential amino acids can be synthesized from other amino acids • A limiting amino acid is one present in the lowest amount relative to the requirement – Lysine, methionine & tryptophane are ...
... • An essential amino acid is one that can not be synthesized at a rate which would provide normal growth • Nonessential amino acids can be synthesized from other amino acids • A limiting amino acid is one present in the lowest amount relative to the requirement – Lysine, methionine & tryptophane are ...
Previously in Cell Bio
... model14. The a-subunit is shown as checkered, and the b-subunit as a solid line. The two hairpin loops in each subunit are marked ...
... model14. The a-subunit is shown as checkered, and the b-subunit as a solid line. The two hairpin loops in each subunit are marked ...
Free Form Amino Acids
... wheat, soy and dairy products and are formulated without the use of preservatives, artificial flavors or colors. Solgar's L-Arginine/L-Ornithine Vegetable Capsules are a pure mixture of natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body mu ...
... wheat, soy and dairy products and are formulated without the use of preservatives, artificial flavors or colors. Solgar's L-Arginine/L-Ornithine Vegetable Capsules are a pure mixture of natural freem form amino acids. Long chains of molecularly bonded individual amino acids form protein. The body mu ...
Organic Molecules
... • Heat, changes in pH, salts, and detergents can disrupt the hydrogen bonds that maintain a protein’s shape • When a protein loses its shape and no longer functions, it is denatured (蛋白質變性) ...
... • Heat, changes in pH, salts, and detergents can disrupt the hydrogen bonds that maintain a protein’s shape • When a protein loses its shape and no longer functions, it is denatured (蛋白質變性) ...
College oration - Birkbeck, University of London
... and Janet Thornton has played a decisive, indeed and indispensable role in its development. Indeed, one of her colleagues has said that ‘Janet Thornton could be described as Miss Structural Bioinformatics’, an epithet that, when compared with ‘The Queen of Sheba’ or ‘The Lady of the Lamp’, perhaps l ...
... and Janet Thornton has played a decisive, indeed and indispensable role in its development. Indeed, one of her colleagues has said that ‘Janet Thornton could be described as Miss Structural Bioinformatics’, an epithet that, when compared with ‘The Queen of Sheba’ or ‘The Lady of the Lamp’, perhaps l ...
CSCE590/822 Data Mining Principles and Applications
... Proteins Large organic compounds made of amino acids Proteins play a crucial role in virtually all biological processes with a broad range of functions. The activity of an enzyme or the function of a protein is governed by the three-dimensional structure ...
... Proteins Large organic compounds made of amino acids Proteins play a crucial role in virtually all biological processes with a broad range of functions. The activity of an enzyme or the function of a protein is governed by the three-dimensional structure ...
lecture 5
... residue of a PPI might be involved in H-bond formation with N:, producing C-N bond with more single-bond character - The pipecolic amide moiety of FK506, which probably mimics the proline residue of peptide or protein substrates, is bound in a hydrophobic pocket of FKBP, presumably at the active sit ...
... residue of a PPI might be involved in H-bond formation with N:, producing C-N bond with more single-bond character - The pipecolic amide moiety of FK506, which probably mimics the proline residue of peptide or protein substrates, is bound in a hydrophobic pocket of FKBP, presumably at the active sit ...
Biopolymers
... twist, and fold, reversibly. Consider protein shown below. “Polypeptide” on far left is already a polymer (amino acids are the monomer). ...
... twist, and fold, reversibly. Consider protein shown below. “Polypeptide” on far left is already a polymer (amino acids are the monomer). ...
Progeria
... This protein is what holds the cells nucleus together When this protein is defected it makes the nucleus unstable This is the process that leads to premature aging ...
... This protein is what holds the cells nucleus together When this protein is defected it makes the nucleus unstable This is the process that leads to premature aging ...
Preparation and transformation of competent bacteria: Calcium
... 8. Where in the human genome is this gene located? 9. What is the function of this protein? 10. What specific role does it play in the cell? 11. What is the RefSeq accession number for the mRNA of this gene? 12. What is the RefSeq accession number for the protein sequence (it is the product of the g ...
... 8. Where in the human genome is this gene located? 9. What is the function of this protein? 10. What specific role does it play in the cell? 11. What is the RefSeq accession number for the mRNA of this gene? 12. What is the RefSeq accession number for the protein sequence (it is the product of the g ...
protein - mustafaaltinisik.org.uk
... other with one nonpolar side chain interacting with the nonpolar side chain of the other. The hydrophilic side chains are exposed to the aqueous environment. ...
... other with one nonpolar side chain interacting with the nonpolar side chain of the other. The hydrophilic side chains are exposed to the aqueous environment. ...
DNA - Transcription & Translation
... tRNA complexes bind to mRNA codon by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one ...
... tRNA complexes bind to mRNA codon by forming complementary base pairs with the tRNA anticodon The ribosome moves from codon to codon along the mRNA. Amino acids are added one by one ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.