NME2.35: amino acid and protein metabolism 13/03/08
... o Amino acids – most important source o Enteric bacterial action o Muscle (purine nucleotide cycle) o Oxidative deamination of glutamate o Amines – from diet, hormones etc. Ammonia is neurotoxic and its plasma concentration is kept within narrow limits (20-50μM) o The liver is primarily responsible ...
... o Amino acids – most important source o Enteric bacterial action o Muscle (purine nucleotide cycle) o Oxidative deamination of glutamate o Amines – from diet, hormones etc. Ammonia is neurotoxic and its plasma concentration is kept within narrow limits (20-50μM) o The liver is primarily responsible ...
Poster
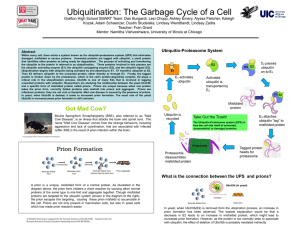
... Within every cell, there exists a system known as the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) that eliminates damaged, misfolded or excess proteins. Unwanted proteins are tagged with ubiquitin, a small protein that identifies other proteins as being ready for degradation. The process of activating and tra ...
... Within every cell, there exists a system known as the ubiquitin-proteasome system (UPS) that eliminates damaged, misfolded or excess proteins. Unwanted proteins are tagged with ubiquitin, a small protein that identifies other proteins as being ready for degradation. The process of activating and tra ...
Caffeine as a cause of coral bleaching: Effects of caffeine on
... If untreated, the caffeine in sewage effluent reaches the open ocean where it may affect marine life. Studies have shown that low concentrations of caffeine can induce bleaching in coral; i.e. caffeine causes coral to release their algal symbionts (zooxanthellae). Corals may recover from this, but b ...
... If untreated, the caffeine in sewage effluent reaches the open ocean where it may affect marine life. Studies have shown that low concentrations of caffeine can induce bleaching in coral; i.e. caffeine causes coral to release their algal symbionts (zooxanthellae). Corals may recover from this, but b ...
Communication - Dundee Life Sciences
... three characteristic domains: an N-terminal charged domain (usually basic), a hydrophobic core domain and a more polar C-terminal domain (reviewed in Ref. 2). Similar signals have been shown to target proteins across the chloroplast thylakoid membrane (3), and it is now clear that a prokaryotic-like ...
... three characteristic domains: an N-terminal charged domain (usually basic), a hydrophobic core domain and a more polar C-terminal domain (reviewed in Ref. 2). Similar signals have been shown to target proteins across the chloroplast thylakoid membrane (3), and it is now clear that a prokaryotic-like ...
Sept20
... weight lifting, and American football. However, in spite of their tremendous popularity, their effectiveness is controversial. The research literature is divided on whether anabolic steroids enhance physical performance. Yet, almost all athletes who consume these substances acclaim their beneficial ...
... weight lifting, and American football. However, in spite of their tremendous popularity, their effectiveness is controversial. The research literature is divided on whether anabolic steroids enhance physical performance. Yet, almost all athletes who consume these substances acclaim their beneficial ...
homework 3 assigned
... Homework 3, due Friday, May 12 (10 points) Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corr ...
... Homework 3, due Friday, May 12 (10 points) Given the following table of the amino acid associated with each triple of nucleotides, construct a map that has triples of nucleotides as keys and amino acids as values. Append a main function that converts a string of nucleotides into a vector of the corr ...
Carbohydrates
... Proteins involved in signaling & adhesion at the cell surface recognize & bind heparan sulfate chains. E.g., binding of some growth factors (small proteins) to cell surface receptors is enhanced by their binding also to heparan sulfates. Regulated cell surface Sulf enzymes may remove sulfate groups ...
... Proteins involved in signaling & adhesion at the cell surface recognize & bind heparan sulfate chains. E.g., binding of some growth factors (small proteins) to cell surface receptors is enhanced by their binding also to heparan sulfates. Regulated cell surface Sulf enzymes may remove sulfate groups ...
Macromolecule Basics
... • They are made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Their building block is a single sugar called a monosaccharide (mono = single) • When 2 sugars combine it is called a disaccharide (di = two) • When 3 or more sugars combine it is called a ...
... • They are made from carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Their building block is a single sugar called a monosaccharide (mono = single) • When 2 sugars combine it is called a disaccharide (di = two) • When 3 or more sugars combine it is called a ...
the pros of protein go green with plant protein know your nuts
... because they must come from the food you eat. A food is considered a “complete” protein when it contains all nine essential amino acids. Complete proteins mainly come from animal-based products (meat, poultry, dairy, eggs, fish), soy and certain grains, such as quinoa. Plant-based foods, such as nut ...
... because they must come from the food you eat. A food is considered a “complete” protein when it contains all nine essential amino acids. Complete proteins mainly come from animal-based products (meat, poultry, dairy, eggs, fish), soy and certain grains, such as quinoa. Plant-based foods, such as nut ...
One Gene - One Polypeptide
... of sequences nucleotides in varying orders and lengths. A molecule of DNA may be hundreds of thousands of nucleotides long, but is broken up into sequences of several hundred to several thousand nucleotides called genes that each code for a single polypeptide. Polypeptides are chains of amino acids ...
... of sequences nucleotides in varying orders and lengths. A molecule of DNA may be hundreds of thousands of nucleotides long, but is broken up into sequences of several hundred to several thousand nucleotides called genes that each code for a single polypeptide. Polypeptides are chains of amino acids ...
Lecture 4 - Biological Molecules Part II
... catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly without being used up in a reaction, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life • An enzyme is denoted by the suffix “-ase” ...
... catalyst to speed up chemical reactions • Enzymes can perform their functions repeatedly without being used up in a reaction, functioning as workhorses that carry out the processes of life • An enzyme is denoted by the suffix “-ase” ...
mRNA Codon/Amino Acid Chart
... • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that matches the mRNA codon. • Warn students against using the tRNA anticodon w ...
... • Find a codon’s first base in the first column of the chart; stay in this row. • Find the second base in the middle of the chart, stay in this box. • Locate the third base in the far right column, this is the amino acid that matches the mRNA codon. • Warn students against using the tRNA anticodon w ...
Nutrients - Food a fact of life
... Protein is needed for growth, development and repair of the body. Excess protein can be broken down and used as a source of energy. Protein is made up of different combinations of amino acids. These are the building blocks of protein. Amino acids are compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, ni ...
... Protein is needed for growth, development and repair of the body. Excess protein can be broken down and used as a source of energy. Protein is made up of different combinations of amino acids. These are the building blocks of protein. Amino acids are compounds containing carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, ni ...
Research Essay
... Proteins catalyze reactions, transport oxygen and nutrients, transport signals (hormones), provide immune responses, storage, and provide regeneration. They are composed of amino acids and have four levels of structure, all stemming from the amino acid sequence, primary structure. We know about prot ...
... Proteins catalyze reactions, transport oxygen and nutrients, transport signals (hormones), provide immune responses, storage, and provide regeneration. They are composed of amino acids and have four levels of structure, all stemming from the amino acid sequence, primary structure. We know about prot ...
E. Nucleotide sequences that define an intron. Mutations in
... B. The genetic code is degenerate because many amino acids are encoded by more than one codon (e.g. there are six codons for leucine). The occurrence of nonstandard WatsonCrick base-pairing (wobble) between the bases in position 3 of the codon and position 1 of the anticodon allows some tRNAs to tra ...
... B. The genetic code is degenerate because many amino acids are encoded by more than one codon (e.g. there are six codons for leucine). The occurrence of nonstandard WatsonCrick base-pairing (wobble) between the bases in position 3 of the codon and position 1 of the anticodon allows some tRNAs to tra ...
VMD training material
... What kinds of interactions keep the four hemoglobin proteins together? Can you identify residues that could contribute to interprotein stability? Split in three teams and make a list of findings, then discuss findings in class. How was the structure solved? ...
... What kinds of interactions keep the four hemoglobin proteins together? Can you identify residues that could contribute to interprotein stability? Split in three teams and make a list of findings, then discuss findings in class. How was the structure solved? ...
Chapter Twelve Protein Synthesis: Translation of the
... ribosome translocation as prokaryotes • there is no E site on eukaryotic ribosomes, only A and ...
... ribosome translocation as prokaryotes • there is no E site on eukaryotic ribosomes, only A and ...
3.13 Amino acids, proteins and DNA
... • The primary structure folds back on itself and held together by hydrogen bonds. • The given shape looks like a ‘pleat’ with the R groups alternating up and down along the ...
... • The primary structure folds back on itself and held together by hydrogen bonds. • The given shape looks like a ‘pleat’ with the R groups alternating up and down along the ...
Low Circulating Amino Acids and Protein Quality: An
... static, representing the net effect of changes in production and utilization of an amino acid, unlike the dynamic flux. For example, plasma citrulline flux, which indicates enterocyte mass and function, is not reflected in its plasma concentration (Kao et al., 2016). Thus, among ...
... static, representing the net effect of changes in production and utilization of an amino acid, unlike the dynamic flux. For example, plasma citrulline flux, which indicates enterocyte mass and function, is not reflected in its plasma concentration (Kao et al., 2016). Thus, among ...
Biochemistry 2000 Sample Questions Proteins
... (22c) At pH 12, this peptide will have a net charge of -2. pH 12 is higher than all pKas of side chains (His, Tyr) and main chain carboxylate and amino groups. Thus, all groups will be deprotonated. The Cterminal carboxylate group and Tyr will have a negative charge and the other groups will be unch ...
... (22c) At pH 12, this peptide will have a net charge of -2. pH 12 is higher than all pKas of side chains (His, Tyr) and main chain carboxylate and amino groups. Thus, all groups will be deprotonated. The Cterminal carboxylate group and Tyr will have a negative charge and the other groups will be unch ...
BS3 Crosslinking
... Bis (sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate (BS3) crosslinking was performed as described previously (Grosshans et al., 2001, 2002; Conrad et al., 2008). BS3 is a membrane-impermeable agent, which selectively crosslinks cell-surface proteins to form high-molecular-mass aggregates. Because intracellular protein ...
... Bis (sulfosuccinimidyl) suberate (BS3) crosslinking was performed as described previously (Grosshans et al., 2001, 2002; Conrad et al., 2008). BS3 is a membrane-impermeable agent, which selectively crosslinks cell-surface proteins to form high-molecular-mass aggregates. Because intracellular protein ...
Chlorella CGF
... spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
... spherical or elliptical, containing a single elongated chloroplast that fills most cell. Fine powder, hygroscopic dark green color, characteristic flavor and odor. ...
No Slide Title
... *All restraints were picked so that they were incorrect **All restraints were picked so that they were correct ...
... *All restraints were picked so that they were incorrect **All restraints were picked so that they were correct ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.