Are You Getting It??
... The three base- pairs formed have equal strength. They bind in a antiparallel orientation. The first base in a codon can wobble. The first base in an anticodon can be a rare base. An anticodon can bind to only one codon. ...
... The three base- pairs formed have equal strength. They bind in a antiparallel orientation. The first base in a codon can wobble. The first base in an anticodon can be a rare base. An anticodon can bind to only one codon. ...
Biological Molecules: Structure and Methods of Analysis
... is best used for making relative comparisons of the amount of carbohydrate among a group of samples. To test for the presence and quantity of specific carbohydrates, enzyme-based assays are used. Why do you think that an enzyme-based assay would provide specificity in a carbohydrate assay? A test fo ...
... is best used for making relative comparisons of the amount of carbohydrate among a group of samples. To test for the presence and quantity of specific carbohydrates, enzyme-based assays are used. Why do you think that an enzyme-based assay would provide specificity in a carbohydrate assay? A test fo ...
ANSWERS - Unit 1 Review File
... 34. The linear sequence of amino acids found in an enzyme is called its: a) tertiary structure b) primary structure c) secondary structure d) quaternary structure 35. Proteins may denature when: a)pH is changed b) oxygen is present c) they form enzymes d) substrate concentration is increased 36. Whe ...
... 34. The linear sequence of amino acids found in an enzyme is called its: a) tertiary structure b) primary structure c) secondary structure d) quaternary structure 35. Proteins may denature when: a)pH is changed b) oxygen is present c) they form enzymes d) substrate concentration is increased 36. Whe ...
TRANSLATION
... • In the ribosomes the mRNA forms the template for producing the specific sequence of amino acids of a particular polypepetide. • In the cytoplasm there is another form of RNA called transfer RNA or tRNA. ...
... • In the ribosomes the mRNA forms the template for producing the specific sequence of amino acids of a particular polypepetide. • In the cytoplasm there is another form of RNA called transfer RNA or tRNA. ...
Slide 1 - E-Learning/An-Najah National University
... shifted, and the downstream gene was transcribed as nonsense. However, when they made three deletions, the correct reading frame was restored, and the sequences downstream were transcribed correctly. They obtained the same results when they made additions to the DNA consisting of one, two, or th ...
... shifted, and the downstream gene was transcribed as nonsense. However, when they made three deletions, the correct reading frame was restored, and the sequences downstream were transcribed correctly. They obtained the same results when they made additions to the DNA consisting of one, two, or th ...
Bacterial Rhodopsin Light-driven Proton Pump
... 1. Retinal (VitA aldehyde or retinaldehyde; one of 3 forms of VitA) is parallel to the plane of the membrane, bound to K216 in the middle of helix 7. 2. The internal cavity is divided into two half channels, cytoplasmic and external (the H+ pathway) 3. The internal half channel is more hydrophobic. ...
... 1. Retinal (VitA aldehyde or retinaldehyde; one of 3 forms of VitA) is parallel to the plane of the membrane, bound to K216 in the middle of helix 7. 2. The internal cavity is divided into two half channels, cytoplasmic and external (the H+ pathway) 3. The internal half channel is more hydrophobic. ...
No Slide Title
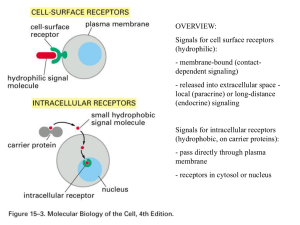
... - membrane-bound (contactdependent signaling) - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
... - membrane-bound (contactdependent signaling) - released into extracellular space local (paracrine) or long-distance (endocrine) signaling Signals for intracellular receptors (hydrophobic, on carrier proteins): - pass directly through plasma membrane - receptors in cytosol or nucleus ...
A1982PK03800001
... horseradish peroxidases contain hydroxy1 proline and t.amport’s paper about the proteins of cell walls, especially the hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein fraction, which seemed a possible candidate as a crosslinking agent that determined the capacity of walls to be loosened and stretched. The idea occ ...
... horseradish peroxidases contain hydroxy1 proline and t.amport’s paper about the proteins of cell walls, especially the hydroxyproline-rich glycoprotein fraction, which seemed a possible candidate as a crosslinking agent that determined the capacity of walls to be loosened and stretched. The idea occ ...
Membrane protein structure and assembly
... Heijne Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 7, 909–918 (December 2006) | doi:10.1038/nrm2063 ...
... Heijne Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 7, 909–918 (December 2006) | doi:10.1038/nrm2063 ...
Protein Structure
... proteins are positively charged due to the basic groups on lysine and arginine, whereas, at high pH, proteins are negatively charged due to the acidic groups on aspartic and glutamic acids. The peptide backbone of proteins is composed of amino acids having polar, non-polar, aromatic and charged resi ...
... proteins are positively charged due to the basic groups on lysine and arginine, whereas, at high pH, proteins are negatively charged due to the acidic groups on aspartic and glutamic acids. The peptide backbone of proteins is composed of amino acids having polar, non-polar, aromatic and charged resi ...
3. Related Pathways
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
... Organisms are able to metabolize nutrients other than carbohydrates during times of starvation Once broken down, these monomers are able to feed into various parts of glycolysis or the Krebs cycle (Fig.1, p.117) ...
E. Aminoglycosides
... bactericidal agents in most of the cases. Why targeting the bacterial protein synthesis will be selective: Different diffusion rates between bacterial and ...
... bactericidal agents in most of the cases. Why targeting the bacterial protein synthesis will be selective: Different diffusion rates between bacterial and ...
Stage proposé par « Prénom NOM
... During spermiogenesis, several proteins that are needed for the proper male germ cell differentiation are under translational control. Such proteins are expressed at very specific steps in elongating spermatids. We have recently shown that Poly(A) Binding Protein (PABP) interacting protein 2 (Paip2) ...
... During spermiogenesis, several proteins that are needed for the proper male germ cell differentiation are under translational control. Such proteins are expressed at very specific steps in elongating spermatids. We have recently shown that Poly(A) Binding Protein (PABP) interacting protein 2 (Paip2) ...
Biol 1107 Biomolecules Lab Fall 2003
... is best used for making relative comparisons of the amount of carbohydrate among a group of samples. To test for the presence and quantity of specific carbohydrates, enzyme -based assays are used. Why do you think that an enzyme-based assay would provide specificity in a carbohydrate assay? A test f ...
... is best used for making relative comparisons of the amount of carbohydrate among a group of samples. To test for the presence and quantity of specific carbohydrates, enzyme -based assays are used. Why do you think that an enzyme-based assay would provide specificity in a carbohydrate assay? A test f ...
Secondary structure
... 3. The oxygen and hydrogen atom of the peptide bonds have the potential for hydrogen bonding. 4. Bulky groups on side chains of amino acid residues in polypeptide cause steric hindrance when present close to gather. 5. Hydrophobic residues try to be together away from water. 6. +ive or –ive charge o ...
... 3. The oxygen and hydrogen atom of the peptide bonds have the potential for hydrogen bonding. 4. Bulky groups on side chains of amino acid residues in polypeptide cause steric hindrance when present close to gather. 5. Hydrophobic residues try to be together away from water. 6. +ive or –ive charge o ...
Untitled
... exhibit different degrees of interaction with charged chromatography media according to differences in their overall charge, charge density and surface charge distribution. The charged groups within a molecule that contribute to the net surface charge possess different pKa values depending on their ...
... exhibit different degrees of interaction with charged chromatography media according to differences in their overall charge, charge density and surface charge distribution. The charged groups within a molecule that contribute to the net surface charge possess different pKa values depending on their ...
Introduction to bioinformatics
... http://www.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/~robert/bioinf/lecture1/index.html http://www.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/~robert/bioinf/lecture2/index.html ...
... http://www.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/~robert/bioinf/lecture1/index.html http://www.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/~robert/bioinf/lecture2/index.html ...
Slide 1
... – The combination of sequence of amino acids – The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein is called the PRIMARY STRUCTURE of the protein ...
... – The combination of sequence of amino acids – The linear sequence of amino acids in a protein is called the PRIMARY STRUCTURE of the protein ...
Chapter 7: Three-Dimensional Structure of Proteins
... For each of these methods of separating proteins, describe the principle of the method, and tell what property of proteins allows their separation by this technique. (6 pts) (a) ion-exchange chromatography (b) size-exclusion (gel filtration) chromatography ...
... For each of these methods of separating proteins, describe the principle of the method, and tell what property of proteins allows their separation by this technique. (6 pts) (a) ion-exchange chromatography (b) size-exclusion (gel filtration) chromatography ...
Gene Section EIF4EBP1 (Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E binding protein 1)
... Two pseudogenes with homology to 4E-BP1 exist in the human genome, located at 14q11.2 (LOC768328) and 22q12 (EIF4EBP1P), with the latter pseudogene present on the antisense strand of the gene locus encoding chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 8 (CHD8). ...
... Two pseudogenes with homology to 4E-BP1 exist in the human genome, located at 14q11.2 (LOC768328) and 22q12 (EIF4EBP1P), with the latter pseudogene present on the antisense strand of the gene locus encoding chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 8 (CHD8). ...
2009 exam with answers
... 6C. Consider the amino acid sequence in the region marked by the 10 X’s. Starting with #1 at the top, suppose some of the amino acids are as indicated below. Make your best guesses for the 7 remaining positions, using 7 different amino acids, and explain your reasoning at the right: ...
... 6C. Consider the amino acid sequence in the region marked by the 10 X’s. Starting with #1 at the top, suppose some of the amino acids are as indicated below. Make your best guesses for the 7 remaining positions, using 7 different amino acids, and explain your reasoning at the right: ...
File
... lipids and carbohydrates during metabolism or from the transamination of essential amino acids ...
... lipids and carbohydrates during metabolism or from the transamination of essential amino acids ...
slide
... Where they are in contact with the aqueous environment, they have hydrophilic regions of amino acids. ...
... Where they are in contact with the aqueous environment, they have hydrophilic regions of amino acids. ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.