Polypeptide and protein structure
... The Collagen Triple Helix The most abundant protein in vertebrates Organized in water-insoluble fibers Have a great strength Consists of three polypeptide chains wrapped around each other in a ropelike twist, or triple helix Has a repeating sequence of the amino acids; X1—X2(Pro, ProOH)—G ...
... The Collagen Triple Helix The most abundant protein in vertebrates Organized in water-insoluble fibers Have a great strength Consists of three polypeptide chains wrapped around each other in a ropelike twist, or triple helix Has a repeating sequence of the amino acids; X1—X2(Pro, ProOH)—G ...
Tsui, S, Dai, T, Warren, ST and Yen, P: Association of the mouse infertility factor DAZL1 with actively translating polyribosomes. Biology of Reproduction 62:1655-1660 (2000).
... domain and the DAZ repeats, but they have different Cterminal sequences due to a frame shift downstream of the DAZ repeat region. It was proposed that the DAZ genes originated from translocation of an ancestral DAZL1 gene to the Y chromosome, followed by amplification and pruning [10]. A role for DA ...
... domain and the DAZ repeats, but they have different Cterminal sequences due to a frame shift downstream of the DAZ repeat region. It was proposed that the DAZ genes originated from translocation of an ancestral DAZL1 gene to the Y chromosome, followed by amplification and pruning [10]. A role for DA ...
Journal of Applied Microbiology
... proteins with affinity for mucus constituents, where the F80 was subjected to Western blot analysis, using POD-mucin or POD-lactoferrin as a probe. As shown in Fig. 1b, two main reactive proteins with apparent molecular mass of 37 and 48 kDa were detected, indicating the affinity of F80 proteins for ...
... proteins with affinity for mucus constituents, where the F80 was subjected to Western blot analysis, using POD-mucin or POD-lactoferrin as a probe. As shown in Fig. 1b, two main reactive proteins with apparent molecular mass of 37 and 48 kDa were detected, indicating the affinity of F80 proteins for ...
EnzymesLect1 2014
... As with any protein, each monomer is actually produced as a long, linear chain of amino acids, which folds in a particular fashion to produce a three-dimensional product. Individual monomers may then combine via non-covalent interactions to form a multimeric protein. Many enzymes can be unfolded or ...
... As with any protein, each monomer is actually produced as a long, linear chain of amino acids, which folds in a particular fashion to produce a three-dimensional product. Individual monomers may then combine via non-covalent interactions to form a multimeric protein. Many enzymes can be unfolded or ...
Universal Features of Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation Are
... includes 16 major factors, including proteins with homologies to components of metazoan P granules and archaeal proteins. Containing translationally silent transcripts, this mRNP integrates eIF4E and poly(A)-binding protein but excludes P body RNA degradation factors and translation-initiation promo ...
... includes 16 major factors, including proteins with homologies to components of metazoan P granules and archaeal proteins. Containing translationally silent transcripts, this mRNP integrates eIF4E and poly(A)-binding protein but excludes P body RNA degradation factors and translation-initiation promo ...
Vacuolar protein sorting mechanisms in plants
... For exit of proteins from the ER, different types of motifs have been identified that are recognized by COPII. Di-acidic (e.g. DXE/EXE), di-basic (e.g. RKXRK) and di-aromatic motifs in the cytosolic tail of transmembrane proteins were reported to be important for the export of proteins from the ER i ...
... For exit of proteins from the ER, different types of motifs have been identified that are recognized by COPII. Di-acidic (e.g. DXE/EXE), di-basic (e.g. RKXRK) and di-aromatic motifs in the cytosolic tail of transmembrane proteins were reported to be important for the export of proteins from the ER i ...
Active Transport of Amino Acids by Membrane
... The Krebs cycle is incomplete in certain chemolithotrophs (Smith, London & Stanier, T 967), and NADH oxidation may not be coupled with oxidative phosphorylation (Henipfling & Vishniac, 1965 ; Johnson & Abraham, I 969). However, Tlziobacillus nea/-’olitanus and Thiobacillus thioparus possess high con ...
... The Krebs cycle is incomplete in certain chemolithotrophs (Smith, London & Stanier, T 967), and NADH oxidation may not be coupled with oxidative phosphorylation (Henipfling & Vishniac, 1965 ; Johnson & Abraham, I 969). However, Tlziobacillus nea/-’olitanus and Thiobacillus thioparus possess high con ...
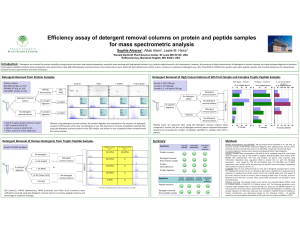
Efficiency assay of detergent removal columns on - G
... and suppress peptide ionization when analyzed by mass spectrometry. New (GB‐S10) detergent removal columns from G‐Biosciences were tested for their efficiency to remove anionic, nonionic or zwitterionic detergents (e.g. SDS, TritonX100 or CHAPS) from protein and tryptic peptide samples with minimal ...
... and suppress peptide ionization when analyzed by mass spectrometry. New (GB‐S10) detergent removal columns from G‐Biosciences were tested for their efficiency to remove anionic, nonionic or zwitterionic detergents (e.g. SDS, TritonX100 or CHAPS) from protein and tryptic peptide samples with minimal ...
Development of an Assay for the Identification of Receptor Binding
... 1. Introduction Bacteriophage receptor binding proteins (RBPs) have recently been developed into a number of tools that make use of their high specificity and robustness [1]. These technologies include diagnostics involving RBPs bound to surfaces [2], or to beads [3,4], for the selective capture of ...
... 1. Introduction Bacteriophage receptor binding proteins (RBPs) have recently been developed into a number of tools that make use of their high specificity and robustness [1]. These technologies include diagnostics involving RBPs bound to surfaces [2], or to beads [3,4], for the selective capture of ...
Protein performance in emulsion stability
... water binding. Emulsion stability is influenced by a great many variables such as meat-type, pH, temperature, concentration, degree of fat cell disruption, and presence of additives and support ingredients. Also of importance are the processing conditions which influences the colloidal suspension of ...
... water binding. Emulsion stability is influenced by a great many variables such as meat-type, pH, temperature, concentration, degree of fat cell disruption, and presence of additives and support ingredients. Also of importance are the processing conditions which influences the colloidal suspension of ...
The proteomics of plant cell membranes
... 2004), mitochondria (Kruft et al., 2001; Millar et al., 2001; Millar and Heazlewood, 2003; Heazlewood et al., 2004), mitochondrial membrane (Brugiere et al., 2004), peroxisome (Fukao et al., 2002; Carter et al., 2004), and tonoplast proteome (Shimaoka et al., 2004), as well as the Arabidopsis cell w ...
... 2004), mitochondria (Kruft et al., 2001; Millar et al., 2001; Millar and Heazlewood, 2003; Heazlewood et al., 2004), mitochondrial membrane (Brugiere et al., 2004), peroxisome (Fukao et al., 2002; Carter et al., 2004), and tonoplast proteome (Shimaoka et al., 2004), as well as the Arabidopsis cell w ...
protein phosphorylation in bacteria
... the specificity of acceptor amino acid. In accordance with it, the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemists has recommended the following names: • Phosphotransferases with a hydroxyl group as an acceptor (i.e. serine or threonine), called protein serine/threonine kinases (E.C ...
... the specificity of acceptor amino acid. In accordance with it, the Nomenclature Committee of the International Union of Biochemists has recommended the following names: • Phosphotransferases with a hydroxyl group as an acceptor (i.e. serine or threonine), called protein serine/threonine kinases (E.C ...
... product was produced. Appending the tag on the Nterminus of the protein of interest may improve expression and solubility, in some cases. Another structural consideration is the peptide linker sequences. The flexibility, hydrophilicity and linker length are important for the production of functional ...
LWT Food Science and Technology
... extensive consumption of energy as alcohol may predispose to obesity and other problems and that cigarette smoking can negate the benefits of moderate beer consumption (Williamson et al., 1987). Some authors have shown that the positive biochemical changes in the moderate alcoholic beverages consumer ...
... extensive consumption of energy as alcohol may predispose to obesity and other problems and that cigarette smoking can negate the benefits of moderate beer consumption (Williamson et al., 1987). Some authors have shown that the positive biochemical changes in the moderate alcoholic beverages consumer ...
The significance of biochemical and molecular sample integrity in
... state and the rapidity of death, may play major roles in determining the postmortem condition of the sample [6–9]. It would therefore be of importance to determine the condition and quality of postmortem tissue, for example, through the quantification of a biological marker in such sample. In a prev ...
... state and the rapidity of death, may play major roles in determining the postmortem condition of the sample [6–9]. It would therefore be of importance to determine the condition and quality of postmortem tissue, for example, through the quantification of a biological marker in such sample. In a prev ...
Phloem RNA-binding proteins as potential components of the long
... promoted the search for phloem-specific proteins whose functions can parallel those of plant viral movement proteins (MPs), but has also enabled the identification of the 16-kD Cucurbita maxima phloem protein (CmPP16), a RBP with immunological crossreactivity and a functional similarity to the MP of t ...
... promoted the search for phloem-specific proteins whose functions can parallel those of plant viral movement proteins (MPs), but has also enabled the identification of the 16-kD Cucurbita maxima phloem protein (CmPP16), a RBP with immunological crossreactivity and a functional similarity to the MP of t ...
Sequence elements of the fusion peptide of human respiratory
... HRSV F shares structural features with the F protein of other paramyxoviruses, despite limited sequence identity. Thus, all F proteins have three main hydrophobic regions: one, at the N terminus, which acts as the signal peptide for translocation into the ER; another region, which is the membrane an ...
... HRSV F shares structural features with the F protein of other paramyxoviruses, despite limited sequence identity. Thus, all F proteins have three main hydrophobic regions: one, at the N terminus, which acts as the signal peptide for translocation into the ER; another region, which is the membrane an ...
Allosteric regulation and catalysis emerge via a common
... between different enzyme conformations limit the rate of catalysis by dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) from Escherichia coli3. Similar NMR experiments revealed that five conformations of DHFR that constitute the key species in the enzyme’s catalytic cycle interconvert at rates that are equal to those ...
... between different enzyme conformations limit the rate of catalysis by dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) from Escherichia coli3. Similar NMR experiments revealed that five conformations of DHFR that constitute the key species in the enzyme’s catalytic cycle interconvert at rates that are equal to those ...
广西医科大学理论课教案(1)
... (2) spend more time to the subject (at least 8 hours for one topic ) (3) persist in thinking the topic and find more information about the topic (4) stick to analyzing and summing-up the contents just learned 3. how to do assessment about the outcome for your study (Our plan in this ...
... (2) spend more time to the subject (at least 8 hours for one topic ) (3) persist in thinking the topic and find more information about the topic (4) stick to analyzing and summing-up the contents just learned 3. how to do assessment about the outcome for your study (Our plan in this ...
HuaLi (215-221) - Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition
... 7.7%, respectively). Each percentage of histidine, arginine, cysteine and serine of BD was significantly lower than that of AS. BD had EAA7 and EAA9 values of 34.436.4% and 40.5-41.7% respectively, slightly higher than AS (33.7% and 40.3%, respectively). The EAA score of proteins in BD and AS was gi ...
... 7.7%, respectively). Each percentage of histidine, arginine, cysteine and serine of BD was significantly lower than that of AS. BD had EAA7 and EAA9 values of 34.436.4% and 40.5-41.7% respectively, slightly higher than AS (33.7% and 40.3%, respectively). The EAA score of proteins in BD and AS was gi ...
The RNA origin of transfer RNA aminoacylation and beyond
... respectively. P3 shown in box with question mark is a putative pair region. Proposed bases that form Watson–Crick pairs in r24min (G43 –U45) and tRNAs (A73 –C75) are underlined and the red-dashed arrow indicates their interactions. Putative bases involving the constitution of the Phe-binding site ar ...
... respectively. P3 shown in box with question mark is a putative pair region. Proposed bases that form Watson–Crick pairs in r24min (G43 –U45) and tRNAs (A73 –C75) are underlined and the red-dashed arrow indicates their interactions. Putative bases involving the constitution of the Phe-binding site ar ...
A Nascent Membrane Protein Is Located Adjacent to ER Membrane
... membrane was investigated by photocrosslinking. Nascent polypeptides of different lengths, each containing a single IgM transmembrane sequence that functions either as a stop-transfer or a signal-anchor sequence, were synthesized by in vitro translation of truncated mRNAs in the presence of N~-(5-az ...
... membrane was investigated by photocrosslinking. Nascent polypeptides of different lengths, each containing a single IgM transmembrane sequence that functions either as a stop-transfer or a signal-anchor sequence, were synthesized by in vitro translation of truncated mRNAs in the presence of N~-(5-az ...
Structural Insights into Triglyceride Storage Mediated by
... and is expressed in all mammalian tissues, with the highest levels in white and brown adipose tissue [12]. The topology of FIT2 was previously predicted by the TMHMM algorithm to contain either five or six transmembrane domains [12]. In order to determine the orientation of the N- and C-terminus and ...
... and is expressed in all mammalian tissues, with the highest levels in white and brown adipose tissue [12]. The topology of FIT2 was previously predicted by the TMHMM algorithm to contain either five or six transmembrane domains [12]. In order to determine the orientation of the N- and C-terminus and ...
Protein

Proteins (/ˈproʊˌtiːnz/ or /ˈproʊti.ɨnz/) are large biomolecules, or macromolecules, consisting of one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within living organisms, including catalyzing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific three-dimensional structure that determines its activity.A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than about 20-30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides, or sometimes oligopeptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residues in a protein is defined by the sequence of a gene, which is encoded in the genetic code. In general, the genetic code specifies 20 standard amino acids; however, in certain organisms the genetic code can include selenocysteine and—in certain archaea—pyrrolysine. Shortly after or even during synthesis, the residues in a protein are often chemically modified by posttranslational modification, which alters the physical and chemical properties, folding, stability, activity, and ultimately, the function of the proteins. Sometimes proteins have non-peptide groups attached, which can be called prosthetic groups or cofactors. Proteins can also work together to achieve a particular function, and they often associate to form stable protein complexes.Once formed, proteins only exist for a certain period of time and are then degraded and recycled by the cell's machinery through the process of protein turnover. A protein's lifespan is measured in terms of its half-life and covers a wide range. They can exist for minutes or years with an average lifespan of 1–2 days in mammalian cells. Abnormal and or misfolded proteins are degraded more rapidly either due to being targeted for destruction or due to being unstable.Like other biological macromolecules such as polysaccharides and nucleic acids, proteins are essential parts of organisms and participate in virtually every process within cells. Many proteins are enzymes that catalyze biochemical reactions and are vital to metabolism. Proteins also have structural or mechanical functions, such as actin and myosin in muscle and the proteins in the cytoskeleton, which form a system of scaffolding that maintains cell shape. Other proteins are important in cell signaling, immune responses, cell adhesion, and the cell cycle. Proteins are also necessary in animals' diets, since animals cannot synthesize all the amino acids they need and must obtain essential amino acids from food. Through the process of digestion, animals break down ingested protein into free amino acids that are then used in metabolism.Proteins may be purified from other cellular components using a variety of techniques such as ultracentrifugation, precipitation, electrophoresis, and chromatography; the advent of genetic engineering has made possible a number of methods to facilitate purification. Methods commonly used to study protein structure and function include immunohistochemistry, site-directed mutagenesis, X-ray crystallography, nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry.