Jeopardy Review for Final Exam
... • Animals whose body fluids match the osmolarity of their environment such as ...
... • Animals whose body fluids match the osmolarity of their environment such as ...
Second Semester Anatomy
... How Do You Taste? • Gustatory cells- respond to chemicals that are dissolved in saliva • Taste buds- receptor sites for tastes. Most are on the tongue. Some are on the roof of the mouth and cheeks • Papillae- on the sides of this structure is where taste buds are found ...
... How Do You Taste? • Gustatory cells- respond to chemicals that are dissolved in saliva • Taste buds- receptor sites for tastes. Most are on the tongue. Some are on the roof of the mouth and cheeks • Papillae- on the sides of this structure is where taste buds are found ...
Chelsea
... Students know why an individual with a compromised immune system (for example, a person with AIDS) may be unable to fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually benign. Students know the roles of phagocytes, B-lymphocytes, and T-lymphocytes in the immune system. ...
... Students know why an individual with a compromised immune system (for example, a person with AIDS) may be unable to fight off and survive infections by microorganisms that are usually benign. Students know the roles of phagocytes, B-lymphocytes, and T-lymphocytes in the immune system. ...
Body Organization - Junction Hill C
... • Covers and protects underlying issue. • When you look at the surface of your skin, you see epithelial tissue. • The cells stick tightly and form a continuous sheet. ...
... • Covers and protects underlying issue. • When you look at the surface of your skin, you see epithelial tissue. • The cells stick tightly and form a continuous sheet. ...
Page 1 of 2 KLFY TV 10 - Acadiana`s Local News, Weather and
... In those with no pain, the brain regions displayed a state of equilibrium. When one region was active, the other regions calmed down. But in people with chronic pain, the front region of the cortex mostly associated with emotion "never shuts up," study author Dante Chialvo, an associate research pro ...
... In those with no pain, the brain regions displayed a state of equilibrium. When one region was active, the other regions calmed down. But in people with chronic pain, the front region of the cortex mostly associated with emotion "never shuts up," study author Dante Chialvo, an associate research pro ...
Practical Considerations for Structural Integration
... I want to preface this article with some basic facts that will help you to comprehend the biased point of view I wish to develop: • The peripheral nerves approximate a length of 100,000 km. • The central and peripheral nervous systems (CNS, PNS) are composed of 14 billion nerve cells (14,000,000,000 ...
... I want to preface this article with some basic facts that will help you to comprehend the biased point of view I wish to develop: • The peripheral nerves approximate a length of 100,000 km. • The central and peripheral nervous systems (CNS, PNS) are composed of 14 billion nerve cells (14,000,000,000 ...
Spinal Cord Injury Respiratory Care Module 2
... muscles. The lower the injury in the thoracic area the less muscle control that is lost. A high thoracic injury will result in a loss of most of the intercostal and abdominal muscle control. Complete injuries in the cervical area usually result in a total loss of intercostal and abdominal muscle c ...
... muscles. The lower the injury in the thoracic area the less muscle control that is lost. A high thoracic injury will result in a loss of most of the intercostal and abdominal muscle control. Complete injuries in the cervical area usually result in a total loss of intercostal and abdominal muscle c ...
Hypothalamus and Basic Needs
... synapse in the posterior pituitary. This provides a direct neural connection between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. ...
... synapse in the posterior pituitary. This provides a direct neural connection between the hypothalamus and the pituitary. ...
Body Organization - Junction Hill C
... • Covers and protects underlying issue. • When you look at the surface of your skin, you see epithelial tissue. • The cells stick tightly and form a continuous sheet. ...
... • Covers and protects underlying issue. • When you look at the surface of your skin, you see epithelial tissue. • The cells stick tightly and form a continuous sheet. ...
Sensory Neurophys
... the stimulus below perception threshold. Primary sensory neurons may perceive the sound, but higher order neurons dampen the intensity by the time it reaches the auditory cortex. ...
... the stimulus below perception threshold. Primary sensory neurons may perceive the sound, but higher order neurons dampen the intensity by the time it reaches the auditory cortex. ...
Human Body Quiz
... Which body system controls all of your other systems? A. circulatory B. digestive C. nervous D. muscular ...
... Which body system controls all of your other systems? A. circulatory B. digestive C. nervous D. muscular ...
Chapter 7 Notes Part 2
... Whitish, fatty material covering axon Functions: protection, insulation, & increasing transmission rate of impulses Schwann cells—produce myelin sheaths in jelly roll–like fashion Nodes of Ranvier—gaps in myelin sheath along the axon Multiple Sclerosis (MS) – myelin sheaths gradually destr ...
... Whitish, fatty material covering axon Functions: protection, insulation, & increasing transmission rate of impulses Schwann cells—produce myelin sheaths in jelly roll–like fashion Nodes of Ranvier—gaps in myelin sheath along the axon Multiple Sclerosis (MS) – myelin sheaths gradually destr ...
Body Systems - Cloudfront.net
... contracts, causing the elbow to bend. • The tricep muscle contracts, causing the elbow to straighten. This works similar to what simple machine? ...
... contracts, causing the elbow to bend. • The tricep muscle contracts, causing the elbow to straighten. This works similar to what simple machine? ...
the diencephalon - Anatomický ústav 1. LF UK
... Receives input predominantly from a single source Processed information is sent to a localized region of cortex Are modality specific Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized cortical response) ...
... Receives input predominantly from a single source Processed information is sent to a localized region of cortex Are modality specific Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized cortical response) ...
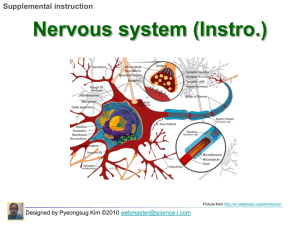
NERVOUS SYSTEM - Rawal College Of Dentistry
... Externally placed white matter Internally present butterfly shaped grey matter Central canal ...
... Externally placed white matter Internally present butterfly shaped grey matter Central canal ...
the nervous system
... In the forearm, the flexor is the biceps muscle which contracts to bend the limb and the extensor is the triceps muscle which contracts to straighten the limb. When one of the pair is stimulated to contract, the other relaxes and is stretched (contraction of the antagonist is prevented by a reflex a ...
... In the forearm, the flexor is the biceps muscle which contracts to bend the limb and the extensor is the triceps muscle which contracts to straighten the limb. When one of the pair is stimulated to contract, the other relaxes and is stretched (contraction of the antagonist is prevented by a reflex a ...
Human Body Notes Website
... can be stretched too much or even torn. Over time the body will heal the damaged muscle. Example: Pulled muscles can occur when a person doesn‘t stretch before sports. ...
... can be stretched too much or even torn. Over time the body will heal the damaged muscle. Example: Pulled muscles can occur when a person doesn‘t stretch before sports. ...
Oegan Systems Compiled Questions
... E9. How does the skin eliminate waste in the body? (1) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ E10. Where are the nephrons located? What do they do? (2) _________________________________________ ...
... E9. How does the skin eliminate waste in the body? (1) ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ E10. Where are the nephrons located? What do they do? (2) _________________________________________ ...
EVEN/ODD
... then tells the body what to do c. 3 main parts i. ___________________ – largest part, where most thinking takes place, solves problems, forms emotions (feelings), makes decisions, and controls how you learn, receives and answers messages from senses 1. divided into 2 halves called __________________ ...
... then tells the body what to do c. 3 main parts i. ___________________ – largest part, where most thinking takes place, solves problems, forms emotions (feelings), makes decisions, and controls how you learn, receives and answers messages from senses 1. divided into 2 halves called __________________ ...
Nervous System
... What are the two main divisions of the nervous system? What are the main structures of each (i.e. the brain is in the CNS, etc.) ...
... What are the two main divisions of the nervous system? What are the main structures of each (i.e. the brain is in the CNS, etc.) ...
Body Systems
... homeostasis by sending chemical messages to the brain that tell the status of pain, temperature, hunger, etc. so that the body can make adjustments using other systems ...
... homeostasis by sending chemical messages to the brain that tell the status of pain, temperature, hunger, etc. so that the body can make adjustments using other systems ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.