Functional Anatomy PPT
... internal organs Muscular system- provides movement both externally and internally ...
... internal organs Muscular system- provides movement both externally and internally ...
7th Human Body Systems Project Ppt Human Body Systems
... • What are the basic parts of the system? • How does it interact with other systems? ...
... • What are the basic parts of the system? • How does it interact with other systems? ...
reGIONS in the body
... Oral and digestive – mouth and cavities of the digestive organs Nasal –located within and posterior to the nose Orbital – house the eyes Middle ear – contain bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations ...
... Oral and digestive – mouth and cavities of the digestive organs Nasal –located within and posterior to the nose Orbital – house the eyes Middle ear – contain bones (ossicles) that transmit sound vibrations ...
the diencephalon
... MGN, LGN, VPL, VPM, VL, VA Receives input predominantly from a single source Processed information is sent to a localized region of cortex Are modality specific Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized cortical response) ...
... MGN, LGN, VPL, VPM, VL, VA Receives input predominantly from a single source Processed information is sent to a localized region of cortex Are modality specific Specific nuclei (after stimulation sharply localized cortical response) ...
CHAPTER OUTLINE
... The cells of a tissue can function in a coordinated manner when the plasma membranes of adjoining cells interact. Three common types of junctions link epithelial cells: tight, gap and adhesion junctions. Connective Tissue Connective tissue binds organs together, provides support and protection, fill ...
... The cells of a tissue can function in a coordinated manner when the plasma membranes of adjoining cells interact. Three common types of junctions link epithelial cells: tight, gap and adhesion junctions. Connective Tissue Connective tissue binds organs together, provides support and protection, fill ...
7th Grade Human Body Systems Project INFORMATION THAT
... - Define and show compact and spongy bone. - Show which bones are in the axial and appendicular skeleton - What organs do your skull and ribs protect? Nervous System: - Main purpose (function) - What do nerves do? - Definition and example of autonomic and voluntary nervous system. - Label the Centra ...
... - Define and show compact and spongy bone. - Show which bones are in the axial and appendicular skeleton - What organs do your skull and ribs protect? Nervous System: - Main purpose (function) - What do nerves do? - Definition and example of autonomic and voluntary nervous system. - Label the Centra ...
Diagram to Review 33
... of diverse forms, including snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. • Most mollusks are marine, though some inhabit fresh water, and some snails and slugs live on land. • Mollusks are soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell of calcium carbonate. – Slugs, sq ...
... of diverse forms, including snails and slugs, oysters and clams, and octopuses and squids. • Most mollusks are marine, though some inhabit fresh water, and some snails and slugs live on land. • Mollusks are soft-bodied animals, but most are protected by a hard shell of calcium carbonate. – Slugs, sq ...
48x36 Poster Template
... cells are named for their ability to give rise to progeny that become mature, myelinating oligodendrocytes in the white matter of the brain. These cells also express Olig2, a basic helixloop-helix transcription factor. ...
... cells are named for their ability to give rise to progeny that become mature, myelinating oligodendrocytes in the white matter of the brain. These cells also express Olig2, a basic helixloop-helix transcription factor. ...
7L3B2 Human Body Systems Notes/Study Guide
... ● The main function of the musculoskeletal system is to provide movement and support for the body, to protect internal organs, and to provide attachment sites for the muscles. ● The main organs of the musculoskeletal system are: 1) Muscles - soft tissue that has the ability to relax and contract in ...
... ● The main function of the musculoskeletal system is to provide movement and support for the body, to protect internal organs, and to provide attachment sites for the muscles. ● The main organs of the musculoskeletal system are: 1) Muscles - soft tissue that has the ability to relax and contract in ...
Endocrine System - DigitalCommons@University of Nebraska
... Endocrine System In complex animals the two principal systems of regulation are the endocrine system and the nervous systems. The endocrine system consists of the ductless endocrine glands, which secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system b ...
... Endocrine System In complex animals the two principal systems of regulation are the endocrine system and the nervous systems. The endocrine system consists of the ductless endocrine glands, which secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. The endocrine system and the autonomic nervous system b ...
THALAMUS - Wikispaces
... • Functionally considered as the great sensory gateway to the cerebral cortex • It relays received information to the cerebral cortex from diverse brain regions. • Axons from every sensory system (except olfaction) synapse in the thalamus as the last relay site before the information reaches the cer ...
... • Functionally considered as the great sensory gateway to the cerebral cortex • It relays received information to the cerebral cortex from diverse brain regions. • Axons from every sensory system (except olfaction) synapse in the thalamus as the last relay site before the information reaches the cer ...
C Fiber Stimulation
... The majority of nocieptive input to the CNS is carried my C fibers. Somatic C fibers terminate principally within lamina 2 (substania gelatinosa) Visceral noicieptive C fibers from the esophagus, larynx, and trachea travel with the vagus nerve to enter the nucleus solitarious in the brain stem Some ...
... The majority of nocieptive input to the CNS is carried my C fibers. Somatic C fibers terminate principally within lamina 2 (substania gelatinosa) Visceral noicieptive C fibers from the esophagus, larynx, and trachea travel with the vagus nerve to enter the nucleus solitarious in the brain stem Some ...
the structure of the human body
... - groups of organs that perform a complex body function e.g. Cardiovascular system organ: - different tissues arranged to perform a specific function e.g. kidney ...
... - groups of organs that perform a complex body function e.g. Cardiovascular system organ: - different tissues arranged to perform a specific function e.g. kidney ...
Body Systems Stations Reference Sheets
... coordinate actions. Thin threads of nerve cells, called neurons, carry messages throughout the body. Sensory nerves carry these messages to the brain through the spinal cord, while motor nerves carry them from the brain to all of the various muscles and glands. A tiny electrical pulse generates when ...
... coordinate actions. Thin threads of nerve cells, called neurons, carry messages throughout the body. Sensory nerves carry these messages to the brain through the spinal cord, while motor nerves carry them from the brain to all of the various muscles and glands. A tiny electrical pulse generates when ...
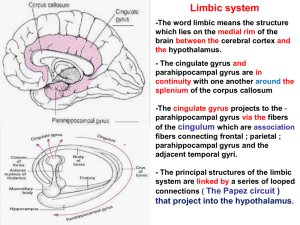
16. Limbic system2010-10-01 05:141.9 MB
... - It lies near the anterior temporal pole, between the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle and the lentiform nucleus. - It appears to provide an affective connotation to experience and social stimuli. - It receives afferents from the inferior temporal association cortex ; the olfactory tract and ...
... - It lies near the anterior temporal pole, between the inferior horn of the lateral ventricle and the lentiform nucleus. - It appears to provide an affective connotation to experience and social stimuli. - It receives afferents from the inferior temporal association cortex ; the olfactory tract and ...
STUDY GUIDE
... List the levels of organization from the most complex to the simplest. 1) Organismic _____________________________________________ ...
... List the levels of organization from the most complex to the simplest. 1) Organismic _____________________________________________ ...
Body System Structures Function
... broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive and circulatory systems. Regulation is the process of body systems working together to m ...
... broken down into smaller molecules that can be absorbed and distributed to cells. The blood stream transports molecules to the cells. The main organ systems that interact in nutrient absorption are the digestive and circulatory systems. Regulation is the process of body systems working together to m ...
gas exchange in human_HKDSE_print
... Oxygen levels is Less effective than changes in blood CO2 level Changes in Co2 and O2 concentration in the blood are detected by chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid artery Information is sent to the medulla oblongata ...
... Oxygen levels is Less effective than changes in blood CO2 level Changes in Co2 and O2 concentration in the blood are detected by chemoreceptors in the aorta and carotid artery Information is sent to the medulla oblongata ...
Unit 10- Human Body
... all body cells. Blood also carries hormones to their target tissues, carbon four compartments and four valves associated with it. dioxide back to the lungs, and other waste products to the excretory system. _____20____ carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and ___21____ (that contain valves to ...
... all body cells. Blood also carries hormones to their target tissues, carbon four compartments and four valves associated with it. dioxide back to the lungs, and other waste products to the excretory system. _____20____ carry oxygenated blood away from the heart, and ___21____ (that contain valves to ...
Human Body Systems
... and coordinates most of the body’s actions and functions; includes the brain, nerves, spinal cord, and sense organs (18) organ (OR-guhn) a group of body tissues that work together to do a special job; examples include the heart, lungs, and skin (4) organism (OR-guh-ni-zuhm) a living thing, such as a ...
... and coordinates most of the body’s actions and functions; includes the brain, nerves, spinal cord, and sense organs (18) organ (OR-guhn) a group of body tissues that work together to do a special job; examples include the heart, lungs, and skin (4) organism (OR-guh-ni-zuhm) a living thing, such as a ...
Central nervous system

The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting of the brain and spinal cord. The central nervous system is so named because it integrates information it receives from, and coordinates and influences the activity of, all parts of the bodies of bilaterally symmetric animals — that is, all multicellular animals except sponges and radially symmetric animals such as jellyfish — and it contains the majority of the nervous system. Arguably, many consider the retina and the optic nerve (2nd cranial nerve), as well as the olfactory nerves (1st) and olfactory epithelium as parts of the CNS, synapsing directly on brain tissue without intermediate ganglia. Following this classification the olfactory epithelium is the only central nervous tissue in direct contact with the environment, which opens up for therapeutic treatments. The CNS is contained within the dorsal body cavity, with the brain housed in the cranial cavity and the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In vertebrates, the brain is protected by the skull, while the spinal cord is protected by the vertebrae, both enclosed in the meninges.