human oct-1 gene located on chromosome 1
... named in series according to their electrophoretic mobility or order of characterisation, but are known as Oct-factors and all recognised Oct proteins are members of the POU class of transcription factors. The gene symbol for the Oct-1 protein is OTF1 for humans and Oct-1 for mouse. In both species ...
... named in series according to their electrophoretic mobility or order of characterisation, but are known as Oct-factors and all recognised Oct proteins are members of the POU class of transcription factors. The gene symbol for the Oct-1 protein is OTF1 for humans and Oct-1 for mouse. In both species ...
Biotech unit Objectives
... DNA sequencing (Sanger method) DNA fingerprinting (RFLP analysis) with and without southern blotting Genetic engineering Creating a microarray assay Electrophoresis Identifying a cloned gene Be able to map a plasmid using DNA fragment sizes produced by electrophoresis. Understand the importance of ...
... DNA sequencing (Sanger method) DNA fingerprinting (RFLP analysis) with and without southern blotting Genetic engineering Creating a microarray assay Electrophoresis Identifying a cloned gene Be able to map a plasmid using DNA fragment sizes produced by electrophoresis. Understand the importance of ...
Ch 18.2-18.5 PPT
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
... transcription DNA methylation: methyl groups added to DNA; tightly packed; transcription Histone acetylation: acetyl groups added to histones; loosened; transcription ...
4.4 Genetic engineering and biotechnology - McLain
... (ii) advantage: [1 max] prevent birth of children with FAP / fewer deaths / less genetic disease; eliminate mutation from the population; reduce stress / uncertainty for parents; disadvantage: [1 max] allows selection of embryos for implantation (which may be unethical); leads to the euthanizing of ...
... (ii) advantage: [1 max] prevent birth of children with FAP / fewer deaths / less genetic disease; eliminate mutation from the population; reduce stress / uncertainty for parents; disadvantage: [1 max] allows selection of embryos for implantation (which may be unethical); leads to the euthanizing of ...
Cellular Control miniQUIZ
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
... Using the diagram above answer the following questions: a) Which segment of the fruit fly develops wings? b) Are plant homeobox genes homologous to the homeobox genes in the fruit fly? 17. Apoptosis is important during development. Define the meaning of apoptosis and give an example. ...
Document
... Genes are made of parts represented in the mRNA (exons) and parts that are transcribed but not present in the mRNA (introns). ...
... Genes are made of parts represented in the mRNA (exons) and parts that are transcribed but not present in the mRNA (introns). ...
molecular scissors to study gene function Marta Oliveira
... interspaced by unique DNA regions that come from several bacterial viruses, which works as a DNA record of previous attacks. It was later proved that the CRISPR loci, together with many enzymes, were in fact a bacterial defense mechanism against life threatening viral attacks, preventing the virus f ...
... interspaced by unique DNA regions that come from several bacterial viruses, which works as a DNA record of previous attacks. It was later proved that the CRISPR loci, together with many enzymes, were in fact a bacterial defense mechanism against life threatening viral attacks, preventing the virus f ...
M220 Lecture 13 DNA is replicated by a process known as semi
... called a mutant. The positioning of the nitrogenous bases in DNA in triplets produces sequences that ultimately build proteins. Four possible nitrogenous bases are used to build each triplet. How many different triplet sequences can be made from the four different bases? The answer is 64 different “ ...
... called a mutant. The positioning of the nitrogenous bases in DNA in triplets produces sequences that ultimately build proteins. Four possible nitrogenous bases are used to build each triplet. How many different triplet sequences can be made from the four different bases? The answer is 64 different “ ...
Viruses as Pathogens in Bacterial Gene Regulation
... Viruses as Pathogens in Bacterial Gene Regulation ...
... Viruses as Pathogens in Bacterial Gene Regulation ...
click here
... family is associated with the 3 + 2 kb fragment pattern, and the 5 kb pattern is associated with the wild type allele. Ans: (d). How do you explain the pattern for individual II-9? 7. deoxyadenosine triphosphate is the nucleotide tri-phosphate normally incorporated during DNA synthesis. Consequently ...
... family is associated with the 3 + 2 kb fragment pattern, and the 5 kb pattern is associated with the wild type allele. Ans: (d). How do you explain the pattern for individual II-9? 7. deoxyadenosine triphosphate is the nucleotide tri-phosphate normally incorporated during DNA synthesis. Consequently ...
amino acids
... Clue: check what is already known about the counterparts (homologues) of this gene in other evolutionarily related species. How to find them? We need a program to search other known genomes for fragments that are very similar to given input (they have to be transformed by the evolution from one to t ...
... Clue: check what is already known about the counterparts (homologues) of this gene in other evolutionarily related species. How to find them? We need a program to search other known genomes for fragments that are very similar to given input (they have to be transformed by the evolution from one to t ...
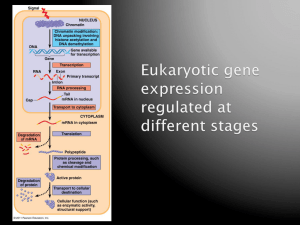
Gene expression An organism`s genome is the complete set of
... An organism’s genome is the complete set of genes in each of its cells. Given an organism, every one of its cells has a copy of the exact same genome, but ◆ not all its cells express the same genes ◆ different genes express under different conditions Measure the levels of the various mRNAs in a cell ...
... An organism’s genome is the complete set of genes in each of its cells. Given an organism, every one of its cells has a copy of the exact same genome, but ◆ not all its cells express the same genes ◆ different genes express under different conditions Measure the levels of the various mRNAs in a cell ...
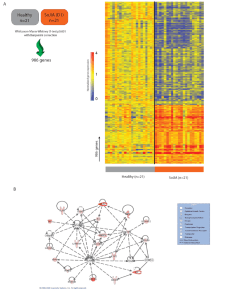
Slide 1
... A. Data were normalized in Beadstudio using the "average" method and imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s measurement in the healthy controls. To identify transcripts differentially expressed betw ...
... A. Data were normalized in Beadstudio using the "average" method and imported into Genespring 7.3 (Agilent) where the expression value for each gene was normalized to the median expression value of that gene’s measurement in the healthy controls. To identify transcripts differentially expressed betw ...
Genetic Engineering
... Plasmid is removed from bacteria cell (host cell) Plasmid is cut with restriction enzymes A gene is inserted into the plasmid Plasmid is returned to the cell When cell replicates it clones the gene The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic orga ...
... Plasmid is removed from bacteria cell (host cell) Plasmid is cut with restriction enzymes A gene is inserted into the plasmid Plasmid is returned to the cell When cell replicates it clones the gene The bacteria then infects other cells, giving them the gene (bacteria cell is called a transgenic orga ...