Chapter 16: The Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... 11. What does “semi-conservative” replication mean? 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between the 5’ and 3’ ends of the DNA molecule? Where are the 5’ and 3’ ends on opposite strands of the double helix? 14. What is the difference between the l ...
... 11. What does “semi-conservative” replication mean? 12. What are the functions of primase? DNA polymerase? Ligase? 13. What is the difference between the 5’ and 3’ ends of the DNA molecule? Where are the 5’ and 3’ ends on opposite strands of the double helix? 14. What is the difference between the l ...
013368718X_CH13_193
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
... 1. DNA contains the sugar ribose. 2. Messenger RNA carries copies of the instructions for making proteins from DNA to other parts of the cell. 3. RNA polymerase transfers amino acids to ribosomes. 4. The process of transcription produces a complementary strand of RNA on a DNA template. 5. The enzyme ...
Unit VII Objectives Biotechnology
... bioinformatics, and genomics. 2. What is meant by the universality of the genetic code? 3. Define polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Describe what is needed for PCR to happen, its process of DNA amplification, and list several uses. 4. Describe the process of gel electrophoresis and how it is used. 5. ...
... bioinformatics, and genomics. 2. What is meant by the universality of the genetic code? 3. Define polymerase chain reaction (PCR). Describe what is needed for PCR to happen, its process of DNA amplification, and list several uses. 4. Describe the process of gel electrophoresis and how it is used. 5. ...
Big
... be properly expressed – Place the recombinant DNA into an organism so that it is taken up and reproduced along with the rest of the organism's genome. ...
... be properly expressed – Place the recombinant DNA into an organism so that it is taken up and reproduced along with the rest of the organism's genome. ...
Table 3.
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
... Multiples melting peaks observed for nuclear gene (more than 2) Amplicon melting transitions not visible or are very small ...
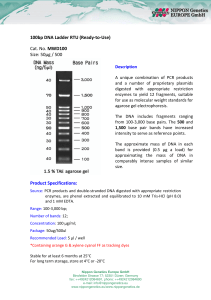
100bp DNA Ladder RTU (Ready-to-Use) Cat. No. MWD100 Size
... 100bp DNA Ladder RTU (Ready-to-Use) Cat. No. MWD100 Size: 50μg / 500 Description A unique combination of PCR products and a number of proprietary plasmids digested with appropriate restriction enzymes to yield 12 fragments, suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophores ...
... 100bp DNA Ladder RTU (Ready-to-Use) Cat. No. MWD100 Size: 50μg / 500 Description A unique combination of PCR products and a number of proprietary plasmids digested with appropriate restriction enzymes to yield 12 fragments, suitable for use as molecular weight standards for agarose gel electrophores ...
AP Biology Potential Essay Questions for Unit 3
... 2. Discuss the variety of gene interactions listed below. Be sure to explain the inheritance patter as well as give an authentic example of each. a. Incomplete/partial dominance b. Epistasis c. Pleiotrophy d. Multiple gene/polygenic inheritance e. Multiple alleles 3. Experiments by the following sci ...
... 2. Discuss the variety of gene interactions listed below. Be sure to explain the inheritance patter as well as give an authentic example of each. a. Incomplete/partial dominance b. Epistasis c. Pleiotrophy d. Multiple gene/polygenic inheritance e. Multiple alleles 3. Experiments by the following sci ...
AP Biology Potential Essay Questions for Unit 4
... 2. Discuss the variety of gene interactions listed below. Be sure to explain the inheritance patter as well as give an authentic example of each. a. Incomplete/partial dominance b. Epistasis c. Pleiotrophy d. Multiple gene/polygenic inheritance e. Multiple alleles 3. Experiments by the following sci ...
... 2. Discuss the variety of gene interactions listed below. Be sure to explain the inheritance patter as well as give an authentic example of each. a. Incomplete/partial dominance b. Epistasis c. Pleiotrophy d. Multiple gene/polygenic inheritance e. Multiple alleles 3. Experiments by the following sci ...
Slide 1
... Protein synthesis: series of steps that convert the DNA code into an organism’s features. Steps… 1. Focus on a single gene on a chromosome in the nucleus 2. DNA code gets converted to mRNA code by transcription (C-G, G-C, T-A, A-U) ...
... Protein synthesis: series of steps that convert the DNA code into an organism’s features. Steps… 1. Focus on a single gene on a chromosome in the nucleus 2. DNA code gets converted to mRNA code by transcription (C-G, G-C, T-A, A-U) ...
Name
... 3. A homeotic gene (1) A) turns on the genes necessary for synthesis of proteins. B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a prod ...
... 3. A homeotic gene (1) A) turns on the genes necessary for synthesis of proteins. B) serves as a master control gene that functions during embryonic development by controlling the developmental fate of groups of cells. C) represses gene transcription and promotes mRNA translation. D) produces a prod ...
DNA Replication
... • Cloning is used in agriculture to produce many copies of high-quality crop plants. • In medicine • to produce identical strands of bacteria for research. • to try to replace damaged cells, tissues, and possibly organs. • GENE cloning is more common than cloning of whole organisms. ...
... • Cloning is used in agriculture to produce many copies of high-quality crop plants. • In medicine • to produce identical strands of bacteria for research. • to try to replace damaged cells, tissues, and possibly organs. • GENE cloning is more common than cloning of whole organisms. ...
All Living things pass on their genetic heritage by common processes.
... Bacteriophage is a DNA bacterial virus of E. coli. Protein (S35) or DNA (P32)-labeled viruses were used to infect E. coli. Blended to separate viruses and bacteria followed by centrifugation: Protein remained outside the bacteria; DNA inside the bacteria. ...
... Bacteriophage is a DNA bacterial virus of E. coli. Protein (S35) or DNA (P32)-labeled viruses were used to infect E. coli. Blended to separate viruses and bacteria followed by centrifugation: Protein remained outside the bacteria; DNA inside the bacteria. ...
cDNA Library, Human HeLa Cell
... Linker-Primer method (Ref.1) by Professor Hiroshi Nojima of Research Institute for Microbial Diseases, Osaka University. This library is unidirectionally cloned by using the oligo (dT)18 linker primer which contains the restriction enzyme site of Not I, and BamHI (Bgl II)-Sma I adaptor. The pAP3neo ...
... Linker-Primer method (Ref.1) by Professor Hiroshi Nojima of Research Institute for Microbial Diseases, Osaka University. This library is unidirectionally cloned by using the oligo (dT)18 linker primer which contains the restriction enzyme site of Not I, and BamHI (Bgl II)-Sma I adaptor. The pAP3neo ...
Protein Synthesis - OpotikiCollegeBiology
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...
... and proteins are built out of amino acids. • How does the chromosome alphabet get changed into structures that join up to make proteins? ...
Chapter One
... DNA is in the nucleus of each cell DNA encodes for RNA (transcription) RNA encodes for Proteins (translation) DNA and RNA are made of nucleotides Protein is made of amino acids A protein’s function is determined by it’s structure, which is determined by it’s sequence • Therefore…DNA encodes protein ...
... DNA is in the nucleus of each cell DNA encodes for RNA (transcription) RNA encodes for Proteins (translation) DNA and RNA are made of nucleotides Protein is made of amino acids A protein’s function is determined by it’s structure, which is determined by it’s sequence • Therefore…DNA encodes protein ...
Advances in genetics
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
... Researchers have cloned pigs and sheep. This method is complex. Involves taking the nucleus of an animal’s body cell and using that to produce a new-animal. ...
Heredity
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
... Inherited traits-traits that are passed on from parents to offsprings. Genes-tiny message units Learned trait-a trait that is not passed on in DNA Dominant trait-a trait that will be expressed if it is inherited. Recessive trait-a trait that is not expressed if paired with a dominant trait Incomplet ...
Simple tandem repeats in mammalian genomes
... Particular proteins (transcription factors) bind to such regulatory sequences, thereby regulating gene expression. There is strong evidence that microsatellites can be part of regulatory sequences. Since they are often polymorphic, this may be a source of genetic variation in regulating gene express ...
... Particular proteins (transcription factors) bind to such regulatory sequences, thereby regulating gene expression. There is strong evidence that microsatellites can be part of regulatory sequences. Since they are often polymorphic, this may be a source of genetic variation in regulating gene express ...