assignmentschapters16-19and11-1
... 4. The chart lists a point mutation that may occur in the original strand of DNA. What happens to the amino acid sequence or protein produced as a result of this mutation? (Note: Position 1 refers to the first base at the 3 end of the transcribed strand. The last base in the DNA strand, at the 5 e ...
... 4. The chart lists a point mutation that may occur in the original strand of DNA. What happens to the amino acid sequence or protein produced as a result of this mutation? (Note: Position 1 refers to the first base at the 3 end of the transcribed strand. The last base in the DNA strand, at the 5 e ...
Control of Gene Expression
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
... Proteins which control the expression of other genes Link the genome with the environment Activated by signals from outside the cell (e.g. hormones, sugar, etc.) Allow RNA polymerase to bind to the promoter so that transcription can begin Gene must also be exposed –DNA must unwind in that area. ...
Problems in Replication and Protein Synthesis
... • Positive regulation – even though the repressor is inactive and the gene is on, protein production must be stimulated. • Ex. If lactose and glucose are both present E. Coli chooses to use glucose and does not produce enzyme to break down lactose (even though the lactose operon is on) ...
... • Positive regulation – even though the repressor is inactive and the gene is on, protein production must be stimulated. • Ex. If lactose and glucose are both present E. Coli chooses to use glucose and does not produce enzyme to break down lactose (even though the lactose operon is on) ...
Mini lab 11.1 and 11.2
... Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic ...
... Completes the assignment or experiment satisfactorily, but the explanations have minor flaws Begins the assignment and explanation satisfactorily; but omits significant parts or fails to complete. Assignment and its explanations are not accurate. Group did not demonstrate understanding or authentic ...
Practice Multiple Choice- Set 1 - mvhs
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
... c) The amount of energy indicates what is passed out as feces d) It indicates the diversity of an environment f) Animals can only be at the top level ...
Chapters 18-19
... 3) Bacteria have many ways to increase their genetic diversity and to control their metabolism a. Explain how transformation, transduction and conjugation increase genetic variation in bacteria b. Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and ...
... 3) Bacteria have many ways to increase their genetic diversity and to control their metabolism a. Explain how transformation, transduction and conjugation increase genetic variation in bacteria b. Describe the operon hypothesis and discuss how it explains the control of messenger RNA production and ...
Basics of DNA
... as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a ...
... as 50 nucleotides and as long as 250 million. Humans have over 3 billion nucleotides or 1 billion codons Each gene codes for a ...
Biotechnology
... There are well over a hundred restriction enzymes, each cutting in a very precise way a specific base sequence of the DNA molecule. ...
... There are well over a hundred restriction enzymes, each cutting in a very precise way a specific base sequence of the DNA molecule. ...
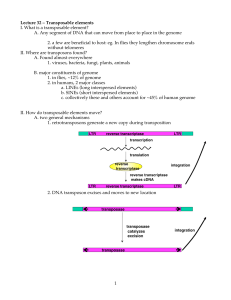
Transposable elements I. What is a transposable element?
... II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (long interspersed elements) b. SINEs (short interspersed elements) c. collectively these and ot ...
... II. Where are transposons found? A. Found almost everywhere 1. viruses, bacteria, fungi, plants, animals B. major constituents of genome 1. in flies, ~12% of genome 2. in humans, 2 major classes a. LINEs (long interspersed elements) b. SINEs (short interspersed elements) c. collectively these and ot ...
How can we tell synthetic from native sequences?
... maximize difference (Avoid first 100 bases of each gene) At least 33% of nucleotides recoded (target tags to regions where amino acids can vary at >1 nucleotide) First and last nucleotides correspond to variable position Melting temperature between 58-60C Amplifies 200-500 bp fragment Primers will n ...
... maximize difference (Avoid first 100 bases of each gene) At least 33% of nucleotides recoded (target tags to regions where amino acids can vary at >1 nucleotide) First and last nucleotides correspond to variable position Melting temperature between 58-60C Amplifies 200-500 bp fragment Primers will n ...
Document
... distinguishing at the same time between coding and non coding DNA. The time has come, in my opinion, for another parallel and complementary switch from a “mechanistic era” to a new one concerning the functional dynamics of gene networks and thereby of protein and metabolic networks. This implies, at ...
... distinguishing at the same time between coding and non coding DNA. The time has come, in my opinion, for another parallel and complementary switch from a “mechanistic era” to a new one concerning the functional dynamics of gene networks and thereby of protein and metabolic networks. This implies, at ...
Principles and Practices of Biosafety
... Donor Organism and Cloned DNA Insertion of well-characterized DNA sequences that are unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity may not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of ...
... Donor Organism and Cloned DNA Insertion of well-characterized DNA sequences that are unlikely to be involved in pathogenicity may not require additional safety measures. In cases where these sequences are not characterized, a situation that is typically encountered when a library of genomic DNA of ...
pdb-d.eng.uiowa.edu
... May end up closer due to bending Typically more global regulatory elements, tissue or time ...
... May end up closer due to bending Typically more global regulatory elements, tissue or time ...
Welkin`s Presentation on Assigning and Correctly
... number. – Most of these will be supported by HHpred and BLAST on NCBI. ...
... number. – Most of these will be supported by HHpred and BLAST on NCBI. ...
Unit 2 MI Study Guide
... allows chloride ions across epithelial cells inside the lungs. An error in the gene causes the transport proteins to not function properly, causing a buildup of mucus in the lungs. The lung tissue is the target tissue for gene therapy. Lung tissue divides slowly or not at all. What gene therapy vect ...
... allows chloride ions across epithelial cells inside the lungs. An error in the gene causes the transport proteins to not function properly, causing a buildup of mucus in the lungs. The lung tissue is the target tissue for gene therapy. Lung tissue divides slowly or not at all. What gene therapy vect ...