GENETICS PROBLEMS - Review Questions
... GENETICS & SOCIETY/TECHNOLOGY/ENV'T - Review Questions 1. Describe the "nuclear transfer" method of cloning frogs. (What kinds of cells were used, and what was done with them?) 2. What was unique about the "nuclear transfer" method of cloning used for Dolly the sheep? 3. What is recombinant DNA? 4. ...
... GENETICS & SOCIETY/TECHNOLOGY/ENV'T - Review Questions 1. Describe the "nuclear transfer" method of cloning frogs. (What kinds of cells were used, and what was done with them?) 2. What was unique about the "nuclear transfer" method of cloning used for Dolly the sheep? 3. What is recombinant DNA? 4. ...
Chapter 11 Concept Check Questions
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
... 3. Desribe the experimental design that allowed Hershey and Chase to distinguish between the two options for genetic material. ...
Previously in Bio308
... How would a neuropeptide get made (in general terms)? What are the basic parts of DNA, RNA, and proteins? What is the difference between hnRNA, mRNA and tRNA? ...
... How would a neuropeptide get made (in general terms)? What are the basic parts of DNA, RNA, and proteins? What is the difference between hnRNA, mRNA and tRNA? ...
Biology Vocabulary 8, test on Thursday, 1/19/17
... selective breeding of closely related organisms to produce desired traits and eliminate undesired traits, resulting in pure lines; however, harmful recessive traits can also be passed on complex inheritance pattern in which the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between those of the two homozygo ...
... selective breeding of closely related organisms to produce desired traits and eliminate undesired traits, resulting in pure lines; however, harmful recessive traits can also be passed on complex inheritance pattern in which the heterozygous phenotype is intermediate between those of the two homozygo ...
Lecture
... Idea: to look at DNA directly from the environment One way: clone really large pieces ...
... Idea: to look at DNA directly from the environment One way: clone really large pieces ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... nonsense mutations (which change an amino acid-encoding codon into a stop codon). Mutations that involve insertion or deletion of nucleotides are called frameshift mutations. Expanding repeat mutations increase the number of copies of three-or four-nucleotide sequences over several generations. This ...
... nonsense mutations (which change an amino acid-encoding codon into a stop codon). Mutations that involve insertion or deletion of nucleotides are called frameshift mutations. Expanding repeat mutations increase the number of copies of three-or four-nucleotide sequences over several generations. This ...
Human Genome Project, Gene Therapy, and Cloning
... nucleotides (A,C,T,G) for ALL of the DNA in a human cell • To determine which sections of DNA represent the individual genes • To store this information in databases for analysis ...
... nucleotides (A,C,T,G) for ALL of the DNA in a human cell • To determine which sections of DNA represent the individual genes • To store this information in databases for analysis ...
transcript - Genetic Alliance UK
... where a cell is in the body, so not all proteins are made in every cell. If genes are incorrectly turned on or off, which can happen in genetic diseases, debilitating symptoms can sometimes occur. DNA code is represented as four letters, with each letter indicating a chemical compound, or ‘base’. DN ...
... where a cell is in the body, so not all proteins are made in every cell. If genes are incorrectly turned on or off, which can happen in genetic diseases, debilitating symptoms can sometimes occur. DNA code is represented as four letters, with each letter indicating a chemical compound, or ‘base’. DN ...
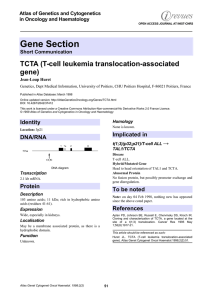
Gene Section TCTA (T-cell leukemia translocation-associated gene) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... No fusion protein, but possibly promoter exchange and gene disregulation. ...
... No fusion protein, but possibly promoter exchange and gene disregulation. ...
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
... There is great potential for the development of useful products through genetic engineering • EX., ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
... There is great potential for the development of useful products through genetic engineering • EX., ________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________ ...
PowerPoint Genetic Technology Notes
... for a genetic disorder such as cystic fibrosis (CF). Genetic tests are now available for diagnosing ___________ of disorders. Personal Identification No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___ ...
... for a genetic disorder such as cystic fibrosis (CF). Genetic tests are now available for diagnosing ___________ of disorders. Personal Identification No individual is exactly like any other genetically—except for ___________ twins, who share the same genome. Chromosomes contain many regions with ___ ...
Slide 1
... • Where is DNA found? • nucleus • Where else? • mitochondria, chloroplast (the endosymbiont theory) • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chroma ...
... • Where is DNA found? • nucleus • Where else? • mitochondria, chloroplast (the endosymbiont theory) • What form does DNA take in the nucleus? • chromosome • How do the 150 million base pairs that make up the human genome fit into the nucleus? • wrapped around histones • coiled and supercoiled chroma ...
Genetically Modified Foods and Organisms
... Plant biotechnology Using plant biotechnology, a single gene may be added to the strand. ...
... Plant biotechnology Using plant biotechnology, a single gene may be added to the strand. ...
Genome
... Constructing a timeline (history) and kinship for millions of life forms on Earth In Darwin’s book Origin of Species is an evolutionary tree, describing hierarchical structure relating species to their most recent common ancestors More recently, gene-sequence similarity as a criterion to uncover ...
... Constructing a timeline (history) and kinship for millions of life forms on Earth In Darwin’s book Origin of Species is an evolutionary tree, describing hierarchical structure relating species to their most recent common ancestors More recently, gene-sequence similarity as a criterion to uncover ...
organic compounds outline
... From Gene to Protein: ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins ______ ...
... From Gene to Protein: ____________________ – a segment of DNA that codes for the production of a specific protein Controls cell activities by what proteins (enzymes) they code for Order of bases determine what amino acids sequence is used in protein function of individual proteins ______ ...
C-13 Part II Non-Mendelian inheritance
... Continuous variation • When multiple genes act together to produce a physical (phenotypic) character, a gradation or range of differences occur. • Examples: height, weight in humans • Referred to as polygenic traits ...
... Continuous variation • When multiple genes act together to produce a physical (phenotypic) character, a gradation or range of differences occur. • Examples: height, weight in humans • Referred to as polygenic traits ...
Unit 1 - Glen Rose FFA
... the genes are located along the DNA molecule chromosomes occur in pairs ...
... the genes are located along the DNA molecule chromosomes occur in pairs ...
Recombinant DNA - Richmond School District
... inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
... inserted into the plasmid will only work if it DOESN’T have any introns. One way to do this is to synthesize the gene in a machine. Another method is to isolate the mRNA for the gene and use “REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE” to make a DNA copy of it. (= complementary DNA ...
So You Think
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...
... won the Nobel Prize for discovering the shape of DNA. ________________ 5. DNA is said to have a ___________ ___________ ________________ shape. ________________ 6. Weak _________________ bonds allow the DNA ________________ molecule to “unzip”. ________________ 7. RNA contains three of the same nucl ...