AP Biology
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
... 24. Distinguish between a point mutation and a frameshift mutation. Which would be more severe? ...
lecture notes
... DNA : deoxyribonucleic acid. Has a sugar backbone attached to a phosphate residue. Is a double helix structure with two complementary chains. Comprises of four different types of bases, A (adenine), T (thymine), C (cytosine), G (guanine) RNA : much like DNA but has U (uracil) instead of T, among ...
... DNA : deoxyribonucleic acid. Has a sugar backbone attached to a phosphate residue. Is a double helix structure with two complementary chains. Comprises of four different types of bases, A (adenine), T (thymine), C (cytosine), G (guanine) RNA : much like DNA but has U (uracil) instead of T, among ...
Reverse Engineering of Metazoan Gene Regulatory
... networks have however been poorly characterized. The recent availability of the human genome sequence, as well as genomic resources for other organisms, has permitted the development of novel methodologies that probe regulatory networks at a systems level rather than at the individual gene level. Mo ...
... networks have however been poorly characterized. The recent availability of the human genome sequence, as well as genomic resources for other organisms, has permitted the development of novel methodologies that probe regulatory networks at a systems level rather than at the individual gene level. Mo ...
Biology Chapter 11-1
... Ex. German Sheppard’s, toy poodles, and Great Danes Hybridization- A cross between dissimilar individuals. (usually between different, but related, species.) Ex. Mules and pigs Mutagens- substances in the environment, such as radiation and chemicals, that cause mutations. Genetic engineering- a form ...
... Ex. German Sheppard’s, toy poodles, and Great Danes Hybridization- A cross between dissimilar individuals. (usually between different, but related, species.) Ex. Mules and pigs Mutagens- substances in the environment, such as radiation and chemicals, that cause mutations. Genetic engineering- a form ...
Lecture_5
... • Direct incorporation - incorporates Cy3-or Cy5dNTP directly into cDNA – RNA to cDNA - reverse transcriptase – DNA to DNA - DNA polymerase – Big problem - Cy3 and Cy5 are not incorporated with same efficiency. ...
... • Direct incorporation - incorporates Cy3-or Cy5dNTP directly into cDNA – RNA to cDNA - reverse transcriptase – DNA to DNA - DNA polymerase – Big problem - Cy3 and Cy5 are not incorporated with same efficiency. ...
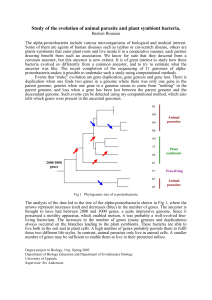
Study of the evolution of animal parasite bacteria and plant symbionts
... plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit from such an association. We know for sure that they descend from a common ancestor, but this ancestor is now extinct. It is of great interest to study how these bacteria evolved so diffe ...
... plants symbionts that enter plant roots and live inside it in a cooperative manner, each partner drawing benefit from such an association. We know for sure that they descend from a common ancestor, but this ancestor is now extinct. It is of great interest to study how these bacteria evolved so diffe ...
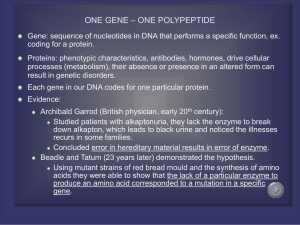
ONE GENE – ONE POLYPEPTIDE
... Ribose sugar (one more O than deoxyribose – an OH at C2) Uracil base instead of thymine (H on C1 instead of CH3), pairs with adenine Single stranded ...
... Ribose sugar (one more O than deoxyribose – an OH at C2) Uracil base instead of thymine (H on C1 instead of CH3), pairs with adenine Single stranded ...
(DNA and RNA).
... GENENGINEER: A scientist specializing in the manipulation of DNA and RNA to change the char- ...
... GENENGINEER: A scientist specializing in the manipulation of DNA and RNA to change the char- ...
AP Biology Chapter 18 Worksheet Part B
... 41. Why are fetal stem cells more valuable to DNA technology than adult stem cells? 42. What does plasmid size have to do with successful competencies? 43. What is the greatest benefit of microarrays? 44. Why are prokaryotic gene regulations so much simpler than eukaryotic ones? 45. List all the com ...
... 41. Why are fetal stem cells more valuable to DNA technology than adult stem cells? 42. What does plasmid size have to do with successful competencies? 43. What is the greatest benefit of microarrays? 44. Why are prokaryotic gene regulations so much simpler than eukaryotic ones? 45. List all the com ...
No Slide Title
... Cystic Fibrosis as Candidate for Gene Therapy 1. Recessive gene on chromosome 7. 2. CFTR is the gene product. 3. CFTR is an ion channel protein. 4. Normal gene sequence has been cloned. 5. Symptoms are localized to specific organs. 6. Adenovirus (cold virus) can be used to deliver normal sequence t ...
... Cystic Fibrosis as Candidate for Gene Therapy 1. Recessive gene on chromosome 7. 2. CFTR is the gene product. 3. CFTR is an ion channel protein. 4. Normal gene sequence has been cloned. 5. Symptoms are localized to specific organs. 6. Adenovirus (cold virus) can be used to deliver normal sequence t ...
BACTERIAL GENETICS
... • A-T and C-G • RNA -ribose instead of deoxyribose and uracil instead of thymine • Central dogma of molecular biology • DNA transcription RNA ribosomes polypeptide • mRNA,tRNA,rRNA. • Genetic information is stored in DNA as code. ...
... • A-T and C-G • RNA -ribose instead of deoxyribose and uracil instead of thymine • Central dogma of molecular biology • DNA transcription RNA ribosomes polypeptide • mRNA,tRNA,rRNA. • Genetic information is stored in DNA as code. ...
DNA Personal Ads
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
... sequence is really dull, and I’m ready to move on to more exciting things. I’m looking for my true love, mRNA. (transcription) ...
Presentation
... • High-copy suppressor screens -high copy plasmid or GAL promoter on CEN plasmid ...
... • High-copy suppressor screens -high copy plasmid or GAL promoter on CEN plasmid ...
Bioinformatics and the Language of DNA A. Tozeren
... the DNA (book of life). DNA various only so slightly between individuals in a species. ...
... the DNA (book of life). DNA various only so slightly between individuals in a species. ...
DNA viruses - WordPress.com
... than the mRNAs found on ribosomes, and in some cases, as much as 30% of the transcribed RNA remains untranslated in the nucleus. The viral messengers, however, like those of animal cells, are monocistronic. Transcription has a temporal organization, with most DNA viruses only a small fraction of the ...
... than the mRNAs found on ribosomes, and in some cases, as much as 30% of the transcribed RNA remains untranslated in the nucleus. The viral messengers, however, like those of animal cells, are monocistronic. Transcription has a temporal organization, with most DNA viruses only a small fraction of the ...
Goal 3
... The “rungs of the DNA ladder” are composed of complementary nitrogenous base pairs (always adenine, A, to thymine, T, and cytosine, C, to guanine, G) joined by weak hydrogen bonds. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA codes for proteins, which is central key to cell function and life. Replication occu ...
... The “rungs of the DNA ladder” are composed of complementary nitrogenous base pairs (always adenine, A, to thymine, T, and cytosine, C, to guanine, G) joined by weak hydrogen bonds. The sequence of nucleotides in DNA codes for proteins, which is central key to cell function and life. Replication occu ...
File
... Clarification: Limited to understanding that genetic engineering is used currently to produce gene products such as human insulin. The great responsibility is making sure that altered genes don’t upset natural ecosystems or cause human suffering. There are also ethical decisions regarding use of ste ...
... Clarification: Limited to understanding that genetic engineering is used currently to produce gene products such as human insulin. The great responsibility is making sure that altered genes don’t upset natural ecosystems or cause human suffering. There are also ethical decisions regarding use of ste ...
Title of Assignment:
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
... 3. A multicellular organism develops from a single zygote, and its phenotype depends on its genotype, which is established at fertilization. 4. Genes are a set of instructions encoded in the DNA sequence of each organism that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins characteristic of that org ...
DNA Worksheet
... 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
... 23. Use the amino acid chart in your notes to translate the sequence of codons (from #16) and write the ...
How DNA Determines Traits - Liberty Union High School District
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyze ...
... How Does DNA Determine the Traits of an Organism Introduction: In this simulation, you will examine the DNA sequence of a fictitious organism: the Snork. Snorks were discovered on the planet Dee Enae in a distant solar system. Snorks only have one chromosome with 6 genes on it. You job is to analyze ...