Structure and Role of DNA Genetic and DNA Genetics
... o DNA polymerase checks the arrangement of bases in the new DNA strands and fix errors Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes(contain genetic information) wraps around proteins and become tightly coiled Every species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in its cells Traits are dertermined by ...
... o DNA polymerase checks the arrangement of bases in the new DNA strands and fix errors Chromosomes and Genes Chromosomes(contain genetic information) wraps around proteins and become tightly coiled Every species has a characteristic number of chromosomes in its cells Traits are dertermined by ...
DNA and the genetic code
... How do bases pair together? Base pairs hold the two strands of the DNA helix together. The rules for base pairing are… ‘A’ always pairs with ‘T’ ...
... How do bases pair together? Base pairs hold the two strands of the DNA helix together. The rules for base pairing are… ‘A’ always pairs with ‘T’ ...
DNA RNA and Protein Synthesis with Answers
... b. fertilization of a sex cell c. sequencing of amino acids in cells d. increasing the number of cells in an organism ...
... b. fertilization of a sex cell c. sequencing of amino acids in cells d. increasing the number of cells in an organism ...
Lecture 20 Methodology for production of transgenic animals To
... transgene. However, the success rate of producing transgenic animals individually by these methods is very low and it may be more efficient to use cloning techniques to increase their numbers. For example, gene transfer studies revealed that only 0.6% of transgenic pigs were born with a desired gene ...
... transgene. However, the success rate of producing transgenic animals individually by these methods is very low and it may be more efficient to use cloning techniques to increase their numbers. For example, gene transfer studies revealed that only 0.6% of transgenic pigs were born with a desired gene ...
Chapter 7
... Transcription is regulated by repressors and activators. What is an inducer? A corepressor? How do these interact with repressors and activators and what happens when they bind to these proteins? How do bacteria sense what is going on in their environment? What is the lac operon and how is it regula ...
... Transcription is regulated by repressors and activators. What is an inducer? A corepressor? How do these interact with repressors and activators and what happens when they bind to these proteins? How do bacteria sense what is going on in their environment? What is the lac operon and how is it regula ...
Dna sequence and Cell Activity
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
... The sequence of bases on the DNA molecule provides a coded message for the manufacture of proteins on the ribosome. Since many proteins manufactured are enzymes, a mutation or change in this genetic code can have serious consequences for cellular metabolism. In the case of insertion or deletion poin ...
Gene Section CBFb (subunit b of core binding factor)
... Other names: PEBP2b (polyomavirus enhancer binding protein b) HGNC (Hugo): CBFB Location: 16q22 ...
... Other names: PEBP2b (polyomavirus enhancer binding protein b) HGNC (Hugo): CBFB Location: 16q22 ...
Lecture
... Basic Local Alignment Search Tool finds regions of local similarity between sequences ...
... Basic Local Alignment Search Tool finds regions of local similarity between sequences ...
DNA and RNA Review
... 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
... 11. How many codons are needed to specify three amino acids? 12. Explain why it is possible for an amino acid to be specified by more than one kind of codon? ...
Lecture 8 (2/15/10) "DNA Forensics, Cancer, and Sequencing"
... built to exist in a frigid climate, with A-positive blood, dark skin, brown eyes, and thick, black hair on a scalp genetically susceptible to baldness. He was a palaeoEskimo, and by comparing his genome to other living people, they deduced that he was member of the Arctic Saqqaq, the first known cul ...
... built to exist in a frigid climate, with A-positive blood, dark skin, brown eyes, and thick, black hair on a scalp genetically susceptible to baldness. He was a palaeoEskimo, and by comparing his genome to other living people, they deduced that he was member of the Arctic Saqqaq, the first known cul ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis: Power Point presentation
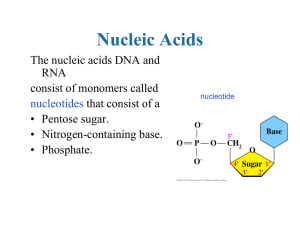
... Nucleic Acids The nucleic acids DNA and RNA consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
... Nucleic Acids The nucleic acids DNA and RNA consist of monomers called nucleotides that consist of a • Pentose sugar. • Nitrogen-containing base. • Phosphate. ...
Defined - cloudfront.net
... – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region ...
... – Some gene mutations change phenotype (physical characteristics) • Example: Can cause a premature stop codon – Some gene mutations don’t change phenotype. • Example: Could be silent or occur in a non-coding region ...
Genetics and Protein Synthesis
... 2. DNA contains adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) ; RNA contains A, G, C, and uracil (U) 3. DNA is double stranded (double helix); RNA is single stranded (single helix) ...
... 2. DNA contains adenine (A), thymine (T), guanine (G), and cytosine (C) ; RNA contains A, G, C, and uracil (U) 3. DNA is double stranded (double helix); RNA is single stranded (single helix) ...
Recombinant DNA
... jellyfish DNA that had been cut with REs Found fragment that bound exactly to mRNA – this was the gene ...
... jellyfish DNA that had been cut with REs Found fragment that bound exactly to mRNA – this was the gene ...
learning objectives
... 2. As the ribosome proceeds along the mRNA, the next amino acid is added to the growing peptide chain. 3. When the process is finished, the ribosome complex falls apart, and the completed protein is released into the cell. Architecture of the Gene (p. 232; Figs. 13.7, 13.8) A. Introns 1. Prokaryotic ...
... 2. As the ribosome proceeds along the mRNA, the next amino acid is added to the growing peptide chain. 3. When the process is finished, the ribosome complex falls apart, and the completed protein is released into the cell. Architecture of the Gene (p. 232; Figs. 13.7, 13.8) A. Introns 1. Prokaryotic ...
Nucleus - Control Center of cell
... Genes are found on Chromosomes •Specific places on Chromosomes contain small segments called ...
... Genes are found on Chromosomes •Specific places on Chromosomes contain small segments called ...
Wanganui High School
... Glossary allele: different version of a gene / alleles are genes that occupy the same position on homologous (similar) chromosomes artificial selection: the process of breeding plants and animals with desirable characteristics in the hope that their offspring will inherit them asexual reproduction: ...
... Glossary allele: different version of a gene / alleles are genes that occupy the same position on homologous (similar) chromosomes artificial selection: the process of breeding plants and animals with desirable characteristics in the hope that their offspring will inherit them asexual reproduction: ...
Dr Price 2nd lecture
... Ribosomal RNA genes are arranged in large clusters, and organisms have many copies of each (200 in humans) Histone genes have multiple copies ...
... Ribosomal RNA genes are arranged in large clusters, and organisms have many copies of each (200 in humans) Histone genes have multiple copies ...
Timeline
... Recombinant DNA pioneer Herbert Boyer co‐founds Genentech, the first company based on the technology. A human gene is expressed in bacteria for the first time. Genentech developed genetic engineering techniques to create micro-organisms that can produce insulin and growth hormone. Procedures are dev ...
... Recombinant DNA pioneer Herbert Boyer co‐founds Genentech, the first company based on the technology. A human gene is expressed in bacteria for the first time. Genentech developed genetic engineering techniques to create micro-organisms that can produce insulin and growth hormone. Procedures are dev ...