Module 5 revised
... Behavior Genetics Behavior Genetics study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on ...
... Behavior Genetics Behavior Genetics study of the relative power and limits of genetic and environmental influences on ...
Quiz 1 - Suraj @ LUMS
... 1. Which of these scientific terms has the greatest degree of certainty? a) hypothesis; b) theory; c) law; d) guess 2. Which of the following is the least inclusive (smallest) unit of classification? a) kingdom; b) species; c) genus; d) class; e) phylum 3. Bacteria belong to the taxonomic kingdom a) ...
... 1. Which of these scientific terms has the greatest degree of certainty? a) hypothesis; b) theory; c) law; d) guess 2. Which of the following is the least inclusive (smallest) unit of classification? a) kingdom; b) species; c) genus; d) class; e) phylum 3. Bacteria belong to the taxonomic kingdom a) ...
Comparative Genomics
... One possibility is horizontal transfer 41 genes may have been transferred in this way For example: MAOs, monoamine oxidases These enzymes deactivate neurotransmitters ...
... One possibility is horizontal transfer 41 genes may have been transferred in this way For example: MAOs, monoamine oxidases These enzymes deactivate neurotransmitters ...
Chapter 13
... 35. Examine the pGLO plasmid, ori, ampr ,the GFP gene, and the portion of the arabinose promoter that allows for the regulation of gene expression of GFP by arabinose sugar (lab) 36. View examples of the use of GFP as a reporter gene (lab) 37. Review steps of gene cloning using a plasmid/bacterium. ...
... 35. Examine the pGLO plasmid, ori, ampr ,the GFP gene, and the portion of the arabinose promoter that allows for the regulation of gene expression of GFP by arabinose sugar (lab) 36. View examples of the use of GFP as a reporter gene (lab) 37. Review steps of gene cloning using a plasmid/bacterium. ...
Control of Gene Expression - Downtown Magnets High School
... • Code for proteins or mRNAs which affect gene expression – Ex: microRNAs ...
... • Code for proteins or mRNAs which affect gene expression – Ex: microRNAs ...
Transgenic Sheep and Goats
... • Sheep fibroblasts (connective tissue cells) growing in tissue culture were treated with a vector that contained these segments of DNA: • 2 regions homologous to the sheep COL1A1 gene. This gene encodes Type 1 collagen. (Its absence in humans causes the inherited disease osteogenesis imperfecta.) ...
... • Sheep fibroblasts (connective tissue cells) growing in tissue culture were treated with a vector that contained these segments of DNA: • 2 regions homologous to the sheep COL1A1 gene. This gene encodes Type 1 collagen. (Its absence in humans causes the inherited disease osteogenesis imperfecta.) ...
hox genes - WordPress.com
... is junk DNA •PROMOTER REGIONS are associated with genes and help initialize transcription of the gene into a protein •GENETIC SWITCHES play a role regulating the EXPRESSION of genes ...
... is junk DNA •PROMOTER REGIONS are associated with genes and help initialize transcription of the gene into a protein •GENETIC SWITCHES play a role regulating the EXPRESSION of genes ...
Gene Regulation I. Gene regulation: The ability of an organism to
... 1. Operon consists of: a. Operator: Segment of DNA that acts as an on/off switch b. Promoter: Where RNA polymerase first binds to the DNA c. Regulatory gene: gene involved in controlling the expression of one or more other genes. A regulator gene may encode a protein, or it may work at the level of ...
... 1. Operon consists of: a. Operator: Segment of DNA that acts as an on/off switch b. Promoter: Where RNA polymerase first binds to the DNA c. Regulatory gene: gene involved in controlling the expression of one or more other genes. A regulator gene may encode a protein, or it may work at the level of ...
Themes in the Development of DNA Science
... 1) Some organisms do not use DNA as the storage molecule for the genetic code. RNA viruses store genetic info as RNA Genes are not immutably fixed on the chromosomes. Transposable genetic elements move around from one chromosome to another and may act as molecular switches to regulate gene expressio ...
... 1) Some organisms do not use DNA as the storage molecule for the genetic code. RNA viruses store genetic info as RNA Genes are not immutably fixed on the chromosomes. Transposable genetic elements move around from one chromosome to another and may act as molecular switches to regulate gene expressio ...
purpose - cloudfront.net
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
... Protein Synthesis Practice 1 PURPOSE To review protein synthesis PROCEDURE Place the steps of protein synthesis in the correct order. _____ DNA rejoins & mRNA leaves the nucleus _____ the mRNA codons pair up with the tRNA anticodons; amino acids are added _____ DNA unzips _____ a mRNA copy of the DN ...
Mutation identification by whole genome sequencing
... 3) allow primers to anneal, polymerase to synthesize DNA, heat to melt dsDNA, and repeat multiple times 4) run in an analyzer to separate DNA products of different sizes and detect them by fluorescence 5) Obtain sequence 2. Next Generation Sequencing by the Illumina method a. Completed in a flow cel ...
... 3) allow primers to anneal, polymerase to synthesize DNA, heat to melt dsDNA, and repeat multiple times 4) run in an analyzer to separate DNA products of different sizes and detect them by fluorescence 5) Obtain sequence 2. Next Generation Sequencing by the Illumina method a. Completed in a flow cel ...
Population Genetics
... Aim: What are population genetics and how do they affect evolution? I. Population Genetics – Genetics today is concerned with inheritance in large groups of sexually reproducing animals. The study of these organisms as a reproducing group is known as population genetics. A. Key Terms 1. Species – a ...
... Aim: What are population genetics and how do they affect evolution? I. Population Genetics – Genetics today is concerned with inheritance in large groups of sexually reproducing animals. The study of these organisms as a reproducing group is known as population genetics. A. Key Terms 1. Species – a ...
GENE EXPRESSION CHAPTER 11
... known commonly for their illegal use by athletes, anabolic steroids are used medically to treat growth abnormalities, anemia, leukemia, kidney failure, and other medical problems. ...
... known commonly for their illegal use by athletes, anabolic steroids are used medically to treat growth abnormalities, anemia, leukemia, kidney failure, and other medical problems. ...
DNA Unit Test Corrections
... 30. What is the normal function of the protein you named in questions #29?________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 31. What are some other functions of proteins in your b ...
... 30. What is the normal function of the protein you named in questions #29?________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________ 31. What are some other functions of proteins in your b ...
Unit VII Study Guide KEY
... And a third important difference is the organization of genes in the prokaryotic chromosome. Multiple genes required for a single metabolic pathway are organized together in groups known as _operons______. In addition to the genes coding for necessary _enzymes_____ for a particular metabolic pathway ...
... And a third important difference is the organization of genes in the prokaryotic chromosome. Multiple genes required for a single metabolic pathway are organized together in groups known as _operons______. In addition to the genes coding for necessary _enzymes_____ for a particular metabolic pathway ...
Molecular Biology Final Exam (Set A)
... basepairs wherever its sequence allows. Since this internal basepairing relies on self-complementary sequence, the way in which an RNA molecule folds is dependent on its nucleotide base sequence, and thus is different for every RNA. The implications of this are that RNA has a much wider range of thr ...
... basepairs wherever its sequence allows. Since this internal basepairing relies on self-complementary sequence, the way in which an RNA molecule folds is dependent on its nucleotide base sequence, and thus is different for every RNA. The implications of this are that RNA has a much wider range of thr ...
Gene Section AF1q (ALL1 fused gene from chromosome 1q)
... probes are welcome : contact rocchi@biologia.uniba.it. ...
... probes are welcome : contact rocchi@biologia.uniba.it. ...
Genetics - DNA
... Each chromosome contains many genes. We inherit two copies of each chromosome (one from each parent) and this is why our chromosomes can be arranged into homologous pairs. A Gene is a section of DNA that contains a specific sequence of bases. This sequence codes for a chain of amino acids that folds ...
... Each chromosome contains many genes. We inherit two copies of each chromosome (one from each parent) and this is why our chromosomes can be arranged into homologous pairs. A Gene is a section of DNA that contains a specific sequence of bases. This sequence codes for a chain of amino acids that folds ...
Supplemental File S10. Homologous
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): The genetic material of most organisms. DNA is a long doublehelical molecule composed of the deoxyribonucleotides-deoxyadenylic acid (A), dexythymidylic acid (T), deoxyguanylic acid (G), and deoxycytidylic acid (G). The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds bet ...
... Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA): The genetic material of most organisms. DNA is a long doublehelical molecule composed of the deoxyribonucleotides-deoxyadenylic acid (A), dexythymidylic acid (T), deoxyguanylic acid (G), and deoxycytidylic acid (G). The two strands are held together by hydrogen bonds bet ...
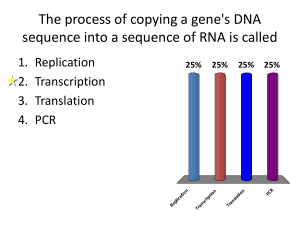
The process of copying a gene`s DNA sequence into a sequence of
... Which of the following statements is true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
... Which of the following statements is true regarding introns? 1. Introns are the parts of mRNA that are translated 2. Introns have no function. 3. In general, human genes have fewer introns than genes of other organisms. 4. Introns may be involved in exon shuffling ...
26. During interphase each chromosome replicates to two
... 33. The smallest unit able to perform the basic functions of life __________________________ 34. Any change made to the DNA molecule? __________________________ 35. If the two alleles for a gene, are both dominant or both recessive, we say they are __________________________. 36. During fertilizatio ...
... 33. The smallest unit able to perform the basic functions of life __________________________ 34. Any change made to the DNA molecule? __________________________ 35. If the two alleles for a gene, are both dominant or both recessive, we say they are __________________________. 36. During fertilizatio ...
NOTE: The provided figures may be useful and beneficial
... 3. Imagine that the non-template sequence in question 3 was transcribed instead of the template sequence. Draw the mRNA sequence and translate it using Figure 17.5. (Be sure to pay attention to the 5’ & 3’ ends.) 4. What enables RNA polymerase to start transcribing a gene at the right place on the D ...
... 3. Imagine that the non-template sequence in question 3 was transcribed instead of the template sequence. Draw the mRNA sequence and translate it using Figure 17.5. (Be sure to pay attention to the 5’ & 3’ ends.) 4. What enables RNA polymerase to start transcribing a gene at the right place on the D ...
Cellular Structure and Function Handout
... ______5. The transport of substances through a membrane against a concentration gradient is accomplished by a. facilitated diffusion b. active transport c. osmosis d. dialysis ______6. The smallest units of structure capable of performing all vital functions of living organisms are a. nucleotides b. ...
... ______5. The transport of substances through a membrane against a concentration gradient is accomplished by a. facilitated diffusion b. active transport c. osmosis d. dialysis ______6. The smallest units of structure capable of performing all vital functions of living organisms are a. nucleotides b. ...
Biology Assessment #3:
... 2. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA (location, function, size/structure/shape, nitrogen bases, etc.) 3. Explain how protein synthesis occurs. Explain the steps of transcription/translation. What is the role of different the types of RNA and of DNA in protein synthesis? 4. How are amino acids coded f ...
... 2. Compare and contrast DNA and RNA (location, function, size/structure/shape, nitrogen bases, etc.) 3. Explain how protein synthesis occurs. Explain the steps of transcription/translation. What is the role of different the types of RNA and of DNA in protein synthesis? 4. How are amino acids coded f ...