Document
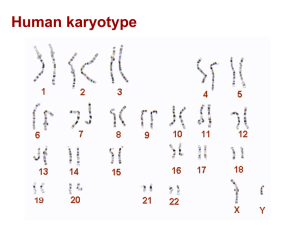
... • Genetic screening involves the testing of DNA. – determines risk of having DMD or passing on a genetic disorder – used to detect specific genes or proteins – can detect some genes related to an increased risk of cancer – can detect some genes known to cause genetic disorders ...
... • Genetic screening involves the testing of DNA. – determines risk of having DMD or passing on a genetic disorder – used to detect specific genes or proteins – can detect some genes related to an increased risk of cancer – can detect some genes known to cause genetic disorders ...
9.6 Genetic Screening and Gene Therapy KEY CONCEPT treatments.
... • Genetic screening involves the testing of DNA. – determines risk of having DMD or passing on a genetic disorder – used to detect specific genes or proteins – can detect some genes related to an increased risk of cancer – can detect some genes known to cause genetic disorders ...
... • Genetic screening involves the testing of DNA. – determines risk of having DMD or passing on a genetic disorder – used to detect specific genes or proteins – can detect some genes related to an increased risk of cancer – can detect some genes known to cause genetic disorders ...
Southern transfer
... has only two copies of a gene and some genes may be transcribed only in a subset of tissues or only at low levels, or both, providing only a small number of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. 2- purifying the sequence of interest from all the other segments of DNA or mRNA molecules present in the cell. ...
... has only two copies of a gene and some genes may be transcribed only in a subset of tissues or only at low levels, or both, providing only a small number of messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule. 2- purifying the sequence of interest from all the other segments of DNA or mRNA molecules present in the cell. ...
Name____________________________ DNA Investigation
... 2) What is a gene? 3) Approximately how many genes are encoded in the DNA of a human? 4) __________________________ is a genetic disease that results in the mutation of hemoglobin protein within our red blood cells. 5) Other than providing the instructions for building a hemoglobin molecule, what ar ...
... 2) What is a gene? 3) Approximately how many genes are encoded in the DNA of a human? 4) __________________________ is a genetic disease that results in the mutation of hemoglobin protein within our red blood cells. 5) Other than providing the instructions for building a hemoglobin molecule, what ar ...
Genetics Introduction:
... mRNA contains genetic code in triplet base codons that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins Transfer RNAs (tRNA) contain triplet base sequences (anticodons) which are complementary to codon sequences in mRNA and position amino acids during translation Translation- a cell interprets a seri ...
... mRNA contains genetic code in triplet base codons that specify the sequence of amino acids in proteins Transfer RNAs (tRNA) contain triplet base sequences (anticodons) which are complementary to codon sequences in mRNA and position amino acids during translation Translation- a cell interprets a seri ...
Detection of different genes heredity
... infections which can cause lung damage. The mucus also makes it difficult for digestion to occur. ...
... infections which can cause lung damage. The mucus also makes it difficult for digestion to occur. ...
Gene Cloning - Fort Bend ISD
... Gene Cloning: Producing multiple identical copies of a gene. Recombinant DNA: Genes or DNA from two difference sources are combined into one molecule. Genetic Engineering: Methods to create recombinant DNA. ...
... Gene Cloning: Producing multiple identical copies of a gene. Recombinant DNA: Genes or DNA from two difference sources are combined into one molecule. Genetic Engineering: Methods to create recombinant DNA. ...
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering
... or PHAs) • Note that in all of these cases, one needs to clone the genes encoding enzymes in order to create or alter a biochemical pathway ...
... or PHAs) • Note that in all of these cases, one needs to clone the genes encoding enzymes in order to create or alter a biochemical pathway ...
Chapter 19
... These genes are not cancerous, but if mutated, could lead to cancer. What is an oncogene? A mutated proto-oncogene which causes too much growth or loss of control over the cell cycle in some way. ...
... These genes are not cancerous, but if mutated, could lead to cancer. What is an oncogene? A mutated proto-oncogene which causes too much growth or loss of control over the cell cycle in some way. ...
04/01
... synergistically to elevate transcription rate. In b-interferon gene transcription, TFs recruit a coactivator (CBP) which is needed for transcription to occur normally. Formation of the enhanceosome and activation of RNA polymerase by coactivator are necessary for efficient transcription. Transcripti ...
... synergistically to elevate transcription rate. In b-interferon gene transcription, TFs recruit a coactivator (CBP) which is needed for transcription to occur normally. Formation of the enhanceosome and activation of RNA polymerase by coactivator are necessary for efficient transcription. Transcripti ...
Unit I: Genes, Nucleic A...d Chromosomes - BioWiki
... polypeptide. In most organisms the pathway for gene expression is the transcription of DNA into RNA, which is then translated into protein. Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant D ...
... polypeptide. In most organisms the pathway for gene expression is the transcription of DNA into RNA, which is then translated into protein. Chapter 2 covers the structures of nucleic acids (DNA and RNA) and methods for analyzing them biochemically. Methods for isolating genes, such as recombinant D ...
Genetics
... • Used to understand control of gene expression in bacteria • Operon consists of three genes needed to degrade lactose • Repressor gene (codes for repressor protein) outside of operon coding region ...
... • Used to understand control of gene expression in bacteria • Operon consists of three genes needed to degrade lactose • Repressor gene (codes for repressor protein) outside of operon coding region ...
Haploid (__)
... -- __________ the formation of DNA molecule --- ________________ the nucleotide Entire human _______ (from all 46 chromosomes)if lined up would be about ________ long --- if just 1 place to start replication it would take _____ BUT each chromosome is replicated in about _____ sections about ______ n ...
... -- __________ the formation of DNA molecule --- ________________ the nucleotide Entire human _______ (from all 46 chromosomes)if lined up would be about ________ long --- if just 1 place to start replication it would take _____ BUT each chromosome is replicated in about _____ sections about ______ n ...
Epigenetics Glossary FINAL
... Allele: Human genes occur in pairs, one on each chromosome of a chromosome pair. The paired genes are called "alleles" and can have a differing form and significance. For instance, in the case of some flowers, the allele on one chromosome may produce a red petal color and the other a white petal col ...
... Allele: Human genes occur in pairs, one on each chromosome of a chromosome pair. The paired genes are called "alleles" and can have a differing form and significance. For instance, in the case of some flowers, the allele on one chromosome may produce a red petal color and the other a white petal col ...
Cell Biology: RNA and Protein synthesis
... Codon and Protein synthesis 2. Translation-Nucleotide sequence of mRNA used to synthesize a sequence of amino acids a. Occurs on the endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) b. mRNA codons are used to specify amino acids c. Ribosomes "read" mRNA codons to synthesize a specific amino acid sequence d. Each o ...
... Codon and Protein synthesis 2. Translation-Nucleotide sequence of mRNA used to synthesize a sequence of amino acids a. Occurs on the endoplasmic reticulum (Rough ER) b. mRNA codons are used to specify amino acids c. Ribosomes "read" mRNA codons to synthesize a specific amino acid sequence d. Each o ...
Intro to Biotechnology
... • The production of human embryos for use in research • Goal of this process is not to create cloned human beings, but rather to harvest stem cells that can be used to study human development and to treat disease. • Stem cells are important to biomedical researchers because they can be used to gener ...
... • The production of human embryos for use in research • Goal of this process is not to create cloned human beings, but rather to harvest stem cells that can be used to study human development and to treat disease. • Stem cells are important to biomedical researchers because they can be used to gener ...
File - Hope Christian College Parent and Student Portal
... bits of DNA…which can then attach to other strands of DNA …as long as the ends have complimentary nucleotides This means that biologists can use a certain enzyme to cut the plasmid at a particular point and insert a gene of interest which has been identified in humans and also removed using a probe ...
... bits of DNA…which can then attach to other strands of DNA …as long as the ends have complimentary nucleotides This means that biologists can use a certain enzyme to cut the plasmid at a particular point and insert a gene of interest which has been identified in humans and also removed using a probe ...
Unit 6 Part 2 Notes Jan 16 2012
... enough to cause a disease or disability. • When researchers use microarrays to detect mutations or polymorphisms in a gene sequence, the target, or immobilized DNA, is usually that of a single gene. • In this case though, the target sequence placed on any given spot within the array will differ from ...
... enough to cause a disease or disability. • When researchers use microarrays to detect mutations or polymorphisms in a gene sequence, the target, or immobilized DNA, is usually that of a single gene. • In this case though, the target sequence placed on any given spot within the array will differ from ...
Editor(s): Laura Hoopes | http://www.nature.com/scitable/topic/gene
... For eukaryotes, cell-cell differences are determined by expression of different sets of genes. For instance, an undifferentiated fertilized egg looks and acts quite different from a skin cell, a neuron, or a muscle cell because of differences in the genes each cell expresses. A cancer cell acts diff ...
... For eukaryotes, cell-cell differences are determined by expression of different sets of genes. For instance, an undifferentiated fertilized egg looks and acts quite different from a skin cell, a neuron, or a muscle cell because of differences in the genes each cell expresses. A cancer cell acts diff ...
DNA Chips
... - Put a wild type copy of gene into those cells & reintroduce those cells into the patient. - Hope that wild type transgene is expressed correctly & wild type protein,which is missing in the mutant cells, is produced. ...
... - Put a wild type copy of gene into those cells & reintroduce those cells into the patient. - Hope that wild type transgene is expressed correctly & wild type protein,which is missing in the mutant cells, is produced. ...
Document
... Representation of predicted R gene product structures and a model coupling the recognition of microbial Avr-dependent ligand and activation of plant defense. Pto can directly bind AvrPto (83, 92). The other R proteins probably bind the corresponding Avr gene products, either directly or in associati ...
... Representation of predicted R gene product structures and a model coupling the recognition of microbial Avr-dependent ligand and activation of plant defense. Pto can directly bind AvrPto (83, 92). The other R proteins probably bind the corresponding Avr gene products, either directly or in associati ...
Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... Details Of The Structure • DNA is formed from two nucleotide polymers each with covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups (backbone structure) and variable nucleotide bases capable of Hydrogen bonding Conserved region ...
... Details Of The Structure • DNA is formed from two nucleotide polymers each with covalent bonds between the sugar and phosphate groups (backbone structure) and variable nucleotide bases capable of Hydrogen bonding Conserved region ...