Glossary of Biotechnology Terms
... cDNA library: a collection of cDNA's, each of which has been inserted in a DNA vector (e.g. a circular DNA plasmid) and replicated in a bacterium such as E. coli. The bacteria maintain a ready pool of the cDNA's and can be cultured to make copies of the library for many experiments. A population of ...
... cDNA library: a collection of cDNA's, each of which has been inserted in a DNA vector (e.g. a circular DNA plasmid) and replicated in a bacterium such as E. coli. The bacteria maintain a ready pool of the cDNA's and can be cultured to make copies of the library for many experiments. A population of ...
TT2007 Lecture 8 HB
... Phenotype- The observable properties of an organism (or cell), which result from the interactions of the genotype and the environment ...
... Phenotype- The observable properties of an organism (or cell), which result from the interactions of the genotype and the environment ...
MUTATIONS TAKS QUESTIONS SPRING 2003 – 10: (22) The
... 10 If one nucleotide is omitted or accidentally repeated in the process of DNA duplication, which of the following is most likely to occur? F Gene deletion G* Gene mutation H Gene insertion J Gene segregation JULY 2006 – 11: 32 A deletion of a DNA base from a gene affects an organism by — F causing ...
... 10 If one nucleotide is omitted or accidentally repeated in the process of DNA duplication, which of the following is most likely to occur? F Gene deletion G* Gene mutation H Gene insertion J Gene segregation JULY 2006 – 11: 32 A deletion of a DNA base from a gene affects an organism by — F causing ...
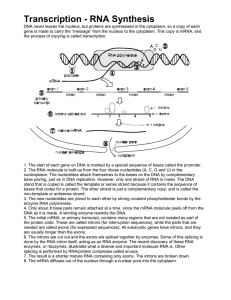
Transcription
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
... non-template or antisense strand. 3. The new nucleotides are joined to each other by strong covalent phosphodiester bonds by the enzyme RNA polymerase. 4. Only about 8 base pairs remain attached at a time, since the mRNA molecule peels off from the DNA as it is made. A winding enzyme rewinds the DNA ...
Recombinant DNA technology
... single-stranded DNA. These are called "sticky ends" because they are able to base pair with any DNA molecule containing the complementary sticky end. In this case, both DNA preparations have complementary sticky ends and thus can pair with each other when mixed. DNA ligase covalently links the two i ...
... single-stranded DNA. These are called "sticky ends" because they are able to base pair with any DNA molecule containing the complementary sticky end. In this case, both DNA preparations have complementary sticky ends and thus can pair with each other when mixed. DNA ligase covalently links the two i ...
Ch 3 White Board Questions on The Cell
... c. genetic information d. a and b e. a and c 19. A. Name the organelle that is the major site of ATP synthesis. B. Name the three organelles involved in protein synthesis or modification of both. C. Name the two organelles that contain enzymes and describe their relative functions. 20. Explain why m ...
... c. genetic information d. a and b e. a and c 19. A. Name the organelle that is the major site of ATP synthesis. B. Name the three organelles involved in protein synthesis or modification of both. C. Name the two organelles that contain enzymes and describe their relative functions. 20. Explain why m ...
Oswald Avery Colin MacLeod Maclyn McCarty 1928
... somatic cells had twice the DNA as gametes but gametes and somatic cells varied in its amount of protein. ...
... somatic cells had twice the DNA as gametes but gametes and somatic cells varied in its amount of protein. ...
Section 11.2 - CPO Science
... • Gregor Mendel did not know about genes, chromosomes, DNA, or meiosis. • In 1903, American scientist Walter Sutton (1877 to 1916) examined the nucleus of the cell of a grasshopper under a microscope. • Sutton observed cell parts separating during cell division. • Soon chromosomes were discovered to ...
... • Gregor Mendel did not know about genes, chromosomes, DNA, or meiosis. • In 1903, American scientist Walter Sutton (1877 to 1916) examined the nucleus of the cell of a grasshopper under a microscope. • Sutton observed cell parts separating during cell division. • Soon chromosomes were discovered to ...
File - MrsCooksBayHighScienceClass
... 2. The difference between autosomal and sex-linked traits. 3. Definition and examples of: Codominance, incomplete dominance, polygenic, dominance, recessive traits, epistatic genes, and gene linkage. 4. Understand that having both uppercase and lowercase of a sex linked trait makes a female a carrie ...
... 2. The difference between autosomal and sex-linked traits. 3. Definition and examples of: Codominance, incomplete dominance, polygenic, dominance, recessive traits, epistatic genes, and gene linkage. 4. Understand that having both uppercase and lowercase of a sex linked trait makes a female a carrie ...
File
... protein of nucleic acids? Fred Griffith Experiment (1928) Hershey and Chase Experiment (1952) 4 Requirements of DNA as the Director of Metabolism The Structure of the Genetic Material: Encoding ...
... protein of nucleic acids? Fred Griffith Experiment (1928) Hershey and Chase Experiment (1952) 4 Requirements of DNA as the Director of Metabolism The Structure of the Genetic Material: Encoding ...
Name
... plants which have 2 or 3 times the normal diploid number of chromosomes. 17. Some plasmids have genes that make bacteria resistant to ,which allows scientists to easily determine which bacteria have been transformed. 18. DNA finger printing has dramatically changed the field of ,which is the study o ...
... plants which have 2 or 3 times the normal diploid number of chromosomes. 17. Some plasmids have genes that make bacteria resistant to ,which allows scientists to easily determine which bacteria have been transformed. 18. DNA finger printing has dramatically changed the field of ,which is the study o ...
Chapter 5
... Chapter 5 Part III. Recombinant DNA technology • Cloning strategies • Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) • Applications ...
... Chapter 5 Part III. Recombinant DNA technology • Cloning strategies • Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) • Applications ...
It all started in the 700s when Chinese used fingerprints to launch
... of significant documents. Afterward, a new field entitled Forensic Science was formed by merging Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics and Biology, toward the designing of novel techniques that will assist in cracking crimes. Sherlock Homes said: ‘’it has long been an axiom of mine that the little things ...
... of significant documents. Afterward, a new field entitled Forensic Science was formed by merging Mathematics, Chemistry, Physics and Biology, toward the designing of novel techniques that will assist in cracking crimes. Sherlock Homes said: ‘’it has long been an axiom of mine that the little things ...
Genetic Engineering
... chromosomes of another organism. It alters an organism's genetic code, and works because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g. a gene for luminescence from a jellyfish can be added to a frog, making it l ...
... chromosomes of another organism. It alters an organism's genetic code, and works because there is only one code for life • The set of instructions for which a gene is responsible work whichever organism the gene is in, e.g. a gene for luminescence from a jellyfish can be added to a frog, making it l ...
Test review Warm-up
... SYSTEM (don’t eat things that you are allergic too…..70% of immune system is in ...
... SYSTEM (don’t eat things that you are allergic too…..70% of immune system is in ...
A.D.Hershey and Martha Chase (1952). Independent Function of
... 1911- Thomas Hunt Morgan - use Drosophila melanogaster to show chromosomes carry genes. ...
... 1911- Thomas Hunt Morgan - use Drosophila melanogaster to show chromosomes carry genes. ...
Biotechnology
... using DNA from different sources- often different species. An example is the introduction of a human gene into an E. coli bacterium. ...
... using DNA from different sources- often different species. An example is the introduction of a human gene into an E. coli bacterium. ...
No Slide Title
... nuc1 and nuc2. • Acetylation leads to recruitment of co-activators, chromatin remodeling complex, and RNA pol II. ...
... nuc1 and nuc2. • Acetylation leads to recruitment of co-activators, chromatin remodeling complex, and RNA pol II. ...
Genetic Code Notes
... mRNA in a row that code for a specific amino acid B. Genetic code – a chart that shows the amino acids that correspond to the codons of mRNA ...
... mRNA in a row that code for a specific amino acid B. Genetic code – a chart that shows the amino acids that correspond to the codons of mRNA ...
What is Mathematical Biology and How is it Useful? Avner Friedman
... — Find trends in the data and analyse them to discover how things work Genes: segments of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that carry instructions for how to construct other cells and contain traits from the parent • Four base pairs of DNA can combine in an infinite amount of orders (factorials can be ap ...
... — Find trends in the data and analyse them to discover how things work Genes: segments of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) that carry instructions for how to construct other cells and contain traits from the parent • Four base pairs of DNA can combine in an infinite amount of orders (factorials can be ap ...