What Processes Produce RNA from DNA and Protein from mRNA
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
... b. For what sequence of amino acids does this mRNA code? (Assume it does not contain introns.) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________ ...
Clone
... produce brown pigment. These enzymes don’t work in the cold, therefore, no pigment is produced in the winter. ...
... produce brown pigment. These enzymes don’t work in the cold, therefore, no pigment is produced in the winter. ...
Document
... • The genomic DNA remains denatured since the complementary strands are at too low a concentration to encounter each other during the period of incubation • The specific oligonucleotides hybridize with complementary sequences in the genomic DNA ...
... • The genomic DNA remains denatured since the complementary strands are at too low a concentration to encounter each other during the period of incubation • The specific oligonucleotides hybridize with complementary sequences in the genomic DNA ...
Hershey and Chase`s Experiment
... Proteins is NOT the Genetic Material... (Hershey and Chase, 1952) A bacteriophage (or, phage) is a type of virus that only infects bacteria. They have a protein coat and a piece of DNA inside. They adhere to the surface of the bacteria and inject their DNA into the bacteria. Their DNA codes for ...
... Proteins is NOT the Genetic Material... (Hershey and Chase, 1952) A bacteriophage (or, phage) is a type of virus that only infects bacteria. They have a protein coat and a piece of DNA inside. They adhere to the surface of the bacteria and inject their DNA into the bacteria. Their DNA codes for ...
Nucleotides
... form the “backbone” of RNA and DNA • RNAs are far less stable than DNA • Polynucleotides Are Directional Macromolecule – “5′- end” or the “3′- end” – the 5′- end is at the left ...
... form the “backbone” of RNA and DNA • RNAs are far less stable than DNA • Polynucleotides Are Directional Macromolecule – “5′- end” or the “3′- end” – the 5′- end is at the left ...
Pharmacogenetics Glossary
... deoxyribonucleic acid - see DNA diploid - a cell or organism that has two complete sets of chromosomes, as opposed to haploid, or those with only one member of each pair of the same chromosomes. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) - a large double-stranded, spiraling molecule that contains genetic instruct ...
... deoxyribonucleic acid - see DNA diploid - a cell or organism that has two complete sets of chromosomes, as opposed to haploid, or those with only one member of each pair of the same chromosomes. DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) - a large double-stranded, spiraling molecule that contains genetic instruct ...
슬라이드 1
... outcome of infections in different ways that can be either beneficial or detrimental to the host. A function of the multiple copy families, scattered throughout the genome, has been reported regulatory functions on the gene expression of nearby located genes. A small minority of such sequences has a ...
... outcome of infections in different ways that can be either beneficial or detrimental to the host. A function of the multiple copy families, scattered throughout the genome, has been reported regulatory functions on the gene expression of nearby located genes. A small minority of such sequences has a ...
CB-Human Genetics
... A. Geneticists study how a trait is passed from one generation to the next B. Genetics versus Environment 1. Many traits are strongly influenced by environmental factors, such as nutrition and exercise (Ex: average height in 1800s in Europe was 10 cm shorter than today due to poor nutrition) 2. Gene ...
... A. Geneticists study how a trait is passed from one generation to the next B. Genetics versus Environment 1. Many traits are strongly influenced by environmental factors, such as nutrition and exercise (Ex: average height in 1800s in Europe was 10 cm shorter than today due to poor nutrition) 2. Gene ...
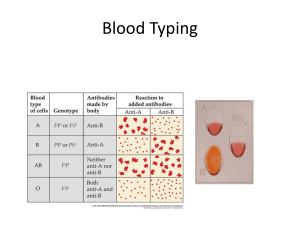
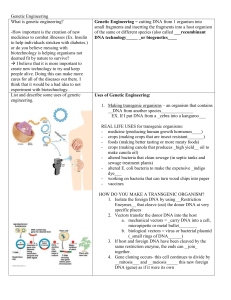
Genetic Engineering Guied Notes
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
... medicines to combat illnesses (Ex. Insulin to help individuals stricken with diabetes.) or do you believe messing with biotechnology is helping organisms not deemed fit by nature to survive? I believe that it is more important to create new technology to try and keep people alive. Doing this can m ...
mei4 - University of Vermont
... • Of the genes known to function during gametogenesis, there are tumor-suppressor genes, oncogenes, DNA repair enzymes, and genes involved in the maintenance of genomic integrity. • The biology of reproduction plays a central role in species proliferation and, during sexual reproduction, in the gene ...
... • Of the genes known to function during gametogenesis, there are tumor-suppressor genes, oncogenes, DNA repair enzymes, and genes involved in the maintenance of genomic integrity. • The biology of reproduction plays a central role in species proliferation and, during sexual reproduction, in the gene ...
Genetics Study Guide Answers What are different forms of a
... 9. What is used to organize possible offspring combinations? 10. A genotype with one recessive and one dominant gene 11. A genotype with two dominant or two recessive genes 12. What are chromosomes that carry the same sets of genes? 13. What carries the genes that determine sex? 14. How are sex cell ...
... 9. What is used to organize possible offspring combinations? 10. A genotype with one recessive and one dominant gene 11. A genotype with two dominant or two recessive genes 12. What are chromosomes that carry the same sets of genes? 13. What carries the genes that determine sex? 14. How are sex cell ...
C-13 Part II Non-Mendelian inheritance
... Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human height ...
... Polygenic inheritance occurs when multiple genes are involved in controlling the phenotype of a trait. The phenotype is an accumulation of contributions by multiple genes. These traits show continuous variation and are referred to as quantitative traits. For example – human height ...
PBS Unit 3 Key Terms
... molecules and is formed by combining two subunits. The synthesis of RNA on a DNA template. An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA. The synthesis of a polypeptide ...
... molecules and is formed by combining two subunits. The synthesis of RNA on a DNA template. An RNA molecule that functions as an interpreter between nucleic acid and protein language by picking up specific amino acids and recognizing the appropriate codons in the mRNA. The synthesis of a polypeptide ...
Bi-150-molbiol
... Humans have 22 pairs of chromosomes, plus the X and Y. Males are XY; females are XX. ...
... Humans have 22 pairs of chromosomes, plus the X and Y. Males are XY; females are XX. ...
Study Questions for the Second Exam in Bio 0200
... What is a photosystem? Where are photosystems located? What are photosystem I and II? How do their functions differ? In what ways is the Calvin Cycle similar to the Krebs Cycle? In what ways is it different? What is C4 photosynthesis? Is it more or less efficient than C3 photosynthesis? What is a nu ...
... What is a photosystem? Where are photosystems located? What are photosystem I and II? How do their functions differ? In what ways is the Calvin Cycle similar to the Krebs Cycle? In what ways is it different? What is C4 photosynthesis? Is it more or less efficient than C3 photosynthesis? What is a nu ...
Protein Synthesis SG
... 27. Describe the basic concept of the operon, including the role of each of the following: promoter, regulatory gene, operator, genes, repressor 28. Explain the difference between how an inducible operon and a repressible operon turn the gene on or off. 29. What is the ideal structure/packaging of D ...
... 27. Describe the basic concept of the operon, including the role of each of the following: promoter, regulatory gene, operator, genes, repressor 28. Explain the difference between how an inducible operon and a repressible operon turn the gene on or off. 29. What is the ideal structure/packaging of D ...
DNA technology notes
... are taken from a cell sample, cut out and matched up in pairs • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • Karyotypes can be used to determine if genetic disorder is present • If too many are present can indicate Down’s syndrome • If some are missing can indicate Turner’s syndrome ...
... are taken from a cell sample, cut out and matched up in pairs • Humans have 23 pairs of chromosomes • Karyotypes can be used to determine if genetic disorder is present • If too many are present can indicate Down’s syndrome • If some are missing can indicate Turner’s syndrome ...
TIP Translation - dna
... Name: _____________________ Date: ____________ Class:_________ DNA Translation Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What materials make up each nucleotide in a DNA molecule? a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a r ...
... Name: _____________________ Date: ____________ Class:_________ DNA Translation Quiz Multiple Choice Identify the choice that best completes the statement or answers the question. ____ 1. What materials make up each nucleotide in a DNA molecule? a. amino acid, base, and protein c. mRNA, tRNA, and a r ...
Biology Benchmark Exam #4 2010
... hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan built his fleet of viral "trucks," all with the hemoglobin ...
... hemoglobin, the molecule in red blood cells that carries oxygen. Mulligan hoped that the genetically modified virus would no longer tell the cell it had entered to make more virus particles. It would just order hemoglobin proteins. Mulligan built his fleet of viral "trucks," all with the hemoglobin ...
Crossword Puzzle: Protein Synthesis
... 1. The number of codons that exist 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for mak ...
... 1. The number of codons that exist 3. Sequence of nucleotides on DNA to with RNA polymerase will attach to start transcription 4. mRNA copying DNA's nucleotide sequence 5. 3 nucleotides on tRNA that match to a specific codon on mRNA 6. Type of RNA that helps make up ribosomes 7. Instructions for mak ...