Molecular genetics of gene expression
... What is next-generation DNA sequencing? What is the impact or potential impact? ...
... What is next-generation DNA sequencing? What is the impact or potential impact? ...
Protein Synthesis Quick Questions
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
... separates the 2 strands • RNA polymerase then uses one strand of DNA as a template for assembling an mRNA complementary strand • This creates a strand of mRNA which can carry the genetic code out of the nucleus to complete the second step of protein synthesis. ...
BIO2093_DMS3_phylogeny - COGEME Phytopathogenic Fungi
... • Amino acid sequences evolve more slowly than DNA sequences. • Concatenated protein sequences can be used to make species trees. • Protein sequences can be used to create a phylogenetic history of a gene, including duplication and loss. ...
... • Amino acid sequences evolve more slowly than DNA sequences. • Concatenated protein sequences can be used to make species trees. • Protein sequences can be used to create a phylogenetic history of a gene, including duplication and loss. ...
Checklist unit 18: Regulation of Gene Expression
... for an entire molecular pathway, including the operator, the promoter, and the genes they control (in prokaryotes, all genes related to specific pathway are found in one continuous strip of DNA). A mechanism for positive gene regulation (an increase in gene expression) is the activator protein, whic ...
... for an entire molecular pathway, including the operator, the promoter, and the genes they control (in prokaryotes, all genes related to specific pathway are found in one continuous strip of DNA). A mechanism for positive gene regulation (an increase in gene expression) is the activator protein, whic ...
Epigenetics
... X:autosome translocation • In this case, X-inactivation is not random - the normal X is always inactivated, because the translocation interferes with the inactivation process • Therefore, the normal DMD gene is switched off, and the other one is disrupted by the translocation • So these girls show t ...
... X:autosome translocation • In this case, X-inactivation is not random - the normal X is always inactivated, because the translocation interferes with the inactivation process • Therefore, the normal DMD gene is switched off, and the other one is disrupted by the translocation • So these girls show t ...
Compare the activities of the enzymes in prokaryotic transcription to
... What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide that this DNA sequence encodes? ...
... What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide that this DNA sequence encodes? ...
SBI 3CI Diagnostic Quiz October 10, 2014 – Microbiology Name
... A vaccine is a dead version of the actual disease. Gene therapy will remove defective cells from your body. 2 members of the same species don’t always produce fertile offspring Vaccines are considered a form of passive immunity. Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been spliced open and strands of DNA ad ...
... A vaccine is a dead version of the actual disease. Gene therapy will remove defective cells from your body. 2 members of the same species don’t always produce fertile offspring Vaccines are considered a form of passive immunity. Recombinant DNA is DNA that has been spliced open and strands of DNA ad ...
Part I: To Transcribe! In previous lessons, you`ve learned the
... stored in segments called genes. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids. The amino acids form chains that make a certain protein depending on the order of the nitrogen bases. Just like 26 letters of the alphabet make words, 2 ...
... stored in segments called genes. A gene is a specific sequence of nucleotides in a strand of DNA that codes for a specific sequence of amino acids. The amino acids form chains that make a certain protein depending on the order of the nitrogen bases. Just like 26 letters of the alphabet make words, 2 ...
Constructing a Model of Protein Synthesis
... corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The process by ...
... corresponding amino acids. Another type of RNA called transfer RNA (tRNA) is needed to bring the mRNA and amino acids together. As the code carried by mRNA is “read” on a ribosome, the proper tRNAs arrive in turn and give up the amino acids they carry to the growing polypeptide chain. The process by ...
What is Genetic Modification?
... genetic engineering more widely accepted. Opponents fear that companies will go on to develop other genetically modified plants from which they can make a profit. A situation could develop where the large companies own the rights to all the good crops ...
... genetic engineering more widely accepted. Opponents fear that companies will go on to develop other genetically modified plants from which they can make a profit. A situation could develop where the large companies own the rights to all the good crops ...
RNA
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
... RNA stands for ____________________________________ RNA takes the DNA’s instructions out of the __________________ and into the _______________________ of the cell where there is room for ____________________________________(protein synthesis) ...
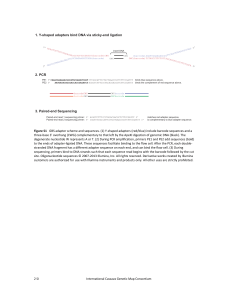
general steps of gene cloning
... DNA ligase: An enzyme that repairs single-stranded discontinuities in double-stranded DNA molecules in the cell. Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together. Ligation: The process of joining two or more DNA fragments together Recombinant: A transformed cell that contai ...
... DNA ligase: An enzyme that repairs single-stranded discontinuities in double-stranded DNA molecules in the cell. Purified DNA ligase is used in gene cloning to join DNA molecules together. Ligation: The process of joining two or more DNA fragments together Recombinant: A transformed cell that contai ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;12)(p36;p13) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... 5' ETV6 - 3' MDS2; exons 1 and 2 of ETV6 are fused to exons 6 and 7 of MDS2; fusion is not in frame; the reciprocal fusion gene is not expressed. ...
... 5' ETV6 - 3' MDS2; exons 1 and 2 of ETV6 are fused to exons 6 and 7 of MDS2; fusion is not in frame; the reciprocal fusion gene is not expressed. ...
PowerPoint 簡報
... 2. When people noticed about they had in-take some kind of GM Food which is under the condition without their permission or being noticed, a sound raised up by the consumer organization around the world "force labeling all the GM Food". For this labeling, it means consumers can boycott GM Food whic ...
... 2. When people noticed about they had in-take some kind of GM Food which is under the condition without their permission or being noticed, a sound raised up by the consumer organization around the world "force labeling all the GM Food". For this labeling, it means consumers can boycott GM Food whic ...
Ingenious Genes Curriculum Links for AQA GCSE Biology (8461
... Students should be able to discuss the importance of understanding the human genome. This is limited to the: • search for genes linked to different types of disease • understanding and treatment of inherited disorders 4.6.1.5 DNA structure (biology only) Students should be able to describe DNA as a ...
... Students should be able to discuss the importance of understanding the human genome. This is limited to the: • search for genes linked to different types of disease • understanding and treatment of inherited disorders 4.6.1.5 DNA structure (biology only) Students should be able to describe DNA as a ...
Molecular Basis of Inherited Epilepsy
... Illustrations of experimental approaches used to identify and characterize epilepsy genes. A, Linkage analysis uses large, multigenerational kindreds segregating an epilepsy phenotype. The shaded pedigree symbols represent affected individuals. Pairs of vertical lines beneath each pedigree symbol re ...
... Illustrations of experimental approaches used to identify and characterize epilepsy genes. A, Linkage analysis uses large, multigenerational kindreds segregating an epilepsy phenotype. The shaded pedigree symbols represent affected individuals. Pairs of vertical lines beneath each pedigree symbol re ...
Unit 6B Learning Targets
... iii. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid, which can be deduced by using a genetic code chart. Many amino acids have more than one codon. iv. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA. v. The amino acid is transferred to the growing peptide chain. vi. The process contin ...
... iii. Each codon encodes a specific amino acid, which can be deduced by using a genetic code chart. Many amino acids have more than one codon. iv. tRNA brings the correct amino acid to the correct place on the mRNA. v. The amino acid is transferred to the growing peptide chain. vi. The process contin ...
Quiz Review: Chapter 11: Eukaryotic Genome Organization Chapter
... Why are eukaryotic genomes more complex than the genome of prokaryotes? Eukaryotic genomes must code for organelles and complex proteins that are not present in prokaryotic cells. The eukaryotic genome contains two types of DNA sequences, what are they? Coding sequences called EXONS and non-coding s ...
... Why are eukaryotic genomes more complex than the genome of prokaryotes? Eukaryotic genomes must code for organelles and complex proteins that are not present in prokaryotic cells. The eukaryotic genome contains two types of DNA sequences, what are they? Coding sequences called EXONS and non-coding s ...
pNZ:vig Vector information: IRES
... Suitable host strain: NZ9000 and other NICE system vectors derivatives ...
... Suitable host strain: NZ9000 and other NICE system vectors derivatives ...