No Slide Title
... • One end is hydrophilic, the other hydrophobic • Often polymers (few large instead of many small subunits, fatty acid derivatives) • Used for: – Energy storage, e.g., fats and oils – Chemical messengers (hormones) , e.g., steroids – Chemical defenses , e.g., terpenes ...
... • One end is hydrophilic, the other hydrophobic • Often polymers (few large instead of many small subunits, fatty acid derivatives) • Used for: – Energy storage, e.g., fats and oils – Chemical messengers (hormones) , e.g., steroids – Chemical defenses , e.g., terpenes ...
Chapter 27: Human Genetics Vocabulary
... 1 X chromosome has more genes than the Y chromosome 2 Color vision is a gene on the X chromosome but not on the Y 3 C normal color vision is dominant to c colorblindness 4 CC normal vision female Cc normal vision female who carries the gene cc colorblind female CY normal vision ...
... 1 X chromosome has more genes than the Y chromosome 2 Color vision is a gene on the X chromosome but not on the Y 3 C normal color vision is dominant to c colorblindness 4 CC normal vision female Cc normal vision female who carries the gene cc colorblind female CY normal vision ...
Finding Genes in Eukaryotes
... many organisms there is a detectable preference for G or C over A and T in the third (“wobble”) position in a codon all organisms do not utilize synonymous codons with the same frequency - consequently there is a codon bias there is an unequal usage of amino acids in proteins sufficient to cau ...
... many organisms there is a detectable preference for G or C over A and T in the third (“wobble”) position in a codon all organisms do not utilize synonymous codons with the same frequency - consequently there is a codon bias there is an unequal usage of amino acids in proteins sufficient to cau ...
Nature vs. Nurture
... • Believed that one found that ________ could _______ any ran in families individual to become • He concluded ___________, no that _________ matter the _________ was the cause the person came from ...
... • Believed that one found that ________ could _______ any ran in families individual to become • He concluded ___________, no that _________ matter the _________ was the cause the person came from ...
Protein Synthesis
... region on DNA known as the promoter, which signals the start of a gene Promoters are specific to genes RNA polymerase does not need a primer Transcription factors assemble at the promoter forming a transcription initiation complex – activator proteins help stabilize the complex ...
... region on DNA known as the promoter, which signals the start of a gene Promoters are specific to genes RNA polymerase does not need a primer Transcription factors assemble at the promoter forming a transcription initiation complex – activator proteins help stabilize the complex ...
Chromosomes and Mutations Chromosomes and
... How are genes mutated? • Genes can be mutated when the DNA is mutated or when the chromosomes are mutated • There are two types of DNA (gene) mutations: • Point Mutations: a change in a single base pair • Frameshift Mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA ...
... How are genes mutated? • Genes can be mutated when the DNA is mutated or when the chromosomes are mutated • There are two types of DNA (gene) mutations: • Point Mutations: a change in a single base pair • Frameshift Mutations: a single base is added or deleted from DNA ...
class notes
... p53 protein. The expression of several target genes is then activated by binding of the activated p53 to their regulatory regions. These genes are involved in processes that slow down the development of tumors. For example, some genes inhibit cell-cycle progression or the development of blood vessel ...
... p53 protein. The expression of several target genes is then activated by binding of the activated p53 to their regulatory regions. These genes are involved in processes that slow down the development of tumors. For example, some genes inhibit cell-cycle progression or the development of blood vessel ...
Genetic Mutation - Raymond Williams Foundation
... ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations of ‘enzymes, DNA, ‘the gene pool’, ‘randomness, and genetic drift…’ , ‘induced mutations’ , ‘dis ...
... ‘ mutation – the raw material of evolution… fuel for the Darwinian factory’; ‘What is Life? – unlike, say a pebble, living beings store information and also develop it over time…’; attempted explanations of ‘enzymes, DNA, ‘the gene pool’, ‘randomness, and genetic drift…’ , ‘induced mutations’ , ‘dis ...
Grand challenges in bioinformatics.
... According to this genetic determinism principle, we should eventually be able to predict the function of every gene in the genome by its sequence information alone. Implicitly, this assumes that the environment of each gene is also computable from the complete genome sequence because the function of ...
... According to this genetic determinism principle, we should eventually be able to predict the function of every gene in the genome by its sequence information alone. Implicitly, this assumes that the environment of each gene is also computable from the complete genome sequence because the function of ...
Module - Discovering the Genome
... Discovering the Genome: Tour of the Genome Module – For Teachers p. 2 of 4 ...
... Discovering the Genome: Tour of the Genome Module – For Teachers p. 2 of 4 ...
Human Genetics
... Human genetics: What's different? Nothing (in principle) Unmatched by other organisms for phenotypic complexity ...
... Human genetics: What's different? Nothing (in principle) Unmatched by other organisms for phenotypic complexity ...
Tumor-suppressor genes - School District of New Berlin
... Restricted to the use of New Berlin Eisenhower High School (New Berlin, WI) Students, Faculty and Staff. Contact the Science Department for usage permissions. ...
... Restricted to the use of New Berlin Eisenhower High School (New Berlin, WI) Students, Faculty and Staff. Contact the Science Department for usage permissions. ...
Biology Name: Directions: Read Section 13.3(pgs. 372
... Effects of Mutations For Questions 10–17, write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 10. The cellular machinery that replicates DNA inserts an incorrect base A. most of the time. B. about half the time. C. roughly once in every million bases. D. roughly once in every 10 million ...
... Effects of Mutations For Questions 10–17, write the letter of the correct answer on the line at the left. 10. The cellular machinery that replicates DNA inserts an incorrect base A. most of the time. B. about half the time. C. roughly once in every million bases. D. roughly once in every 10 million ...
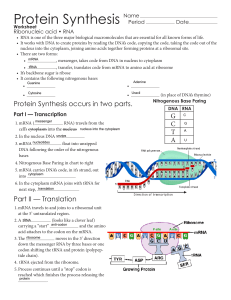
Protein Synthesis - Issaquah Connect
... at the 5’ untranslated region. 2. A tRNA (looks like a clover leaf) anti-codon carrying a “start” and the amino acid attaches to the codon on the mRNA. 3. The ribosome moves in the 3’ direction down the messenger RNA by three bases or one codon shifting the tRNA and protein (polypeptide chain). 4. ...
... at the 5’ untranslated region. 2. A tRNA (looks like a clover leaf) anti-codon carrying a “start” and the amino acid attaches to the codon on the mRNA. 3. The ribosome moves in the 3’ direction down the messenger RNA by three bases or one codon shifting the tRNA and protein (polypeptide chain). 4. ...
The Structure of DNA
... What’s the relationship? What is the relationship between: DNA, CHROMOSOMES, GENES, AMINO ACIDS, PROTEINS, and TRAITS ...
... What’s the relationship? What is the relationship between: DNA, CHROMOSOMES, GENES, AMINO ACIDS, PROTEINS, and TRAITS ...
learning objectives
... 1. Cloning involves getting thousands of bacterial colonies to grow, which together make up a clone library. E. Stage 4: Screening 1. The screening part of genetic engineering is often the most time-intensive, and investigators must first eliminate any clones that do not contain vectors. ...
... 1. Cloning involves getting thousands of bacterial colonies to grow, which together make up a clone library. E. Stage 4: Screening 1. The screening part of genetic engineering is often the most time-intensive, and investigators must first eliminate any clones that do not contain vectors. ...
Genetics Slides
... have 2 X’s) would have the usual 2 alleles for each gene. • Males, however, only have 1 X chromosome and thus 1 allele at many loci If a male inherits a recessive gene on his X, it is expressed • Example – X-linked recessive red/green color blindness gene; X-linked hemophilia ...
... have 2 X’s) would have the usual 2 alleles for each gene. • Males, however, only have 1 X chromosome and thus 1 allele at many loci If a male inherits a recessive gene on his X, it is expressed • Example – X-linked recessive red/green color blindness gene; X-linked hemophilia ...
Biotechnology:
... This allows for genes to be "cut & pasted" between organisms. This can be seen with production of human insulin. The DNA sequence of insulin is identified and cut out using a restriction enzyme. A plasmid from E. coli is removed and cut open using the same restriction enzyme Since both fragments hav ...
... This allows for genes to be "cut & pasted" between organisms. This can be seen with production of human insulin. The DNA sequence of insulin is identified and cut out using a restriction enzyme. A plasmid from E. coli is removed and cut open using the same restriction enzyme Since both fragments hav ...
SBI 4UW DNA Barcoding Assignment
... i) Research the common name of each animal identified above, where it lives, and its conservation status (ie. endangered, threatened, etc.) Explain if this animal can legally be hunted and if trade for its pelt or other body parts would be legal or not. This should be written on a new piece of paper ...
... i) Research the common name of each animal identified above, where it lives, and its conservation status (ie. endangered, threatened, etc.) Explain if this animal can legally be hunted and if trade for its pelt or other body parts would be legal or not. This should be written on a new piece of paper ...
Document
... This requires a special type of vector that contains a minigene consisting of two exons flanking an intron sequence, the first exon being preceded by the sequence signals needed to initiate transcription in a eukaryotic cell .To use the vector the piece of DNA to be studied is inserted into a rest ...
... This requires a special type of vector that contains a minigene consisting of two exons flanking an intron sequence, the first exon being preceded by the sequence signals needed to initiate transcription in a eukaryotic cell .To use the vector the piece of DNA to be studied is inserted into a rest ...
Gene Interaction that produces novel Phenotype
... • Genomic imprinting: differential expression of genetic material depending on whether it is inherited from the male or female parent. • Epigenetics: Phenomena due to alterations to DNA that do not include changes in the base sequence; often affect the way in which the DNA sequences are expressed. ...
... • Genomic imprinting: differential expression of genetic material depending on whether it is inherited from the male or female parent. • Epigenetics: Phenomena due to alterations to DNA that do not include changes in the base sequence; often affect the way in which the DNA sequences are expressed. ...
Section 1.1 Name:
... look like)? The answer to this lies in the proteins your cell’s produce. The bulk of what we look like and our ability to survive come from the enzymes and tissues in our bodies being made of proteins. Proteins are made in a process called “protein synthesis.” The genes directing protein production ...
... look like)? The answer to this lies in the proteins your cell’s produce. The bulk of what we look like and our ability to survive come from the enzymes and tissues in our bodies being made of proteins. Proteins are made in a process called “protein synthesis.” The genes directing protein production ...