Transcription and Translation
... (RER) – makes proteins that leave the cell (insulin, hormones, enzymes) ...
... (RER) – makes proteins that leave the cell (insulin, hormones, enzymes) ...
Integration within Health-care records
... We have demonstrated the significance of information fusion based tools for bio-geo health care informatics. • As a data warehouse for various data sets involved in bio-geo health care informatics studies. • To provide and demonstrate a set of information fusion tools for disease research. ...
... We have demonstrated the significance of information fusion based tools for bio-geo health care informatics. • As a data warehouse for various data sets involved in bio-geo health care informatics studies. • To provide and demonstrate a set of information fusion tools for disease research. ...
ppt
... The basic experimental techniques involved in gene cloning have now been described. A DNA molecule needs to display several features to be able to act as a vehicle for gene cloning. Most important, it must be able to replicate within the host cell, so that numerous copies of the recombinant DNA mole ...
... The basic experimental techniques involved in gene cloning have now been described. A DNA molecule needs to display several features to be able to act as a vehicle for gene cloning. Most important, it must be able to replicate within the host cell, so that numerous copies of the recombinant DNA mole ...
Document
... 3. In each of us a huge B-cell repertoire is generated consisting of B-cell clones with different H- and L-chain variable domains 4. This potential B-cell repertoire is able to recognize a wide array of antigens ...
... 3. In each of us a huge B-cell repertoire is generated consisting of B-cell clones with different H- and L-chain variable domains 4. This potential B-cell repertoire is able to recognize a wide array of antigens ...
Name_____________________________________ Which is the
... 40. A mutation in DNA generates a UGA stop codon in the middle of the RNA coding for a particular protein. A second mutation in the cell leads to a single nucleotide change in a tRNA that allows the correct translation of the protein; that is the second mutation “suppresses” the defect caused by the ...
... 40. A mutation in DNA generates a UGA stop codon in the middle of the RNA coding for a particular protein. A second mutation in the cell leads to a single nucleotide change in a tRNA that allows the correct translation of the protein; that is the second mutation “suppresses” the defect caused by the ...
Analysis of Gene Sequences
... their effects on phenotype. Now, in the era of genomic sequencing, many genes of no known function can be detected by looking for patterns in DNA sequences. The simplest method which works for bacterial and phage genes (but not for most eukaryotic genes as we will see later) is to look for stretches ...
... their effects on phenotype. Now, in the era of genomic sequencing, many genes of no known function can be detected by looking for patterns in DNA sequences. The simplest method which works for bacterial and phage genes (but not for most eukaryotic genes as we will see later) is to look for stretches ...
Fertilisation, development and DNA
... organs i.e. ovary, testes, vagina, penis, uterus, oviduct and sperm. I can state that both sex cells only contain half the genetic information of a normal body cell. I can describe the fertilization process as the fusing of an egg and a sperm so it has a complete set of genetic information to make a ...
... organs i.e. ovary, testes, vagina, penis, uterus, oviduct and sperm. I can state that both sex cells only contain half the genetic information of a normal body cell. I can describe the fertilization process as the fusing of an egg and a sperm so it has a complete set of genetic information to make a ...
Evolution notes lecture Genetic Variation and Gene Regulation Fall
... Contains a series of genes, e.g., lac operon. Genes have regulation sites—signal areas for beginning transcription, stopping. Genes include introns and exons Exons (expressed sequences) are coding regions for transcription of m-RNA and translation into proteins Introns are non-coding regio ...
... Contains a series of genes, e.g., lac operon. Genes have regulation sites—signal areas for beginning transcription, stopping. Genes include introns and exons Exons (expressed sequences) are coding regions for transcription of m-RNA and translation into proteins Introns are non-coding regio ...
Bio 111
... If red blood cells are taken from the body and placed in a hypertonic solution, what happens to the cells? a. The cells swell and burst because water moves into the cells. b. The cells shrivel up because water leaves the cells. c. The cells remain unchanged due to equal solute concentration inside a ...
... If red blood cells are taken from the body and placed in a hypertonic solution, what happens to the cells? a. The cells swell and burst because water moves into the cells. b. The cells shrivel up because water leaves the cells. c. The cells remain unchanged due to equal solute concentration inside a ...
BINF 730 Biological Sequence Analysis Lecture 1 Biological
... DNA starting at a start codon and ending at a STOP codon ...
... DNA starting at a start codon and ending at a STOP codon ...
Lecture: How do neurons work
... in the skin, and if an inhibitor could be developed, it might lead to a therapy for acne. You want to find out more about this enzyme. You plan to 1. clone the gene 2. express it in E. coli 3. make lots of the protein and study it's properties How would you clone this gene into E. coli? -- assume yo ...
... in the skin, and if an inhibitor could be developed, it might lead to a therapy for acne. You want to find out more about this enzyme. You plan to 1. clone the gene 2. express it in E. coli 3. make lots of the protein and study it's properties How would you clone this gene into E. coli? -- assume yo ...
Biology 445K Winter 2007 DNA Fingerprinting • For Friday 3/9 lab: in
... the genome that consist of repeated sequences. The repeat size is usually 10-60 base pairs long and the number of repeats varies from less than ten to several dozen. These sites, which are scattered throughout the genome, are usually “anonymous” markers in the sense that the repeat number does not a ...
... the genome that consist of repeated sequences. The repeat size is usually 10-60 base pairs long and the number of repeats varies from less than ten to several dozen. These sites, which are scattered throughout the genome, are usually “anonymous” markers in the sense that the repeat number does not a ...
Answer Guided Reading Questions
... _____ 45. Which of the following tools of recombinant DNA technology is incorrectly paired with its use? A. restriction enzyme-production of RFLPs B. electrophoresis-separation of DNA fragments C. reverse transcriptase-production of cDNA from mRNA D. DNA polymerase-used in a polymerase chain reactio ...
... _____ 45. Which of the following tools of recombinant DNA technology is incorrectly paired with its use? A. restriction enzyme-production of RFLPs B. electrophoresis-separation of DNA fragments C. reverse transcriptase-production of cDNA from mRNA D. DNA polymerase-used in a polymerase chain reactio ...
Practice Exam III
... Genetics 310 Practice exam III-1 1. What are the two types of molecules found in eukaryotic chromosomes? DNA and protein 2. True or False? __F_ Man has more DNA per genome than all other organisms. __F_ The number of chromosomes is a direct reflection of the amount of DNA/genome in a species. __F_ A ...
... Genetics 310 Practice exam III-1 1. What are the two types of molecules found in eukaryotic chromosomes? DNA and protein 2. True or False? __F_ Man has more DNA per genome than all other organisms. __F_ The number of chromosomes is a direct reflection of the amount of DNA/genome in a species. __F_ A ...
Nucleic Acids and Protein Synthesis
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
... Mutations are any change in the genetic code: 1. DNA may not replicate properly and the incorrect base attached 2. There may be a mistake in transcription 3. There may be a mistake in translation ...
Microarrays Central dogma
... - What mRNAs are present in the cell and in what quantities => inferences regarding the state of the cell. - Transcriptome: The complete collection of the organism’s mRNAs . - Why not study the proteins? - The function of a protein is determined not just by its amino acid sequence, but also the spec ...
... - What mRNAs are present in the cell and in what quantities => inferences regarding the state of the cell. - Transcriptome: The complete collection of the organism’s mRNAs . - Why not study the proteins? - The function of a protein is determined not just by its amino acid sequence, but also the spec ...
PURINE COMPOUNDS Both the pyrimidine bases (uracil, cytosine), and
... Both the pyrimidine bases (uracil, cytosine), and the purine bases (adenine, guanine) are building blocks in the synthesis of DNA and RNA nucleotides. In the replication process, nucleotides are joined to one another to form DNA strands. It is less clear how the purine antagonists function, but they ...
... Both the pyrimidine bases (uracil, cytosine), and the purine bases (adenine, guanine) are building blocks in the synthesis of DNA and RNA nucleotides. In the replication process, nucleotides are joined to one another to form DNA strands. It is less clear how the purine antagonists function, but they ...
Data Mining - functional statistical genetics/bioinformatics
... whether an a priori defined set of genes shows statistically significant, concordant differences between two biological states ...
... whether an a priori defined set of genes shows statistically significant, concordant differences between two biological states ...
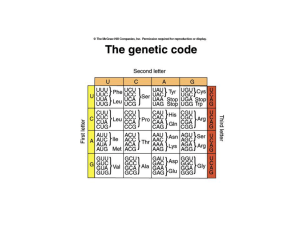
Features of the genetic code
... • A capping enzyme adds a G to the first nucleotide in the transcript in the unusual 5’-5’ direction (phosphate to phosphate bond). Then a methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be cr ...
... • A capping enzyme adds a G to the first nucleotide in the transcript in the unusual 5’-5’ direction (phosphate to phosphate bond). Then a methyl thransferase adds methyl groups (-CH3) to the G and one or more of the first few bases of the RNA transcript. Capping and methylation is believed to be cr ...
Lecture 9 - Bacterial Genetics Chpt. 8
... What are mutations? • Change in the base sequence of the DNA • Do they always change the genetic code? ...
... What are mutations? • Change in the base sequence of the DNA • Do they always change the genetic code? ...
1 - Testbankexam
... recombinational analysis is that two genes that are far apart on a chromosome will have a higher frequency of recombination than two genes that are close together. Thus, if recombination between the gene of interest and a marker is very low, then the gene is likely located near that marker gene. ...
... recombinational analysis is that two genes that are far apart on a chromosome will have a higher frequency of recombination than two genes that are close together. Thus, if recombination between the gene of interest and a marker is very low, then the gene is likely located near that marker gene. ...
Chapter 3
... DNA replication is described as semiconservative because purines pair only with pyrimidines. half of the old molecule is conserved in each new molecule. thymine is always used in order to conserve uracil in the nucleotide pool. deoxyribose sugar has less oxygen than ribose sugar. all new molecules o ...
... DNA replication is described as semiconservative because purines pair only with pyrimidines. half of the old molecule is conserved in each new molecule. thymine is always used in order to conserve uracil in the nucleotide pool. deoxyribose sugar has less oxygen than ribose sugar. all new molecules o ...
1 Protein Synthesis Simulation Lab This lab was originally created
... 4. The original DNA strand serves as a template. What does the term template mean? 5. Draw the first three nucleotide sequences of the RNA molecule whose bases you determined in question 3. Remember that RNA is only half as large as a DNA molecule. 6. What protein fragment would the mRNA sequence yo ...
... 4. The original DNA strand serves as a template. What does the term template mean? 5. Draw the first three nucleotide sequences of the RNA molecule whose bases you determined in question 3. Remember that RNA is only half as large as a DNA molecule. 6. What protein fragment would the mRNA sequence yo ...