Leukaemia Section inv(19)(p13q13) TCF3/TFPT, t(19;19)(p13;q13) TCF3/TFPT Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... some cases, and out of frame in others. The reciprocal transcript was not found. ...
... some cases, and out of frame in others. The reciprocal transcript was not found. ...
Tyrosine kinase receptor-activated signal transduction
... pathways. Stimulation of cells expressing the EGF-R/ Ret chimera resulted in phosphorylation of paxillin, a cytoskeletal protein, and cellular transformation (Romano et al., 1994; Santoro et al., 1994b). In addition, stimulation of the EGF-R/Ret chimera in SK-N-MC neuroepithelioma cells leads to cel ...
... pathways. Stimulation of cells expressing the EGF-R/ Ret chimera resulted in phosphorylation of paxillin, a cytoskeletal protein, and cellular transformation (Romano et al., 1994; Santoro et al., 1994b). In addition, stimulation of the EGF-R/Ret chimera in SK-N-MC neuroepithelioma cells leads to cel ...
HG-6-64-1 in A375, HCT-116, HT-29
... Growth factor treatments or breast tissue make up only a tiny fraction of data used for inference. ...
... Growth factor treatments or breast tissue make up only a tiny fraction of data used for inference. ...
Exam #1
... ___________21. The larger the organism, the more the plasmids it has. ___________22. Bacteria have two copies of a single chromosome. ___________23. Histone proteins occur in supercoiled eukaryotic chromosomes. ___________24. Eukaryotes have one copy each of multiple chromosomes ___________25. The h ...
... ___________21. The larger the organism, the more the plasmids it has. ___________22. Bacteria have two copies of a single chromosome. ___________23. Histone proteins occur in supercoiled eukaryotic chromosomes. ___________24. Eukaryotes have one copy each of multiple chromosomes ___________25. The h ...
Pressure - People Server at UNCW
... conserved at the adaptation P (dark line for each species). This implies that the membrane volume is also conserved. Gibbs and Somero (1989) ...
... conserved at the adaptation P (dark line for each species). This implies that the membrane volume is also conserved. Gibbs and Somero (1989) ...
Signaling
... e) Janus family of non-receptor TK s also bind some receptors receptors i) growth hormone receptors ii) prola ctin receptors iii) some cytokine receptors ...
... e) Janus family of non-receptor TK s also bind some receptors receptors i) growth hormone receptors ii) prola ctin receptors iii) some cytokine receptors ...
Analytical and Chromatography - Sigma
... Following DNA binding, a transcription factor exerts an influence over gene expression. This is done through interaction with other transcription factors or with the basal transcriptional machinery in order to affect the efficiency of formation or binding of the transcription complex. These associat ...
... Following DNA binding, a transcription factor exerts an influence over gene expression. This is done through interaction with other transcription factors or with the basal transcriptional machinery in order to affect the efficiency of formation or binding of the transcription complex. These associat ...
Neuro Objectives 17
... NMDA receptor (activated by glutamate): NMDA acts as an agonist, primary excitatory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Na+ and Ca2+ influx for depolarization (learning and memory) c. GABA receptor (activated by GABA): primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Cl- influx for h ...
... NMDA receptor (activated by glutamate): NMDA acts as an agonist, primary excitatory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Na+ and Ca2+ influx for depolarization (learning and memory) c. GABA receptor (activated by GABA): primary inhibitory neurotransmitter of the CNS, increase in Cl- influx for h ...
Ras and macropinocytosis: trick and treat
... includes steps that stimulate the uptake of nutrients, especially glucose and glutamine, to sustain cell growth and proliferation. Macropinocytosis, a clathrin- and caveolin-independent endocytotic process that had previously been linked to the action of oncogenic Ras and Src, is now shown to contri ...
... includes steps that stimulate the uptake of nutrients, especially glucose and glutamine, to sustain cell growth and proliferation. Macropinocytosis, a clathrin- and caveolin-independent endocytotic process that had previously been linked to the action of oncogenic Ras and Src, is now shown to contri ...
What are you made of?
... Cells – Protein synthesis!!! Phase 4 4. Proteins!!! When the tRNA has translated all of the mRNA, and each of the amino acids have been joined together, your finished protein is either used by the cell, or packaged and exported in the ER or Golgi complex to other parts of the ...
... Cells – Protein synthesis!!! Phase 4 4. Proteins!!! When the tRNA has translated all of the mRNA, and each of the amino acids have been joined together, your finished protein is either used by the cell, or packaged and exported in the ER or Golgi complex to other parts of the ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... phosphorylates, among other substrates, DARPP-32, which, when phosphorylated, will inhibit protein phosphatase-1. Activation of D1-family receptors will result in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). A prominent substrate of PKA that alters gene transcription is CREB (cAMPresponse ...
... phosphorylates, among other substrates, DARPP-32, which, when phosphorylated, will inhibit protein phosphatase-1. Activation of D1-family receptors will result in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). A prominent substrate of PKA that alters gene transcription is CREB (cAMPresponse ...
Gene Section LPAR1 (lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... functioning that receptors are embedded into membranes for proper structure. The LPAR1 spans the plasma membrane seven times in a barrel conformation with three extracellular and three intracellular loops. At steady state, LPAR1 is located on the plasma membrane at the cell surface until it binds LP ...
... functioning that receptors are embedded into membranes for proper structure. The LPAR1 spans the plasma membrane seven times in a barrel conformation with three extracellular and three intracellular loops. At steady state, LPAR1 is located on the plasma membrane at the cell surface until it binds LP ...
Role of the Master regulator HetR in the cellular differentiation
... A: Nostoc grown in the presence of combined nitrogen: the filaments are only composed of vegetative cells performing oxygenic photosynthesis. B: in response to combined nitrogen starvation, 1 every 10/15 vegetative cell differentiate into a heterocyst specialized in atmospheric nitrogen fixation. C: ...
... A: Nostoc grown in the presence of combined nitrogen: the filaments are only composed of vegetative cells performing oxygenic photosynthesis. B: in response to combined nitrogen starvation, 1 every 10/15 vegetative cell differentiate into a heterocyst specialized in atmospheric nitrogen fixation. C: ...
Document
... The major purpose of the complement pathways is to provide a means of removing or destroying antigen, regardless of whether or not it has become coated with antibody The key function of complement is probably the opsonization of microorganisms and immune complexes; microorganisms coated (i.e. opso ...
... The major purpose of the complement pathways is to provide a means of removing or destroying antigen, regardless of whether or not it has become coated with antibody The key function of complement is probably the opsonization of microorganisms and immune complexes; microorganisms coated (i.e. opso ...
research title proposal - Pontificia Universidad Javeriana, Cali
... Most biological functions are mediated by protein interactions. These interactions can be physical, such as when two proteins form a complex, or “logical,” such as when one or more proteins control the behavior of one or more other proteins without physical interaction. Metabolic pathways provide us ...
... Most biological functions are mediated by protein interactions. These interactions can be physical, such as when two proteins form a complex, or “logical,” such as when one or more proteins control the behavior of one or more other proteins without physical interaction. Metabolic pathways provide us ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER THREE
... 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells 8. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. -Prokaryotic Cells: an organism that consists of a single cell that does not have a nucl ...
... 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells 8. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. -Prokaryotic Cells: an organism that consists of a single cell that does not have a nucl ...
Slide 1
... G-GTP, catalyzes synthesis of cAMP. 5. Protein Kinase A (cAMP Dependent Protein Kinase) catalyzes phosphorylation of various cellular proteins, altering their activity. ...
... G-GTP, catalyzes synthesis of cAMP. 5. Protein Kinase A (cAMP Dependent Protein Kinase) catalyzes phosphorylation of various cellular proteins, altering their activity. ...
How life works
... Ribosomes synthasise proteins from a set of 20 amino acids using information encoded on DNA or RNA via messenger RNA. The complex structure of a protein determines how it will interact with other molecules, many proteins act as catalysts in important biochemical reactions (these are known as enzymes ...
... Ribosomes synthasise proteins from a set of 20 amino acids using information encoded on DNA or RNA via messenger RNA. The complex structure of a protein determines how it will interact with other molecules, many proteins act as catalysts in important biochemical reactions (these are known as enzymes ...
Model Description Sheet
... share a significant genetic commonality. It has been shown that many breast cancer patients test positive for high levels of Estrogen Receptor (ERα), a protein that regulates the differentiation and maintenance of neural, skeletal, cardiovascular, and reproductive tissues in their cells. ERα aids in ...
... share a significant genetic commonality. It has been shown that many breast cancer patients test positive for high levels of Estrogen Receptor (ERα), a protein that regulates the differentiation and maintenance of neural, skeletal, cardiovascular, and reproductive tissues in their cells. ERα aids in ...
Gene Section PKD1 (protein kinase D1) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... homology (PH) and kinase domain (KD). Several domain specific protein interactions and functions have been described (see figure below). ...
... homology (PH) and kinase domain (KD). Several domain specific protein interactions and functions have been described (see figure below). ...
Recombinant Human Platelet-Derived Growth Factor BB PDGF
... Introduction: PDGF-BB is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family. The four members of this family are mitogenic factors for cells of mesenchymal origin and are characterized by a motif of eight cysteines. This gene product can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer w ...
... Introduction: PDGF-BB is a member of the platelet-derived growth factor family. The four members of this family are mitogenic factors for cells of mesenchymal origin and are characterized by a motif of eight cysteines. This gene product can exist either as a homodimer (PDGF-BB) or as a heterodimer w ...
Structures define the functions of proteins
... In the acetylated form, the positve charge of the lysine e-amino group is neuralized. This eliminate its interaction with a DNA phosphate group. So the greater the acetylation of histone N-terminus, the less likely chromatin is to form condensed 30-nm fibers and possibly higher-order folded ...
... In the acetylated form, the positve charge of the lysine e-amino group is neuralized. This eliminate its interaction with a DNA phosphate group. So the greater the acetylation of histone N-terminus, the less likely chromatin is to form condensed 30-nm fibers and possibly higher-order folded ...
Poster Presentation
... When CaCl2 was added we found that only a few of the transcription factors responded by bursting. The transcription factors that responded to calcium are Crz1 and Msn2. When sorbital is added to the solution it causes osmotic shock to the yeast cells. The transcription factors that were found to exh ...
... When CaCl2 was added we found that only a few of the transcription factors responded by bursting. The transcription factors that responded to calcium are Crz1 and Msn2. When sorbital is added to the solution it causes osmotic shock to the yeast cells. The transcription factors that were found to exh ...
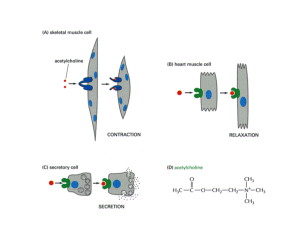
Paracrine signalling

Paracrine signaling is a form of cell-cell communication in which a cell produces a signal to induce changes in nearby cells, altering the behavior or differentiation of those cells. Signaling molecules known as paracrine factors diffuse over a relatively short distance (local action), as opposed to endocrine factors (hormones which travel considerably longer distances via the circulatory system), juxtacrine interactions, and autocrine signaling. Cells that produce paracrine factors secrete them into the immediate extracellular environment. Factors then travel to nearby cells in which the gradient of factor received determines the outcome. However, the exact distance that paracrine factors can travel is not certain.Although paracrine signaling elicits a diverse array of responses in the induced cells, most paracrine factors utilize a relatively streamlined set of receptors and pathways. In fact, different organs in the body -even between different species - are known to utilize a similar sets of paracrine factors in differential development. The highly conserved receptors and pathways can be organized into four major families based on similar structures: Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family, Hedgehog family, Wnt family, and TGF-β superfamily. Binding of a paracrine factor to its respective receptor initiates signal transduction cascades, eliciting different responses.