04 Basic Concepts of Other Imaging Modalities 08
... • Obtained by rotating a narrow beam of radiation in the horizontal plane • The film is rotated in the opposite direction while the object (jaws) is ...
... • Obtained by rotating a narrow beam of radiation in the horizontal plane • The film is rotated in the opposite direction while the object (jaws) is ...
Dental CT scanners and physical quality parameters El
... useful in the diagnosis and treatment planning of several oral and maxillofacial diseases. The quality of the resulting image is dictated by many factors related to the patient, unit and operator. Materials and methods: In this work, two dental CBCT units; namely: Scanora 3D and 3D Accuitomo 80 were ...
... useful in the diagnosis and treatment planning of several oral and maxillofacial diseases. The quality of the resulting image is dictated by many factors related to the patient, unit and operator. Materials and methods: In this work, two dental CBCT units; namely: Scanora 3D and 3D Accuitomo 80 were ...
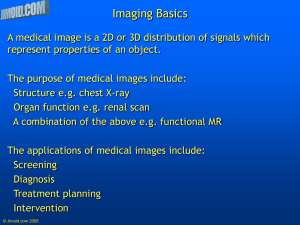
Medical Imaging
... X-ray, Ultrasound, CT, PET, MRI, and many others Uses physics, math, engineering tools, biology, (...) to image different part of the interior of the human body. ...
... X-ray, Ultrasound, CT, PET, MRI, and many others Uses physics, math, engineering tools, biology, (...) to image different part of the interior of the human body. ...
RT 101 - Mohawk Valley Community College
... 8. Compare the sources of ionizing radiation, describing the various interactions xray may have with matter. 9. Identify the various methods of controlling radiation dose to patients and occupationally based on the “no threshold concept”. 10. Describe the portions of the x-ray beam: primary, seconda ...
... 8. Compare the sources of ionizing radiation, describing the various interactions xray may have with matter. 9. Identify the various methods of controlling radiation dose to patients and occupationally based on the “no threshold concept”. 10. Describe the portions of the x-ray beam: primary, seconda ...
X-ray Fluoroscopy Imaging Systems
... dark current, but low noise - suitable for organs Plumbicon - gamma 1; quick response, small dark current, but high noise suitable for cardiac examinations ...
... dark current, but low noise - suitable for organs Plumbicon - gamma 1; quick response, small dark current, but high noise suitable for cardiac examinations ...
X-ray fluoroscopy imaging in the invasive cardiac laboratory
... Which statement is true regarding the relationship between decreasing field of view and increased patient dose rate for flat panel fluoroscopy systems? a) The size of the output phosphor is constant. b) Decreasing minifaction gain requires increase tube output. c) Detector target dose remains consta ...
... Which statement is true regarding the relationship between decreasing field of view and increased patient dose rate for flat panel fluoroscopy systems? a) The size of the output phosphor is constant. b) Decreasing minifaction gain requires increase tube output. c) Detector target dose remains consta ...
Radiology
... radiography to determine if they allow x-rays to pass through. Limit the beam to the size of the film with a cone or lead diaphragm. Do not direct the x-ray beam into another room or work area. Install an aluminum filter (1 to 2 mm thick) at the tube housing opening to eliminate radiation from usele ...
... radiography to determine if they allow x-rays to pass through. Limit the beam to the size of the film with a cone or lead diaphragm. Do not direct the x-ray beam into another room or work area. Install an aluminum filter (1 to 2 mm thick) at the tube housing opening to eliminate radiation from usele ...
Development and Role of Megavoltage Cone Beam Computed
... External beam radiation therapy has now the ability to deliver doses that conform tightly to a tumor volume. The steep dose gradients planned in these treatments make it increasingly important to reproduce the patient position and anatomy at each treatment fraction. Fo ...
... External beam radiation therapy has now the ability to deliver doses that conform tightly to a tumor volume. The steep dose gradients planned in these treatments make it increasingly important to reproduce the patient position and anatomy at each treatment fraction. Fo ...
X-Rays - LSU School of Medicine
... and soft tissue calcifications (vs. CT, x ray) • Long imaging times (in general) • Limited spatial resolution • Patient cooperation is needed • Some medical devices prohibitive ...
... and soft tissue calcifications (vs. CT, x ray) • Long imaging times (in general) • Limited spatial resolution • Patient cooperation is needed • Some medical devices prohibitive ...
AHM 244 PowerPoint
... Uses high-intensity magnetic fields (magnets), radio waves and computer analysis to create cross-sectional images ...
... Uses high-intensity magnetic fields (magnets), radio waves and computer analysis to create cross-sectional images ...
magnetic resonance imaging
... Prepare patients for radiologic examinations by explaining the procedure, removing jewelry and other articles through which X-rays cannot pass, and positioning patients so that the parts of the body can be appropriately aligned ...
... Prepare patients for radiologic examinations by explaining the procedure, removing jewelry and other articles through which X-rays cannot pass, and positioning patients so that the parts of the body can be appropriately aligned ...
x-ray imaging - X-ICAD
... Another advantage of the DICOM 3.0 format is that the media created can easily be put into other DICOM archiving solutions without having to convert the data. Image Archiving The Scanning station offloads digital x-ray images to the diagnostic workstation where image processing ensures high quality ...
... Another advantage of the DICOM 3.0 format is that the media created can easily be put into other DICOM archiving solutions without having to convert the data. Image Archiving The Scanning station offloads digital x-ray images to the diagnostic workstation where image processing ensures high quality ...
Angiography
... In Film - Screen radiography an x-ray tube generates a beam of x-rays aimed at the patient X-rays passing through patient are filtered to reduce scatter and noise and then strike an undeveloped film, held tight to a screen of light emitting phosphors in a light-tight cassette The film is then develo ...
... In Film - Screen radiography an x-ray tube generates a beam of x-rays aimed at the patient X-rays passing through patient are filtered to reduce scatter and noise and then strike an undeveloped film, held tight to a screen of light emitting phosphors in a light-tight cassette The film is then develo ...
Imaging Highlights
... • Used to visualize and examine internal body structures The three most common: 1.Radiography (x-ray) 2.Computed Tomography (CT) 3.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ...
... • Used to visualize and examine internal body structures The three most common: 1.Radiography (x-ray) 2.Computed Tomography (CT) 3.Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) ...
03 Fluoroscopy Dosimetry KAP CM
... Examination that allows real time continuous imaging using x-rays Can be used to demonstrate function or guide an interventional procedure where still images do not convey the required information ...
... Examination that allows real time continuous imaging using x-rays Can be used to demonstrate function or guide an interventional procedure where still images do not convey the required information ...
What is Fluoroscopy?
... Fluoroscopy is a x-ray based medical imaging system that can display real time x-rays of the human body to a screen in which results can be analyzed. Works by sending short x-ray pulses to an image receptor. ...
... Fluoroscopy is a x-ray based medical imaging system that can display real time x-rays of the human body to a screen in which results can be analyzed. Works by sending short x-ray pulses to an image receptor. ...
Chapter 19 - Diagnostic Imaging
... C. Stationary Unit – large, powerful units that cannot be moved D. Fluoroscope – presents a continuous moving image; gastrointestinal studies, myelography, heart and vascular studies; rarely seen due to cost ...
... C. Stationary Unit – large, powerful units that cannot be moved D. Fluoroscope – presents a continuous moving image; gastrointestinal studies, myelography, heart and vascular studies; rarely seen due to cost ...
Question: How does a radiographic image get on a film?
... Any room, any floor Nursing homes Prisons ...
... Any room, any floor Nursing homes Prisons ...
Medical Imaging lecture Powerpoint
... – Poor differentiation between similar tissues (like X-rays) – Can’t create usable images near implanted metallic objects ...
... – Poor differentiation between similar tissues (like X-rays) – Can’t create usable images near implanted metallic objects ...
General Diagnostic Radiology
... on from film exam passing that consists the through radiologist ofsystem, passing the selected interprets. a small body Aamount contrast areas of in Contrast bowel other X-ray imaging or (radiography) may other be procedures. internal introduced is structures. commonly through used X-rays an IV to ...
... on from film exam passing that consists the through radiologist ofsystem, passing the selected interprets. a small body Aamount contrast areas of in Contrast bowel other X-ray imaging or (radiography) may other be procedures. internal introduced is structures. commonly through used X-rays an IV to ...
Fluoroscopy

Fluoroscopy /flɔrˈɒskəpi/ is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope /ˈflɔrɵˌskoʊp/ allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm.Fluoroscopy is similar to radiography and X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) in that it generates images using X-rays. The original difference was that radiography fixed still images on film whereas fluoroscopy provided live moving pictures that were not stored. However, today radiography, CT, and fluoroscopy are all digital imaging modes with image analysis software and data storage and retrieval. The use of X-rays, a form of ionizing radiation, requires the potential risks from a procedure to be carefully balanced with the benefits of the procedure to the patient. Because the patient must be exposed to a continuous source of x-rays instead of a momentary pulse, a fluoroscopy procedure generally subjects a patient to a higher absorbed dose of radiation than an ordinary (still) radiograph. Much research has been directed toward reducing radiation exposure, and recent advances in fluoroscopy technology such as digital image processing and flat panel detectors, have resulted in much lower radiation doses than former procedures.The type of fluoroscopy used in airport security (to check for hidden weapons or bombs) uses lower doses of radiation than medical fluoroscopy. It was formerly also used in retail stores in the form of shoe-fitting fluoroscopes, but such use was discontinued because it is no longer considered acceptable to use radiation exposure, however small the dose, for nonessential purposes. Only important applications such as health care, bodily safety, food safety, nondestructive testing, and scientific research meet the risk-benefit threshold for use. The reason for higher doses in medical applications is that they are more demanding about tissue contrast, and for the same reason they sometimes require contrast media.