Ch 15 ppt Diagnostic
... normal cells and surrounding tissue will also be damaged •X-rays cannot penetrate lead so lead aprons and vests are used Radiologic technologists commonly use lead aprons or vests when working. ...
... normal cells and surrounding tissue will also be damaged •X-rays cannot penetrate lead so lead aprons and vests are used Radiologic technologists commonly use lead aprons or vests when working. ...
Document
... Estimates of the signal and noise in a cardiac X-ray image can be combined to produce an image quality metric (IQM) that represents the signal-to-ratio per unit of X-ray radiation dose to the patient. By actively monitoring image IQ in real-time system parameters can me adjusted to optimise image qu ...
... Estimates of the signal and noise in a cardiac X-ray image can be combined to produce an image quality metric (IQM) that represents the signal-to-ratio per unit of X-ray radiation dose to the patient. By actively monitoring image IQ in real-time system parameters can me adjusted to optimise image qu ...
No Slide Title
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
... Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. ...
RHB Rad Prot & Fluoro Syllabus
... • X-rays hit this concave surface first. • It is made of cesium iodide crystals shaped like tiny needles packed tightly together. • The more crystals, the better the spatial resolution. • The crystals convert the x-ray photons to light energy so the more crystals, the more energy converted to light ...
... • X-rays hit this concave surface first. • It is made of cesium iodide crystals shaped like tiny needles packed tightly together. • The more crystals, the better the spatial resolution. • The crystals convert the x-ray photons to light energy so the more crystals, the more energy converted to light ...
Ridology of GIT -imp points
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Radioisotopes studies Angiography Most common use in GIT : planx-rays, Fluoroscopy Ultrasound : for detdect stone ...
... Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Radioisotopes studies Angiography Most common use in GIT : planx-rays, Fluoroscopy Ultrasound : for detdect stone ...
QC in a Digital World - Diagnostic Accreditation Program
... Optimization of Displays Clean the surface of the display With the display OFF look at reflections on the surface of the display such as lamps, windows, white coats and name tags. Reduce these artifacts as much as possible Display the SMPTE test pattern Ensure you can see the 5% and ...
... Optimization of Displays Clean the surface of the display With the display OFF look at reflections on the surface of the display such as lamps, windows, white coats and name tags. Reduce these artifacts as much as possible Display the SMPTE test pattern Ensure you can see the 5% and ...
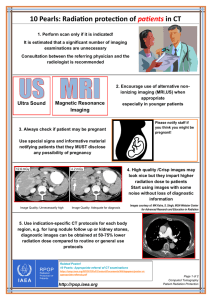
10 Pearls: Radiation protection of patients in CT - RPOP
... Always center the area of interest in isocenter of CT gantry All CT protocols should state the start and end location for different clinical ...
... Always center the area of interest in isocenter of CT gantry All CT protocols should state the start and end location for different clinical ...
Advanced Imaging Equipment
... DQE measures overall image quality as a function of object detail. This is similar to the concept of MODULATION TRANSFER FUNCTION. The higher the DQE, the better the system is at displaying small low-contrast objects. ...
... DQE measures overall image quality as a function of object detail. This is similar to the concept of MODULATION TRANSFER FUNCTION. The higher the DQE, the better the system is at displaying small low-contrast objects. ...
3D Radiography Breakthrough: Applications for Dental Professionals
... Desire to Have 3D Perspective Attempts to give 3D Perspective Computed Tomography (CT) •1972: Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield invented the CT system. •1979: Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded. –Initially, view was only tomographic (slice views) and too large slice intervals (1cm) for dentistry. Dentistr ...
... Desire to Have 3D Perspective Attempts to give 3D Perspective Computed Tomography (CT) •1972: Godfrey Newbold Hounsfield invented the CT system. •1979: Nobel Prize in Medicine was awarded. –Initially, view was only tomographic (slice views) and too large slice intervals (1cm) for dentistry. Dentistr ...
FLUOROSCOPY MODULE Jenniefer Kho, MD
... The flow of electrons from the filament to the target is called the tube current and is described in units of milliamperes (mA). Fluoroscopy is normally performed using 2-6 mA and an accelerating voltage of 75 to 125 kVp. The rate of x-ray production is directly proportional to the tube current, bu ...
... The flow of electrons from the filament to the target is called the tube current and is described in units of milliamperes (mA). Fluoroscopy is normally performed using 2-6 mA and an accelerating voltage of 75 to 125 kVp. The rate of x-ray production is directly proportional to the tube current, bu ...
BACK TO BASICS
... Overview of radiation protection for paediatrics. Why children are different – not “little adults”. “The fact that the x-ray is taken of a non-cooperative child is NOT an excuse for producing an inferior quality image.” Public awareness and Google has highlighted concerns about irradiating children. ...
... Overview of radiation protection for paediatrics. Why children are different – not “little adults”. “The fact that the x-ray is taken of a non-cooperative child is NOT an excuse for producing an inferior quality image.” Public awareness and Google has highlighted concerns about irradiating children. ...
fan beam MVCT image quality
... Meeks SL, Harmon JF, Langen KM, Willoughby TR, Wagner TH, Kupelian PA. Performance characterization of megavoltage computed tomography imaging on a helical tomotherapy unit. Medical Physics, 2005; 32:8 : 2673-2681 ...
... Meeks SL, Harmon JF, Langen KM, Willoughby TR, Wagner TH, Kupelian PA. Performance characterization of megavoltage computed tomography imaging on a helical tomotherapy unit. Medical Physics, 2005; 32:8 : 2673-2681 ...
Useful Websites Related to Radiation and Imaging Technology
... Molecular imaging is a type of medical imaging that provides detailed pictures of what is happening inside the body at the molecular and cellular level that allows physicians to see how the body is functioning and to measure its chemical and biological processes. Learn more: www.DiscoverMI.org (SNMM ...
... Molecular imaging is a type of medical imaging that provides detailed pictures of what is happening inside the body at the molecular and cellular level that allows physicians to see how the body is functioning and to measure its chemical and biological processes. Learn more: www.DiscoverMI.org (SNMM ...
History of radiology
... Primary beam of X-rays traverse the patient. In the patient a part of X-rays is absorbed (photoeffect) and the attenuated beam continues to the detector and creates the image. Another part is scattered (Compton´s effect) The degree of absorption depends on the wavelength and on the effective atomic ...
... Primary beam of X-rays traverse the patient. In the patient a part of X-rays is absorbed (photoeffect) and the attenuated beam continues to the detector and creates the image. Another part is scattered (Compton´s effect) The degree of absorption depends on the wavelength and on the effective atomic ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... from a gas cloud that has been enriched with oxygen and other heavy elements, probably by a supernova that exploded thousands of years ago. ...
... from a gas cloud that has been enriched with oxygen and other heavy elements, probably by a supernova that exploded thousands of years ago. ...
Presentation I MAX
... • State-of-the-art CCD sensor with CsI (Cesium Iodide) layer • The CsI layer (scintillator screen) gives a better dose reduction compared to sensors with « Gadox » or « Lanex » used by most competitors ...
... • State-of-the-art CCD sensor with CsI (Cesium Iodide) layer • The CsI layer (scintillator screen) gives a better dose reduction compared to sensors with « Gadox » or « Lanex » used by most competitors ...
Duet DRF 4343
... dedicated processing capabilities. Fully integrated A complete system that handles the entire digital imaging process, from patient registration to display of the clinical image. The system comprises a Pixium RF 4343 detector, a digital workstation and interfaces to all components in the X-ray room: ...
... dedicated processing capabilities. Fully integrated A complete system that handles the entire digital imaging process, from patient registration to display of the clinical image. The system comprises a Pixium RF 4343 detector, a digital workstation and interfaces to all components in the X-ray room: ...
Slide 1
... Collimators reduce the field size of the X-Ray beam, reducing the amount of scattered radiation. It is practical to limit the beam to the field of the area desired to get better contrast and resolution. “Air Gap” Increases the distance between the object and the film receptors. This causes incre ...
... Collimators reduce the field size of the X-Ray beam, reducing the amount of scattered radiation. It is practical to limit the beam to the field of the area desired to get better contrast and resolution. “Air Gap” Increases the distance between the object and the film receptors. This causes incre ...
Fluoroscopy

Fluoroscopy /flɔrˈɒskəpi/ is an imaging technique that uses X-rays to obtain real-time moving images of the interior of an object. In its primary application of medical imaging, a fluoroscope /ˈflɔrɵˌskoʊp/ allows a physician to see the internal structure and function of a patient, so that the pumping action of the heart or the motion of swallowing, for example, can be watched. This is useful for both diagnosis and therapy and occurs in general radiology, interventional radiology, and image-guided surgery. In its simplest form, a fluoroscope consists of an X-ray source and a fluorescent screen, between which a patient is placed. However, since the 1950s most fluoroscopes have included X-ray image intensifiers and cameras as well, to improve the image's visibility and make it available on a remote display screen. For many decades fluoroscopy tended to produce live pictures that were not recorded, but since the 1960s, as technology improved, recording and playback became the norm.Fluoroscopy is similar to radiography and X-ray computed tomography (X-ray CT) in that it generates images using X-rays. The original difference was that radiography fixed still images on film whereas fluoroscopy provided live moving pictures that were not stored. However, today radiography, CT, and fluoroscopy are all digital imaging modes with image analysis software and data storage and retrieval. The use of X-rays, a form of ionizing radiation, requires the potential risks from a procedure to be carefully balanced with the benefits of the procedure to the patient. Because the patient must be exposed to a continuous source of x-rays instead of a momentary pulse, a fluoroscopy procedure generally subjects a patient to a higher absorbed dose of radiation than an ordinary (still) radiograph. Much research has been directed toward reducing radiation exposure, and recent advances in fluoroscopy technology such as digital image processing and flat panel detectors, have resulted in much lower radiation doses than former procedures.The type of fluoroscopy used in airport security (to check for hidden weapons or bombs) uses lower doses of radiation than medical fluoroscopy. It was formerly also used in retail stores in the form of shoe-fitting fluoroscopes, but such use was discontinued because it is no longer considered acceptable to use radiation exposure, however small the dose, for nonessential purposes. Only important applications such as health care, bodily safety, food safety, nondestructive testing, and scientific research meet the risk-benefit threshold for use. The reason for higher doses in medical applications is that they are more demanding about tissue contrast, and for the same reason they sometimes require contrast media.