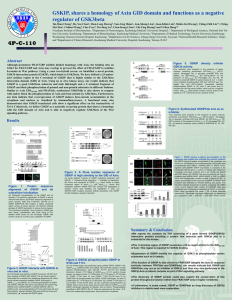
Appendix 1 - HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee
... nomenclature of known gene, .e.g ADAL (adenosine deaminase like). If gene is an ortholog of a gene with known function in another species assign appropriate symbol with “homolog” included in the gene name e.g. CDC6 (cell division cycle 6 homolog). ...
... nomenclature of known gene, .e.g ADAL (adenosine deaminase like). If gene is an ortholog of a gene with known function in another species assign appropriate symbol with “homolog” included in the gene name e.g. CDC6 (cell division cycle 6 homolog). ...
Creation/Evolution - Geoscience Research Institute
... The net effect of wobble base pairing is to reduce the number of tRNAs that must be produced by a cell In reality cells do not make 61 different tRNAs, one for each codon Many tRNAs have anticodons that anneal to several different codons Codons are known for which there are more than one tRNA, altho ...
... The net effect of wobble base pairing is to reduce the number of tRNAs that must be produced by a cell In reality cells do not make 61 different tRNAs, one for each codon Many tRNAs have anticodons that anneal to several different codons Codons are known for which there are more than one tRNA, altho ...
PRINCIPLES OF BEEF CATTLE GENETICS
... sex cells, the egg and the sperm, a reduction division occurs and only one chromosome and one set of genes of each pair goes into a sex cell. This ...
... sex cells, the egg and the sperm, a reduction division occurs and only one chromosome and one set of genes of each pair goes into a sex cell. This ...
Jmol Quick Reference Sheet - MSOE Center for BioMolecular
... Dual Color Scheme: 1. Color of amino acid name and sidechain shading indicate: hydrophobic amino acids (yellow); hydrophilic non-charged amino acids (white); positive charged amino acids (blue); negative charged amino acids (red); cysteine (green). 2. Atom type indicates carbon (gray), oxygen (red) ...
... Dual Color Scheme: 1. Color of amino acid name and sidechain shading indicate: hydrophobic amino acids (yellow); hydrophilic non-charged amino acids (white); positive charged amino acids (blue); negative charged amino acids (red); cysteine (green). 2. Atom type indicates carbon (gray), oxygen (red) ...
Acyl-ACP thioesterases from Camelina sativa: Cloning
... mature CsFatA protein, corresponding to a signal peptide of 58 amino acid residues (Fig. 1). In the case of the CsFatB protein, we considered Leu-93 to be the first amino acid of the mature enzyme, which would correspond to a signal peptide of 92 amino acids (Fig. 2). Taking into account the presen ...
... mature CsFatA protein, corresponding to a signal peptide of 58 amino acid residues (Fig. 1). In the case of the CsFatB protein, we considered Leu-93 to be the first amino acid of the mature enzyme, which would correspond to a signal peptide of 92 amino acids (Fig. 2). Taking into account the presen ...
Identification of Human Polymorphisms in the Phenylthio
... for the AVI/AVI homozygotes. The rare AVI/AAV heterozygotes had a mean PTC score slightly, but significantly, higher than the AVI/AVI homozygotes. Finally, sequencing the PTC gene from several non-human primates determined that all were homozygous for the PAV form. Thus, the AVI nontaster haplotype ...
... for the AVI/AVI homozygotes. The rare AVI/AAV heterozygotes had a mean PTC score slightly, but significantly, higher than the AVI/AVI homozygotes. Finally, sequencing the PTC gene from several non-human primates determined that all were homozygous for the PAV form. Thus, the AVI nontaster haplotype ...
Structural adaptation of enzymes to low
... Psychrophilic organisms live at such low temperatures, where most other species cannot grow and to survive they need to produce enzymes able to perform efficiently their catalysis under these extreme environmental conditions. At the same temperatures, enzymes from mesophilic or thermophilic organism ...
... Psychrophilic organisms live at such low temperatures, where most other species cannot grow and to survive they need to produce enzymes able to perform efficiently their catalysis under these extreme environmental conditions. At the same temperatures, enzymes from mesophilic or thermophilic organism ...
What is similarity and homology? What is a good match? How does
... Repeats and low complexity regions constitute more than one third of the human genome. Highly locally biased composition occurs in regions of many proteins and in DNA. E.g. structural proteins in hair. Low complexity regions may give rise to high alignment scores – but are usually biologically unint ...
... Repeats and low complexity regions constitute more than one third of the human genome. Highly locally biased composition occurs in regions of many proteins and in DNA. E.g. structural proteins in hair. Low complexity regions may give rise to high alignment scores – but are usually biologically unint ...
Myoglobin from equine skeletal muscle (M0630)
... these histidines binds to the oxygen of the water molecule, which is bound to the heme. The position and the functional competence of the heme depends on the hydrophobic amino acids that line the inside of the heme pocket. The function of myoglobin is oxygen storage and transfer (from hemoglobin to ...
... these histidines binds to the oxygen of the water molecule, which is bound to the heme. The position and the functional competence of the heme depends on the hydrophobic amino acids that line the inside of the heme pocket. The function of myoglobin is oxygen storage and transfer (from hemoglobin to ...
RNA Polymerase - California Lutheran University
... determined how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order • Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid • Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for mutations – Frameshift mutations ...
... determined how the order of nucleotides in DNA encoded amino acid order • Codon – block of 3 DNA nucleotides corresponding to an amino acid • Introduced single nulcleotide insertions or deletions and looked for mutations – Frameshift mutations ...
Physiology of metabolic processes in the body. Composition of diet
... Why are these two hormones battling for opposing uses of the same amino acids? Isn't that non-productive? Actually, the phenomenon serves an important purpose. The release of these two opposing hormones ensures that the amino acids are used for protein synthesis (because of the extra insulin) but t ...
... Why are these two hormones battling for opposing uses of the same amino acids? Isn't that non-productive? Actually, the phenomenon serves an important purpose. The release of these two opposing hormones ensures that the amino acids are used for protein synthesis (because of the extra insulin) but t ...
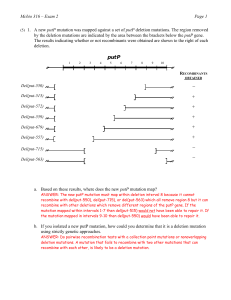
Exam 2
... 5. The F-plasmid can be stabily maintained in both Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. However, Hfr’s are formed much less frequently in S. typhimurium than in E. coli. In addition, there are many fewer insertion sites in S. typhimurium compared to E. coli. Given what you know about how Hfr ...
... 5. The F-plasmid can be stabily maintained in both Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli. However, Hfr’s are formed much less frequently in S. typhimurium than in E. coli. In addition, there are many fewer insertion sites in S. typhimurium compared to E. coli. Given what you know about how Hfr ...
Dear teacher/student
... hair and eyes, the development of syndromes and illnesses (Huntingtons disease, sickle cell anemia, color blindness) and biological processes (photosynthesis, digestion, insulin production). As of now there exists no single database where one can easily find genes and proteins that are involved in a ...
... hair and eyes, the development of syndromes and illnesses (Huntingtons disease, sickle cell anemia, color blindness) and biological processes (photosynthesis, digestion, insulin production). As of now there exists no single database where one can easily find genes and proteins that are involved in a ...
CHAPTER 3 ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
... – Called gene cloning DNA sequences can be altered (mutated) to generate a desired change. – The new DNA is called recombinant DNA. Once the DNA is transferred, the new host cell begins to make the new DNA and produce the new proteins. – Organisms that contain recombinant DNA are called ...
... – Called gene cloning DNA sequences can be altered (mutated) to generate a desired change. – The new DNA is called recombinant DNA. Once the DNA is transferred, the new host cell begins to make the new DNA and produce the new proteins. – Organisms that contain recombinant DNA are called ...
Natural Selection
... Altering Gene Number or Position • Chromosomal mutations that delete, disrupt, or rearrange many loci are typically harmful • Duplication of small pieces of DNA increases genome size and is usually less harmful • Duplicated genes can take on new functions by further mutation • An ancestral odor-det ...
... Altering Gene Number or Position • Chromosomal mutations that delete, disrupt, or rearrange many loci are typically harmful • Duplication of small pieces of DNA increases genome size and is usually less harmful • Duplicated genes can take on new functions by further mutation • An ancestral odor-det ...
Chem 322 - Exam #4 - Spring 2003 - Answers
... The isomers are diastereomers. (d) This compound is achiral. At room temperature tetrahedral nitrogen rapidly inverts its configuration – the unshared pair of electrons passes through the nitrogen and comes out the other side, then repeats the process in the reverse direction – over and over. Conseq ...
... The isomers are diastereomers. (d) This compound is achiral. At room temperature tetrahedral nitrogen rapidly inverts its configuration – the unshared pair of electrons passes through the nitrogen and comes out the other side, then repeats the process in the reverse direction – over and over. Conseq ...
Prokaryotic Regulatory RNAs Cole Franks Proteins have been
... coenzyme B12 and the mRNA. It was also noteworthy that the 5’ untranslated regions of the mRNAs from the operons reorganized themselves by spontaneous cleavage in the presence of coenzyme B12. Analysis showed that there was actually direct binding of coenzyme B12 by these mRNAs (Mandal and Breaker, ...
... coenzyme B12 and the mRNA. It was also noteworthy that the 5’ untranslated regions of the mRNAs from the operons reorganized themselves by spontaneous cleavage in the presence of coenzyme B12. Analysis showed that there was actually direct binding of coenzyme B12 by these mRNAs (Mandal and Breaker, ...
Chapter 25 DNA metabolism
... H. Viral DNA Polymerases provide targets for antiviral therapy Many DNA viruses encode their own DNA polymerase, so if you can specifically inhibit this enzyme, you have killed the virus 25.2 DNA Repair if RNA or protein damaged, simply make a new copy if DNA damaged have a problem back in chapter 1 ...
... H. Viral DNA Polymerases provide targets for antiviral therapy Many DNA viruses encode their own DNA polymerase, so if you can specifically inhibit this enzyme, you have killed the virus 25.2 DNA Repair if RNA or protein damaged, simply make a new copy if DNA damaged have a problem back in chapter 1 ...
Fatty acid synthesis
... acetyl CoA carboxylase 7 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP + 7 CO2 + 7 H2O → 7 malonyl-CoA + 7 H+ + 7 ADP + 7 Pi ...
... acetyl CoA carboxylase 7 acetyl-CoA + 7 ATP + 7 CO2 + 7 H2O → 7 malonyl-CoA + 7 H+ + 7 ADP + 7 Pi ...
Meiosis
... Overview of Meiosis • Homologous chromosomes: similarly constructed chromosomes with the same shape and that contain genes for the same traits (homologues) • Just like in mitosis, meiosis occurs after interphase, when the cell grows, DNA is replicated, and chromosomes are duplicated. ...
... Overview of Meiosis • Homologous chromosomes: similarly constructed chromosomes with the same shape and that contain genes for the same traits (homologues) • Just like in mitosis, meiosis occurs after interphase, when the cell grows, DNA is replicated, and chromosomes are duplicated. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Antigenic variation in Trypanosoma brucei
... VSG expression is controlled at the level of transcription initiation Regulation of promoter activity is used to control gene expression in many organisms ...
... VSG expression is controlled at the level of transcription initiation Regulation of promoter activity is used to control gene expression in many organisms ...
S1 Supporting Information
... MU412 has replaced 1.3 kb of the r3b2 coding region by the pyrG gene. The mutant alleles in MU450 and MU451 have completely eliminated the 136157 coding region and replaced it by the pyrG gene. All those mutant strains were considered null mutants. Transformants harboring mutant alleles were also o ...
... MU412 has replaced 1.3 kb of the r3b2 coding region by the pyrG gene. The mutant alleles in MU450 and MU451 have completely eliminated the 136157 coding region and replaced it by the pyrG gene. All those mutant strains were considered null mutants. Transformants harboring mutant alleles were also o ...
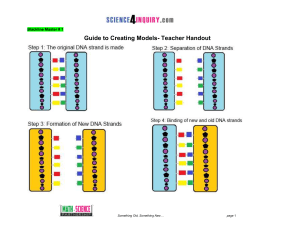
Activity Name - Science4Inquiry.com
... Inversion Mutation: reverse one section of bases (a whole gene) Original Strand: ...
... Inversion Mutation: reverse one section of bases (a whole gene) Original Strand: ...
Point mutation

A point mutation, or single base modification, is a type of mutation that causes a single nucleotide base change, insertion, or deletion of the genetic material, DNA or RNA. The term frameshift mutation indicates the addition or deletion of a base pair. A point mutant is an individual that is affected by a point mutation.Repeat induced point mutations are recurring point mutations, discussed below.